ADS8322YB Burr-Brown Corporation, ADS8322YB Datasheet - Page 8

ADS8322YB
Manufacturer Part Number
ADS8322YB
Description
16-Bit/ 500kHz/ MicroPower Sampling ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
Manufacturer
Burr-Brown Corporation
Datasheet
1.ADS8322YB.pdf
(10 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ADS8322YB
Manufacturer:
BB
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADS8322YB/250
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
5 600
Company:
Part Number:
ADS8322YB/250
Manufacturer:
Texas Instruments
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADS8322YB/250G4
Manufacturer:
Texas Instruments
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADS8322YB/2K
Manufacturer:
Texas Instruments
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADS8322YB/2KG4
Manufacturer:
Texas Instruments
Quantity:
10 000
limited between –0.1V and 0.5V, allowing the input to reject
small signals which are common to both the +IN and –IN
inputs. The +IN input has a range of –0.1V to +V
The input current on the analog inputs depends upon a
number of factors: sample rate, input voltage, and source
impedance. Essentially, the current into the ADS8322 charges
the internal capacitor array during the sample period. After
this capacitance has been fully charged, there is no further
input current. The source of the analog input voltage must be
able to charge the input capacitance (25pF) to a 16-bit
settling level within the acquisition time (400ns) of the
device. When the converter goes into Hold mode, the input
impedance is greater than 1G .
Care must be taken regarding the absolute analog input
voltage. To maintain the linearity of the converter, the –IN
input should not drop below GND – 100mV or exceed
GND + 0.5V. The +IN input should always remain within
the range of GND – 100mV to V
these ranges, the converter’s linearity may not meet specifi-
cations. To minimize noise, low-bandwidth input signals
with lowpass filters should be used.
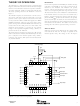
DIGITAL INTERFACE
TIMING AND CONTROL
See the timing diagram in the Timing Characteristics section
for detailed information on timing signals and their require-
ment.
The ADS8322 uses an external clock (CLOCK) which
controls the conversion rate of the CDAC. With a 10MHz
external clock, the A/D converter sampling rate is 500kHz,
which corresponds to a 2 s maximum throughput time.
Conversions are initiated by bringing the CONVST pin
LOW for a minimum of 20ns (after the 20ns minimum
requirement has been met, the CONVST pin can be brought
HIGH), while CS is LOW. The ADS8322 will switch from
Sample-to-Hold mode on the falling edge of the CONVST
command. Following the first rising edge of the external
clock after a CONVST LOW, the ADS8322 will begin
conversion (this first rising edge of the external clock repre-
sents the start of clock cycle one; the ADS8322 requires 16
rising clock edges to complete a conversion). The BUSY
output will go HIGH immediately following CONVST go-
ing LOW. BUSY will stay HIGH through the conversion
process and return LOW when the conversion has ended.
Both RD and CS can be HIGH during and before a conver-
sion (although CS must be LOW when CONVST goes LOW
to initiate a conversion). Both the RD and CS pins are
brought LOW in order to enable the parallel output bus with
the conversion.
8
A
+ 100mV. Outside of
A
+ 0.1V.
TABLE I. Ideal Input Voltages and Output Codes.
READING DATA
The ADS8322 outputs full parallel data in Straight Binary
format, as shown in Table I. The parallel output will be
active when CS and RD are both LOW. The output data
should not be read 125ns prior to the falling edge of
CONVST and 10ns after the falling edge. Any other combi-
nation of CS and RD will tri-state the parallel output. Refer
to Table I for ideal output codes.
BYTE
The output data will appear as a full 16-bit word on DB15-
DB0 (MSB-LSB), if BYTE is LOW. The result may also be
read on an 8-bit bus by using only DB7-DB0. In this case two
reads are necessary. The first, as before, leaving BYTE LOW
and reading the 8 least significant bits on DB7-DB0, then
bringing BYTE HIGH. When BYTE is HIGH, the upper 8 bits
(D15-D8) will appear on DB7-DB0.
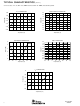
NOISE
Figure 2 shows the transition noise of the ADS8322. A low-
level DC input was applied to the analog-input pins and the
converter was put through 8,192 conversions. The digital
output of the A/D converter will vary in output code due to
the internal noise of the ADS8322. This is true for all 16-bit
SAR-type A/D converters. Using a histogram to plot the
output codes, the distribution should appear bell-shaped
FIGURE 2. Histogram of 8,192 Conversions of a Low Level
DESCRIPTION
Full-Scale Range
Least Significant
Bit (LSB)
+Full Scale
Midscale
Midscale – 1LSB
Zero
DC Input.
0014
54
ANALOG VALUE
2 • V
2V
V
REF
REF
2 • V
0015
300
REF
V
– 1 LSB
0V
– 1 LSB
REF
/65535
REF
Code
5052
0016
1111 1111 1111 1111
1000 0000 0000 0000
0111 1111 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
BINARY CODE
0017
1968
STRAIGHT BINARY
DIGITAL OUTPUT
0018
818
ADS8322
SBAS215
HEX CODE
FFFF
7FFF
8000
0000