qt60325 Quantum Research Group, qt60325 Datasheet - Page 18

qt60325
Manufacturer Part Number
qt60325
Description
32, 48, 64 Key Qmatrix Keypanel Sensor Ics
Manufacturer
Quantum Research Group
Datasheet
1.QT60325.pdf
(42 pages)
enough to ensure adequate signal risetime and may need to
be augmented with external 10k pullups.
The host must wait until DRDY’ goes low before an SPI
transfer to retrieve data. For multi-byte responses, the host
must observe DRDY' to see when it goes high again after
each data byte, then low again, before executing another
transfer to get the next data byte. The host should send null
bytes (0x00) to retrieve data.
If the DRDY’ line does not go low after a command, the
command was not properly received or it was inappropriate.
The delay to DRDY’ low depends on how many bytes of data
are being loaded into eeprom; Table 4-1. Absolute worst case
delays are found in Section 7; these timings occur only rarely,
for example if the device happens to be busy with adjacent
key suppression calculations, which occurs only at the
moment when a key is first detected.
A typical Slave-only function sequence is as follows:
lQ
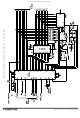
Figure 4-4 Filtering SPI Slave-Only Connections
Figure 4-5 Filtering SPI Master-Slave Connections
1) The host pulls SS’ low, then transfers a command to the
2) For 2-byte functions, (1) is repeated with a m50µs delay.
sensor. The host then releases SS’ to float high. DRDY’ is
unaffected in this step.
Xn
Yn
Xn
Yn
SPI Clock Rate
46.875kHz
Recommended Values of Ra & Ca for Figures 4-4 and 4-5
93.75kHz
100
100
22pF
22pF
1.5MHz
375kHz
47pF
47pF
220
220
X drives
(1 of 8
shown)
Y Lines
(1 of 8
shown)
X drives
(1 of 8
shown)
Y Lines
(1 of 8
shown)
QT60xx5 Circuit
QT60xx5 Circuit
RESET
RESET
DRDY
DRDY
MISO
MOSI
MISO
MOSI
SCK
SCK
SS
SS
1,000
2,200
2,200
680
Ra
1nF
1nF
+5
+5
Ca
Ca
Ca
Ca
Ca
Ca
10K
10K
+5
10K
Ra
Ra
Ra
Ra
Ra
1K
Ra
Ra
Ra
1K
Ca
Ca
Ca
Ca
Ca
(MS not
shown)
(MS not
shown)
© Quantum Research Group Ltd.
100pF
270pF
470pF
1nF
Ca
P_IN
P_OUT1
MISO
MOSI
P_OUT2
SS
SCK
MISO
MOSI
P_OUT
Host MCU
SCK
Host MCU
18
The host must release the SS’ line in step (7) even between
multiple byte responses because the QT60xx5 waits for the
SS’ line to return high before signalling that the next byte is
ready for collection.
The host should check the DRDY’ line and wait for it to go
high before transmitting another byte. Until the DRDY’ line is
released the sensor is still processing a data return, even if
the complete response data has been fully transferred; the
sensor may still be busy when the host finishes the byte
transfer and may not be able to digest a new command
immediately.
See Section 3.18, page 15, for a description of the Alert pin
which can be used to reduce communication traffic.
4.4 SPI Master-Slave Mode
Refer to Figures 4-1 and 4-3. In Master-Slave mode the host
and sensor take turns being Master; the host always initiates
in Master mode during an exchange. The current Master
always controls all 3 signals. The sensor takes a variable
amount of time to respond to the host, depending on the
function and current and pending tasks. SPI Master/Slave
mode is selected by tying Pin 37 (MS) low via a 10K resistor.
Pin 37 is also an oscilloscope sync output (see Section
3.20 and command ^R, page 29) and should never be tied
directly to either supply rail. The host, like the sensor, must
idle in slave mode when not sending a command.
Master/Slave requires 3 signals to operate:
MOSI - Master out / Slave in data pin - bidirectional - an input
SCK - SPI clock - bidirectional - an input pin when receiving
SS’ - Slave select - bidirectional framing control. When the
3) When the sensor has the command echo or requested
4) The host detects that the sensor has pulled DRDY’ low
5) The host obtains the byte from the sensor by transmitting
6) The sensor releases DRDY’ to float high.
7) After the host detects that DRDY' has floated high the
8) For multi-byte responses, steps (3) through (7) are
data ready to send back to the host, it loads it into its SPI
register and pulls DRDY’ low.
and in turn the host pulls SS’ low.
a dummy byte (0x00) to the sensor.
host must allow SS’ to also float high.
repeated until the return data is completely sent.
pin while the host is transmitting data; an output when the
sensor is transmitting data. The MOSI of the host and
slave should be tied together. The MISO lines are not used
on either part and should be left open.
data; an output pin when sending. The host must shift out
data on the falling edge of SCK; the QT60xx5 clocks data
in on the rising edge of SCK. Important note: SCK from
the host must be low before asserting SS’ low or high at
either end of a byte or the transmission will fail. SCK
should idle low; if in doubt, a 10K pulldown resistor should
be used. When the sensor returns data it becomes the
Master; data is shifted out by it on the falling edge of SCK
and should be clocked in by the host on the rising edge.
sensor is in slave mode, this pin accepts the SS’ control
signal from the host. In either data direction, SS' must go
low before and any during data transfer; it should not go
high again until SCK has returned low at the end of a byte.
www.qprox.com
QT60xx5 / R1.05