11c90 National Semiconductor Corporation, 11c90 Datasheet - Page 6

11c90
Manufacturer Part Number
11c90
Description
650 Mhz Prescalers
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.11C90.pdf
(10 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
11c90DC
Manufacturer:
MIT
Quantity:
5 704
Part Number:
11c90DC
Manufacturer:
F
Quantity:
20 000
Functional Description
The 11C90 contains four ECL Flip-Flops an ECL to TTL
converter and a Schottky TTL output buffer with an active
pull-up Three of the Flip-Flops operate as a synchronous
shift counter driving the fourth Flip-Flop operating as an
asynchronous toggle The internal feedback logic is such
that the TTL output and the Q ECL output are HIGH for six
clock periods and LOW for five clock periods The Mode
Control (M) inputs can modify the feedback to make the
output HIGH for five clock periods and LOW for five clock
periods as indicated in the Count Sequence Table
The feedback logic is such that the instant the output goes
HIGH the circuit is already committed as to whether the
output period will be 10 or 11 clock periods long This
means that subsequent changes in an M input signal in-
cluding decoding spikes will have no effect on the current
output period The only timing restriction for an M input sig-
nal is that it be in the desired state at least a setup time
before the clock that follows the HHLL state shown in the
table The allowable propagation delay through external log-
ic to an M input is maximized by designing it to use the
positive transition of the 11C90 output as its active edge
This gives an allowable delay of ten clock periods minus
the CP to Q delay of the 11C90 and the M to CP setup time
If the external logic uses the negative output transition as its
active edge the allowable delay is reduced to five clock
periods minus the previously mentioned delay and setup
time
Capacitively coupled triggering is simplified by the 400X re-
sistor which connects pin 15 to the internal V
By connecting this to the CP input as shown in Figure 3 the
clock is automatically centered about the input threshold A
clock duty cycle of 50% provides the fastest operation
since the Flip-Flops are Master-Slave types with offset clock
thresholds between master and slave This feature ensures
that the circuit will operate with clock waveforms having
very slow rise and fall times and thus there is no maximum
frequency restriction Recommended minimum and maxi-
mum clock amplitude as a function of a frequency and tem-
perature are shown in the graph labeled Figure 2 When the
CP or any other input is driven from another ECL circuit
normal ECL termination methods are recommended One
method is indicated in Figure 4 Other ECL termination
methods are discussed in the F100K ECL Design Guide
(Section 5 of Databook)
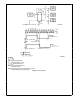
FIGURE 2 AC Coupled Triggering Characteristics
BB
reference
TL F 9892 – 5
6
Figure 5 Some types of TTL outputs will only pull up to
Figure 6
V
When an M input is to be driven from a TTL output operating
from the same V
resistor can be used to pull the TTL output up as shown in
within two diode drops of V
11C90 inputs The resistor will pull the signal up through the
threshold region although this final rise may be somewhat
slow depending on wiring capacitance A resistor network
that gives faster rise and also lower impedance is shown in
FIGURE 4 Clocking by ECL Source via Terminated Line
FIGURE 6 Faster Low Impedance TTL to ECL Interface
EE
FIGURE 5 Using Internal Pull-Up with TTL Source
e b
FIGURE 3 Capacitively Coupled Clocking
5 2V V
CC
Z
R
R
e
O
1
2
CC
0V V
X
X
X
and ground (V
TT
80 6
130
50
e b
CC
2 0V
which is not high enough for
121
196
75
EE
) the internal 2 kX
100
162
261
TL F 9892 – 10
TL F 9892 – 11
TL F 9892 – 12
TL F 9892 – 13