at42qt100a ATMEL Corporation, at42qt100a Datasheet - Page 11

at42qt100a
Manufacturer Part Number
at42qt100a
Description
Qtouch? Charge Transfer Ic
Manufacturer
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet
1.AT42QT100A.pdf
(18 pages)
4. Circuit Guidelines
4.1
4.2
4.3
9531A–AT42–02/09
More Information
Sample Capacitor
Power Supply and PCB Layout
Refer to Application Note QTAN0002, Secrets of a Successful QTouch
Sensors Design Guide (both downloadable from the Touch Technology area of Atmel’s website)
for more information on construction and design methods.
Cs is the charge sensing sample capacitor. The required Cs value depends on the thickness of
the panel and its dielectric constant. Thicker panels require larger values of Cs. Typical values
are 2 nF to 50 nF depending on the sensitivity required; larger values of Cs demand higher
stability and better dielectric to ensure reliable sensing.
The Cs capacitor should be a stable type, such as X7R ceramic or PPS film. For more consistent
sensing from unit to unit, 5 percent tolerance capacitors are recommended. X7R ceramic types
can be obtained in 5 percent tolerance at little or no extra cost. In applications where high
sensitivity (long burst length) is required the use of PPS capacitors is recommended.
See
500 µA in Fast mode.
If the power supply is shared with another electronic system, care should be taken to ensure that
the supply is free of digital spikes, sags, and surges which can adversely affect the QT100A.
The QT100A will track slow changes in Vdd, but it can be badly affected by rapid voltage
fluctuations. It is highly recommended that a separate voltage regulator be used just for the
QT100A to isolate it from power supply shifts caused by other components.
If desired, the supply can be regulated using a Low Dropout (LDO) regulator, although such
regulators often have poor transient line and load stability. Refer to Application Note QTAN0002,
Secrets of a Successful QTouch™ Design, and the Touch Sensors Design Guide for further
information on power supply considerations.
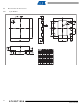
Parts placement: The chip should be placed to minimize the SNSK trace length to reduce low
frequency pickup, and to reduce stray Cx which degrades gain. The Cs and Rs resistors (see
Figure 1-1 on page
trace between Rs and the SNSK pin is very short, thereby reducing the antenna-like ability of
this trace to pick up high frequency signals and feed them directly into the chip. A ground plane
can be used under the chip and the associated discrete components, but the trace from the Rs
resistor and the electrode should not run near ground, to reduce loading. For best EMC
performance the circuit should be made entirely with SMT components.
Electrode trace routing: Keep the electrode trace (and the electrode itself) away from other
signal, power, and ground traces including over or next to ground planes. Adjacent switching
signals can induce noise onto the sensing signal; any adjacent trace or ground plane next to, or
under, the electrode trace will cause an increase in Cx load and desensitize the device. Refer to
the Touch Sensors Design Guide for further information.
Important Note: for proper operation a 100 nF (0.1 µF) ceramic bypass capacitor must be
used directly between Vdd and Vss, to prevent latch-up if there are substantial Vdd
transients; for example, during an ESD event. The bypass capacitor should be placed
very close to the Vss and Vdd pins.
Section 5.2 on page 12
3) should be placed as close to the body of the chip as possible so that the
for the power supply range. At 3V current drain averages less than
AT42QT100A
™
Design, and the Touch
11