MT9043 Zarlink Semiconductor, MT9043 Datasheet
MT9043
Available stocks
Related parts for MT9043
MT9043 Summary of contents
Page 1
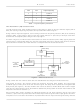
... The MT9043 generates ST-BUS clock and framing signals that are phase locked to either a 19.44 MHz, 2.048MHz, 1.544MHz, or 8kHz input reference. The MT9043 is compliant with AT&T TR62411 and Bellcore GR-1244-CORE, Stratum 4 Enhanced, and Stratum 4; and ETSI ETS 300 011. It will meet the jitter/wander tolerance, jitter transfer, intrinsic jitter, frequency accuracy, capture range, phase change slope, and MTIE requirements for these specifications ...
Page 2
... RST Reset (Input). A logic low at this input resets the MT9043. To ensure proper operation, the device must be reset after reference signal frequency changes and power-up. The RST pin should be held low for a minimum of 300ns. While the RST pin is low, all frame pulses except RST and TSP and all clock outputs except C6o, C16o and C19o are at logic high ...
Page 3
... Internal Connection. Tie low for normal operation Mode/Control Select (Input). This input determines the state (Normal or Freerun) of operation. The logic level at this input is gated in by the rising edge of F8o. See Table Internal Connection. Tie low for normal operation. MT9043 Description 3 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. Data Sheet ...
Page 4
... Reference Select MUX Circuit The MT9043 accepts two simultaneous reference input signals and operates on their falling edges. Either the primary reference (PRI) signal or the secondary reference (SEC) signal can be selected as input to the TIE Corrector Circuit. The selection is based on the Control, Mode and Reference Selection of the device. See Table 1 and Table 4 ...
Page 5
... Since internal delay circuitry maintains the alignment between the old virtual reference and the new virtual reference, a phase error may exist between the selected input reference signal and the output signal of the DPLL. This phase error is a function of the difference in phase between the two input reference signals during reference MT9043 FS2 FS1 ...
Page 6
... The state diagram of Figure 7 indicates the state changes during which the TIE corrector circuit is activated. Digital Phase Lock Loop (DPLL) As shown in Figure 4, the DPLL of the MT9043 consists of a Phase Detector, Limiter, Loop Filter, Digitally Controlled Oscillator, and a Control Circuit. Phase Detector - the Phase Detector compares the virtual reference signal from the TIE Corrector circuit with the feedback signal from the Frequency Select MUX circuit, and provides an error signal corresponding to the phase difference between the two ...
Page 7
... The frame pulse outputs (F0o, F8o, F16o, TSP, and RSP) are generated directly from the C16 clock. The T1 and E1 signals are generated from a common DPLL signal. Consequently, all frame pulse and clock outputs are locked to one another for all operating states, and are also locked to the selected input reference in Normal Mode. See Figures 14 & 15. MT9043 T1 Divider C1.5o 12MHz ...
Page 8
... RSEL Figure 6 - Control State Machine Block Diagram Master Clock The MT9043 can use either a clock or crystal as the master timing source. For recommended master timing circuits, see the Applications - Master Clock section. Control and Mode of Operation The active reference input (PRI or SEC) is selected by the RSEL pin as shown in Table 2. ...
Page 9
... FS2 and FS1 as shown in Table 1. Fast Lock Mode Fast Lock Mode is a submode of Normal Mode used to allow the MT9043 to lock to a reference more quickly than Normal mode will allow. Typically, the PLL will lock to the incoming reference within 500 ms if the FLOCK pin is set high ...
Page 10
... Frequency Accuracy Frequency accuracy is defined as the absolute tolerance of an output clock signal when it is not locked to an external reference, but is operating in a free running mode. For the MT9043, the Freerun accuracy is equal to the Master Clock (OSCi) accuracy. Capture Range Also referred to as pull-in range ...
Page 11
... See AC Electrical Characteristics - Performance for Maximum Phase Lock Time. MT9043 provides a fast lock pin (FLOCK), which, when set high enables the PLL to lock to an incoming reference within approximately 500 ms. ...
Page 12
... Movement to Normal State from any state requires a valid input signal MT9043 and Network Specifications The MT9043 fully meets all applicable PLL requirements (intrinsic jitter, jitter/wander tolerance, jitter/wander transfer, frequency accuracy, capture range, phase change slope and MTIE during reference rearrangement) for the following specifications. ...
Page 13
... Another consideration in determining the accuracy of the master timing source is the desired capture range. The sum of the accuracy of the master timing source and the capture range of the MT9043 will always equal 230ppm. For example, if the master timing source is 100ppm, then the capture range will be 130ppm. ...
Page 14
... The output clock should be connected directly (not AC coupled) to the OSCi input of the MT9043, and the OSCo output should be left open as shown in Figure 8. Crystal Oscillator - Alternatively, a Crystal Oscillator may be used. A complete oscillator circuit made crystal, resistor and capacitors is shown in Figure 9. 1uH inductor: may improve stability and is optional The accuracy of a crystal oscillator depends on the crystal tolerance as well as the load capacitance tolerance ...
Page 15
... Capacitor’s discharge time Resistor value (3.3 MΩ Capacitor value (1µ Negative going threshold voltage of the T- Schmitt Trigger (2 3 MT9043 MT9043 +3.3V R 10kΩ RST R P 1kΩ C 10nF Figure 10 - Power-Up Reset Circuit 15 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. Data Sheet ...
Page 16
... A digital alternative to the RC-time-constant circuit is presented in Figure 12. The circuit in Figure 12 can be used to generate a steady lock signal. The circuit monitors the MT9043’s LOCK pin, as long as it detects a positive pulse every 1.024 seconds or less, the Advanced Lock output will remain high positive pulse is detected on the LOCK output within 1 ...
Page 17
... OSCi = Clock 3 CMOS high-level input voltage 4 CMOS low-level input voltage 5 Input leakage current 6 High-level output voltage 7 Low-level output voltage * Supply voltage and operating temperature are as per Recommended Operating Conditions. MT9043 Voltages are with respect to ground (V ) unless otherwise stated. SS Symbol PIN I PIN T ...
Page 18
... Supply voltage and operating temperature are as per Recommended Operating Conditions. * Timing for input and output signals is based on the worst case result of the CMOS thresholds. * See Figure 10. ALL SIGNALS t t IRF, ORF Figure 13 - Timing Parameter Measurement Voltage Levels MT9043 Sym Min ±0ppm ±32ppm ±100ppm -100 ±0ppm -230 ± ...
Page 19
... C19o pulse width high 28 C19o pulse width low 29 F0o pulse width low 30 F8o pulse width high 31 F16o pulse width low 32 Output clock and frame pulse rise or fall time 33 Input Controls Setup Time 34 Input Controls Hold Time MT9043 Sym IRF t R8D t R15D t R2D t R19D t ...
Page 20
... PRI/SEC 8kHz PRI/SEC 1.544MHz PRI/SEC 2.048MHz PRI/SEC 19.44MHz F8o NOTES: 1. Input to output delay values are valid after a TCLR or RST with no further state changes Figure 14 - Input to Output Timing (Normal Mode) MT9043 R15D R2D R19D Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. Data Sheet ...
Page 21
... F8o F0o F16o t C16WL C16o t t C8W C8W C8o t C4W C4o C2o t C6W C6o C1.5o t C19WL C19o Figure 14 - Output Timing 1 MT9043 t F0WL t F16WL t F16S t C4W t C2W t C6W t C15W t C19WH 21 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. Data Sheet t F8WH F0D F16H t C16D ...
Page 22
... Intrinsic jitter at C4o (4.096MHz) 8 Intrinsic jitter at C8o (8.192MHz) 9 Intrinsic jitter at C16o (16.384MHz) 10 Intrinsic jitter at TSP (8kHz) 11 Intrinsic jitter at RSP (8kHz) 12 Intrinsic jitter at C19o (19.44MHz) † See “Notes” following AC Electrical Characteristics tables. MT9043 t RSPD t TSPW t TSPD Figure 15 - Output Timing ...
Page 23
... Jitter attenuation for 10Hz@0.10UIpp input 4 Jitter attenuation for 60Hz@0.10UIpp input 5 Jitter attenuation for 300Hz@0.10UIpp input 6 Jitter attenuation for 3600Hz@0.005UIpp input † See “Notes” following AC Electrical Characteristics tables. MT9043 Sym Min Max Units 0.015 UIpp 0.010 UIpp ...
Page 24
... Jitter attenuation for 10Hz@20UIpp input 4 Jitter attenuation for 60Hz@20UIpp input 5 Jitter attenuation for 300Hz@20UIpp input 6 Jitter attenuation for 10kHz@0.3UIpp input 7 Jitter attenuation for 100kHz@0.3UIpp input † See “Notes” following AC Electrical Characteristics tables. MT9043 Sym Min Max Units ...
Page 25
... Jitter at output for 2400Hz@1.50UIpp input with 40Hz to 100kHz filter 12 13 Jitter at output for 100kHz@0.20UIpp input with 40Hz to 100kHz filter 14 † See “Notes” following AC Electrical Characteristics tables. MT9043 Sym Min Max Units 2.9 UIpp 0.09 UIpp 1.3 UIpp ...
Page 26
... Jitter tolerance for 300Hz input 5 Jitter tolerance for 400Hz input 6 Jitter tolerance for 700Hz input 7 Jitter tolerance for 2400Hz input 8 Jitter tolerance for 10kHz input 9 Jitter tolerance for 100kHz input † See “Notes” following AC Electrical Characteristics tables. MT9043 Sym Min Max Units 0.80 UIpp 1-3,5,9 -14,21-22,24-26,28 0.70 UIpp 1-3,5,9 -14,21-22,24-26,28 0.60 ...
Page 27
... No filter. 37. 40Hz to 100kHz bandpass filter. 38. With respect to reference input signal frequency. 39. After a RST or TCLR. 40. Master clock duty cycle 40% to 60%. MT9043 Sym Min Max Units -0 +0 -32 ...
Page 28
... Zarlink Semiconductor 2003 All rights reserved. ISSUE ACN DATE APPRD. Package Code Previous package codes ...
Page 29
... For more information about all Zarlink products Information relating to products and services furnished herein by Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. or its subsidiaries (collectively “Zarlink”) is believed to be reliable. However, Zarlink assumes no liability for errors that may appear in this publication, or for liability otherwise arising from the application or use of any such information, product or service or for any infringement of patents or other intellectual property rights owned by third parties which may result from such application or use ...