lan91c95 Standard Microsystems Corp., lan91c95 Datasheet - Page 99

lan91c95
Manufacturer Part Number
lan91c95
Description
Isa/pcmcia Full Duplex Single-chip Ethernet And Modem Controller With Ram
Manufacturer
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet
1.LAN91C95.pdf
(144 pages)
- Current page: 99 of 144
- Download datasheet (430Kb)
system the cycle time of a 16 bit transfer will be
at least 2 clocks for the I/O access to the
LAN91C95 + one clock for the memory cycle) =
3 clocks. In absolute time it means 375ns for a
8MHz bus, and 240ns for a 12.5 MHz bus.
The cycle time will not increase when configured
for full duplex mode, because the CSMA/CD
memory arbitration requests are sequenced by
the DMA logic and never overlap.
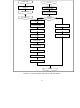
DMA BLOCK
The DMA block resides between the CSMA/CD
block and the arbiter. It can interface both the
data path and the control path of the CSMA/CD
block for different operations.
Its functions include the following:
The specific nature of each operation and its
trigger event are:
1)
Start
CSMA/CD block.
Generate CSMA/CD side addresses for
accessing memory during transmit and
receive operations.
Generate MMU memory requests and verify
success.
Compute byte count and write it in first
locations of receive packet.
Write transmit status word in first locations
of transmit packet.
Determine if enough memory is available
for reception.
De-allocate transmit memory after suitable
completion.
De-allocate receive memory upon error
conditions.
Initiate retransmissions upon collisions (if
less than 16 retries).
Terminate reception and release memory if
packet is too long.
TX operations will begin if TXENA is set
and TX FIFO is not empty. The DMA logic
does not need to use the TX PACKET
NUMBER, it goes directly from the FIFO to
transmission
process
into
the
99
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
the MMU. However the DMA logic controls
the removal of the PACKET NUMBER from
the FIFO.
Generation of CSMA/CD side addresses
into memory: Independent 11 bit counters
are kept for transmit and receive in order to
allow full-duplex operation.
MMU requests for allocation are generated
by the DMA logic upon reception.
initial allocation request is issued when the
CSMA block indicates an active reception. If
allocation succeeds, the DMA block stores
the packet number assigned to it, and
generates write arbitration requests for as
long as the CSMA/CD FIFO is not empty.
In parallel the CSMA/CD completes the
address filtering and notifies the DMA of an
address match. If there is no address
match, the DMA logic will release the
allocated memory and stop reception.
When the CSMA/CD block notifies the DMA
logic that a receive packet was completed,
if the CRC is OK, the DMA will either write
the previously stored packet number into
the RX PACKET NUMBER FIFO (to be
processed by the CPU), or if the CRC is
bad the DMA will just issue a release
command to the MMU (and the CPU will
never see that packet).
Packets with bad CRC can be received if
the RCV_BAD bit in the configuration
register is set.
If AUTO_RELEASE is set, a release is
issued by the DMA block to the MMU after a
successful transmission (TX_SUCC set),
and the TX completion FIFO is clocked
together with the TX FIFO preventing the
packet number from moving into the TX
completion FIFO.
Based on the RX counter value, if a receive
packet exceeds 1532 bytes, reception is
stopped by the DMA and the RX ABORT bit
in the Receive Control Register is set. The
memory
automatically released.
allocated
to
the
packet
The
is
Related parts for lan91c95
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Interface, Integrated USB2.0 Compatible 3-Port Hub
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Lan91c100fd Rev. B Feast Fast Ethernet Controller With Full Duplex Capability
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Feast ? Ast Ethernet Controller
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Com20022i 10 Mbps Arcnet Ansi 878.1 Controller With 2k X 8 On-chip Ram
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.

Part Number:
Description:
Lpc47n207 Lpc Super I/o Irda Hot Docking Chip With Uart Data Brief
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Advanced I/o With X-bus Interface
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Fdc37m707 Enhanced Super I/o Controller With Wake-up Features
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Twenty Pin Uart Tpuart Corporation
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Enhanced Small Device Interface Controller
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.

Part Number:
Description:
Rpm-based Pwm Fan Controller
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Rpm-based Pwm Fan Controller
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Emc1001 1.5?c Smbus Temperature Sensor In Miniature Sot-23
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
1 Degree C Triple Temperature Sensor With Beta Compensation And Hotter Of Two Zones
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
1 Degree C Multiple Temperature Sensor With Beta Compensation And Hottest Of Thermal Zones
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
1 Degree C Triple Temperature Sensor With Resistance Error Correction & Hotter Of Two Zones
Manufacturer:
Standard Microsystems Corp.
Datasheet: