TDA7400 ST Microelectronics, TDA7400 Datasheet - Page 18

TDA7400
Manufacturer Part Number
TDA7400
Description
ADVANCED CAR SIGNAL PROCESSOR
Manufacturer
ST Microelectronics
Datasheet
1.TDA7400.pdf
(28 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
TDA7400
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
TDA7400D
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
TDA7400DTR
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
TDA7400
PEAK+VTH are fed to a comparator which trig-
gers a re-triggerable monoflop. The monoflop’s
output activates the sample-and-hold circuits in
the signalpath for selected duration.
Automatic Noise Controlled Threshold Adjust-
ment (ATC)
There are mainly two independent possibilities for
programming the trigger threshold:
a the low threshold in 8 steps (bits D
b the noise adjusted threshold in 4 steps
The low threshold is active in combination with a
good MPX signal without any noise; the PEAK
voltage is less than 1V. The sensitivity in this op-
eration is high.
If the MPX signal is noisy the PEAK voltage in-
creases due to the higher noise, which is also
rectified. With increasing of the PEAK voltage the
trigger threshold increases, too. This particular
gain is programmable in 4 steps (see fig. ...).
AUTOMATIC THRESHOLD CONTROL MECHA-
NISM
Automatic
Stereoblend Voltage
Besides the noise controlled threshold adjust-
ment there is an additional possibility for influenc-
ing the trigger threshold. It is depending on the
stereoblend control.
The point where the MPX signal starts to become
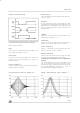
Figure 17. Block Diagram of the Noiseblanker
18/28
the noiseblanker byte)
(bits D
see fig. 14).
3
and D
Threshold
MPX
MPX
4
of the noiseblanker byte,
RECTIFIER
Control
D98AU856
CONTROL
LOWPASS
0
to D
by
2
RECT
of
the
+
+
+
PEAK
noisy is fixed by the RF part. Therefore also the
starting point of the normal noise-controlled trig-
ger adjustment is fixed (fig. 11). In some cases
the behaviour of the noiseblanker can be im-
proved by increasing the threshold even in a re-
gion of higher fieldstrength. Sometimes a wrong
triggering occures for the MPX signal often shows
distortion in this range which can be avoided
even if using a low threshold.
Because of the overlap of this range and the
range of the stereo/mono transition it can be con-
trolled by stereoblend. This threshold increase is
programmable in 3 steps or switched off with bits
D
Over Deviation Detector
If the system is tuned to stations with a high de-
viation the noiseblanker can trigger on the higher
frequencies of the modulation. To avoid this
wrong behaviour, which causes noise in the out-
put signal, the noiseblanker offers a deviation de-
pendent threshold adjustment.
By rectifying the MPX signal a further signal rep-
resenting the actual deviation is obtained. It is
used to increase the PEAK voltage. Offset and
gain of this circuit are programmable in 3 steps
with the bits D
(the first step turns off the detector, see fig. 15).
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF THE MULTI-
PATH DETECTOR
Using the internal multipath detector the audible
effects of a multipath condition can be minimized.
A multipath condition is detected by rectifying the
19kHz spectrum in the fieldstrength signal.
An external capacitor is used to define the attack
and decay times (see block diagram fig. 23). the
-
VTH
0
and D
1
GENERATOR
THRESHOLD
ADDITIONAL
THRESHOLD
MONOFLOP
of the fieldstrength control byte.
CONTROL
6
and D
7
of the stereodecoder byte
HOLDN