tb62218ftg TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION, tb62218ftg Datasheet
tb62218ftg
Related parts for tb62218ftg
tb62218ftg Summary of contents
Page 1
... TOSHIBA BiCD Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TB62218FG, TB62218FTG BiCD Constant-Current Two-Phase Bipolar Stepping Motor Driver IC The TB62218FG/FTG is a two-phase bipolar stepping motor driver using a PWM chopper. Fabricated with the BiCD process, the TB62218FG/FTG is rated at 40 V/2.0 A. The on-chip voltage regulator allows control of a stepping motor with a single V power supply ...
Page 2
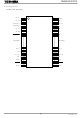
Pin Assignment TB62218FG (HSOP28) IN_A1 1 IN_A2 2 PHASE_A 3 PHASE_B 4 IN_B1 5 IN_B2 6 7 STANDBY FIN(GND) 8 Rs_A OUT_A 11 NC GND 12 OUT_A 13 GND 14 TB62218FG/FTG 28 OSCM 27 Vref_A 26 Vref_B ...
Page 3
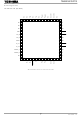
... Pin Assignment TB62218FTG QFN48 ( ) * GND ref_B V 42 ref_A OSCM 43 IN_A1 44 IN_A2 45 PHASE_A 46 PHASE_B *Mark PAD: It must be connected to GND 3 TB62218FG/FTG * GND 21 OUT_B1 20 OUT_B2 19 GND 18 GND ...
Page 4
Block Diagram In the block diagram, part of the functional blocks or constants may be omitted or simplified for explanatory purposes. STANDBY PHASE_A IN_A1 IN_A2 PHASE_B IN_B1 IN_B2 Vref Current Feedback (× STANDBY Note: All the grounding ...
Page 5
Pin Function TB62218FG (HSOP28) Pin No. Pin Name 1 IN_A1 A-phase excitation control input 2 IN_A2 A-phase excitation control input 3 PHASE_A Current direction signal input for A phase 4 PHASE_B Current direction signal input for B phase 5 IN_B1 ...
Page 6
... TB62218FTG (QFN48) Pin Pin Name Function No No-connect 2 IN_B1 B-phase excitation control input 3 IN_B2 B-phase excitation control input STAND BY High: Normal operation mode 4 Low: Standby mode 5 GND Logic ground 6 NC No-connect 7 R Power supply pin of A-phase motor coil and S_A1 the sink current sensing of A-phase motor coil ...
Page 7
Output Function Table Input signal PHASE_A IN_A1 PHASE_B IN_B1 IOUT: The current which flows OUT_X to is defined as minus current. Input signals to IN_X and PHASE_X after the voltage ...
Page 8
Absolute Maximum Ratings Characteristics Motor power supply Motor output voltage Motor output current Logic input voltage Vref standard voltage QFN48 Power dissipation HSOP28 Operating temperature Storage temperature Junction temperature Note guide, the maximum output current should be ...
Page 9
Electrical Characteristics 1 Characteristics Input hysteresis voltage High Digital input current Low Power consumption High-side Output leakage current Low-side Chanel-to-channel current differential Output current error relative to the predetermined value R pin current S Drain-source ON-resistance of the output transistors ...
Page 10
Electrical Characteristics 2 Characteristics V input current ref V decay rate ref TSD threshold (Note 1) V recovery voltage M Overcurrent trip threshold (Note 2) Supply voltage for internal circuitry Note 1: Thermal shutdown (TSD) circuitry When the junction temperature ...
Page 11
AC Electrical Characteristics Characteristics Symbol Phase frequency f t Minimum phase pulse width t pLH (P) MAX Output transistor switching characteristics t pHL (P) MAX t pLH (P) MIN t pHL (P) MIN Blanking time for current spike t prevention ...
Page 12
Current Waveform in Mixed Decay Mode Mixed-Decay mode, the purpose of which is constant-current control, starts out in Fast-Decay mode for 37.5% of the whole period and then is followed by Slow-Decay mode for the remainder of the period. Internal ...
Page 13
Current Waveform in Mixed (Slow + Fast) Decay Mode Timing charts may be simplified for explanatory purposes. • When a current value increases (Mixed-Decay point is fixed to 37.5%) f chop Internal OSCM CLK NF Predefined current level Slow Charge ...
Page 14
Output Transistor Operating Modes Pin OFF Load L1 L2 OFF ON PGND Charge Mode A current flows into the motor coil. Output Transistor Operating Modes CLK U1 Charge ON Slow-Decay Mode ...
Page 15
IC Power Consumption The power consumed by the TB62218FG/FTG is approximately the sum of the following two: 1) the power consumed by the output transistors, and 2) the power consumed by the digital logic and pre-drivers. • The power consumed ...
Page 16
OSC-Charge Delay Since the rising level of the OSC waveform is referenced to convert it into the internal CR CLK waveform, about up to1 us (when CR = 1600 kHz delay occurs between the OSC waveform and internal ...
Page 17
Phase Sequences Two-Phase Excitation Mode Timing charts may be simplified for explanatory purposes. 150 B 100 50 0 -150 -100 - -50 C -100 -150 A PHASE 100 (A) OUT -100% 100% 0% -100% I (B) ...
Page 18
Excitation Timing charts may be simplified for explanatory purposes. 150 C B 100 -150 -100 - - -100 -150 A PHASE G 100 (A) OUT -100% 100% I (B) 0% ...
Page 19
W1-2-Phase Excitation Timing charts may be simplified for explanatory purposes. 150 100 -150 -100 - -50 I -100 J K -150 A PHASE ...
Page 20
Overcurrent Shutdown (ISD) Circuitry ISD Masking Time and ISD On-Time OSC_M oscillation (chopper waveform) min min ISD masking time An overcurrent starts flowing into the output transistors The overcurrent shutdown (ISD) circuitry has a masking time to prevent current spikes ...
Page 21
P – Ta (package power dissipation) D When mounted on a special glass-epoxy two-layer board for QFN48-P-0707-0.5 When mounted on a special glass-epoxy two-layer board for HSOP28-P-450-0.8 (2 layer board, Cu thickness: 55μm, Size × × ...
Page 22
Example Application Circuits TB62218FG The values shown in the following figure are typical values. For input conditions, see Operating Ranges. 3.6 k Ω ...
Page 23
... TB62218FTG The values shown in the following figure are typical values. For input conditions, see Operating Ranges GND 40 V ref ref_A OSCM 43 3.6 k Ω 3.3 V IN_A1 3.3 V IN_A2 3.3 V PHASE_A ...
Page 24
Package Dimensions Weight: 0.79 g (typ.) 24 TB62218FG/FTG 2010-06-10 ...
Page 25
QFN48-P-0707-0.5 Pin#1 Index Mark Area Weight: 0.14 g (typ.) Foot Pattern Example (double- sided board) Surface Backside heatsink: 5.4 mm × 5.4 mm Corner chamfers: C0.5 Chamfer radius: 3-R0.2 Black dots: 0.2 mm through holes 25 TB62218FG/FTG Unit: mm Bottom ...
Page 26
Notes on Contents 1. Block Diagrams Some of the functional blocks, circuits, or constants in the block diagram may be omitted or simplified for explanatory purposes. 2. Equivalent Circuits The equivalent circuit diagrams may be simplified or some parts of ...
Page 27
Points to remember on handling of ICs Over current Protection Circuit Over current protection circuits (referred to as current limiter circuits) do not necessarily protect ICs under all circumstances. If the Over current protection circuits operate against the over current, ...
Page 28
RESTRICTIONS ON PRODUCT USE • This document and any information herein may not be reproduced without prior written permission from TOSHIBA. Even with TOSHIBA’s written permission, reproduction is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration/omission. • Though TOSHIBA works continually ...