lm2735xsdx National Semiconductor Corporation, lm2735xsdx Datasheet - Page 13

lm2735xsdx
Manufacturer Part Number
lm2735xsdx
Description
520khz/1.6mhz - Space-efficient Boost And Sepic Dc-dc Regulator
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.LM2735XSDX.pdf
(38 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
lm2735xsdx/NOPB
Manufacturer:
KTS
Quantity:
6 239
thermal considerations. Other factors that influence thermal
performance are thermal vias, copper weight, and number of
board layers.
Definitions
Heat energy is transferred from regions of high temperature
to regions of low temperature via three basic mechanisms:
radiation, conduction and convection.
Radiation: Electromagnetic transfer of heat between masses
at different temperatures.
Conduction: Transfer of heat through a solid medium.
Convection: Transfer of heat through the medium of a fluid;
typically air.
Conduction & Convection will be the dominant heat transfer
mechanism in most applications.
R
temperature.
R
temperature.
C
perature.
C
perature.
R
impedances, and most data sheets contain associated values
for these two symbols. The units of measurement are °C/
Watt.
R
thermal model below). The capacitors represent delays that
are present from the time that power and its associated heat
is increased or decreased from steady state in one medium
until the time that the heat increase or decrease reaches
steady state on the another medium.
θJA
θJC
θJC
θCA
θJA
θJA
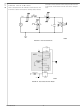
FIGURE 10. Simplified Thermal Impedance Model
: Thermal impedance from silicon junction to ambient air
: Thermal impedance from silicon junction to device case
: Thermal Delay from silicon junction to device case tem-
: Thermal Delay from device case to ambient air tem-
is the sum of smaller thermal impedances (see simplified
& R
θJC
: These two symbols represent thermal
20215841
13
The datasheet values for these symbols are given so that one
might compare the thermal performance of one package
against another. In order to achieve a comparison between
packages, all other variables must be held constant in the
comparison (PCB size, copper weight, thermal vias, power
dissipation, V
on the package performance, but it would be a mistake to use
these values to calculate the actual junction temperature in
your application.
We will talk more about calculating the variables of this equa-
tion later, and how to eventually calculate a proper junction
temperature with relative certainty. For now we need to define
the process of calculating the junction temperature and clarify
some common misconceptions.
R
•
•
•
•
•
It would be wrong to assume that the top case temperature is
the proper temperature when calculating
of a package, not just the top side. This document will refer to
a thermal impedance called
impedance associated with just the top case temperature.
This will allow one to calculate the junction temperature with
a thermal sensor connected to the top case.
θJA
Input Voltage, Output Voltage, Output Current, RDSon.
Ambient temperature & air flow.
Internal & External components power dissipation.
Package thermal limitations.
PCB variables (copper weight, thermal via’s, layers
component placement).
value represents the thermal impedance of all six sides
[Variables]:
IN
, V
OUT
, Load Current etc). This does shed light
.
represents a thermal
www.national.com
value. The