AD544 AD [Analog Devices], AD544 Datasheet

AD544
Available stocks
Related parts for AD544
AD544 Summary of contents
Page 1
... The AD544 is recommended for any op amp applications re- quiring excellent ac and dc performance at low cost. The 2 MHz bandwidth and low offset of the AD544 make it the first choice as an output amplifier for current output D/A converters, such as the AD7541, 12-bit CMOS DAC. ...
Page 2
... Either Input J Grade Grades Input Offset Current J Grade Grades INPUT IMPEDANCE Differential Common Mode 5 INPUT VOLTAGE Differential Common Mode Common-Mode Rejection Grade Grades AD542 AD544 Min Typ Max Min Typ 100 30 250 50 100 20 100 20 250 ...
Page 3
... AD542JH 2.0 mV AD542KH 1.0 mV AD542LH 0.5 mV AD542SH 1.0 mV AD542SH/883B 1.0 mV AD544JH 2.0 mV AD544KH 1.0 mV AD544LH 0.5 mV AD544SH 1.0 mV AD544SH/883B 1.0 mV AD547JH 1.0 mV AD547KH 0.5 mV AD547LH 0.25 mV AD547SCHIPS 0.5 mV AD547SH/883B 0.5 mV REV. B AD542 AD544 Min Typ Max Min Typ 1.1 1.5 1.8 2.0 2.0 2 +70 –55 to +125 –55 to +125 –65 to +150 –65 to +150 +25 C ...
Page 4
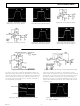
... AD542/AD544/AD547–Typical Characteristics Figure 1. Input Voltage Range vs. Supply Voltage Figure 4. Input Bias Current vs. Supply Voltage Figure 7. Change in Offset Voltage vs. Warm-Up Time Figure 2. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage Figure 5. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature Figure 8. Open Loop Gain vs. Temperature –4– Figure 3. Output Voltage Swing vs. ...
Page 5
... Distortion vs. Frequency REV. B Figure 11. Power Supply Rejection vs. Frequency Figure 14. Large Signal Frequency Response Figure 17. Input Noise Voltage Spectral Density –5– AD542/AD544/AD547 Figure 12. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency Figure 15. AD544 Output Swing and Error vs. Settling Time Figure 18. Total RMS Noise vs. Source Resistance ...
Page 6
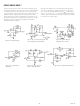
... AD542/AD544/AD547 a. Unity Gain Follower Figure 19. THD Test Circuits Figure 21a. Unity Gain Follower Pulse Response (Large Signal) Figure 22a. Unity Gain Inverter AD542/AD547 b. Follower with Gain = 10 Figure 21b. Unity Gain Follower Pulse Response (Small Signal) Figure 22b. Unity Gain Inverter Pulse Response (Large Signal) – ...
Page 7
... Figure 25. Settling Time Test Circuit The upper trace of the oscilloscope photograph of Figure 26 shows the settling characteristic of the AD544. The lower trace represents the input to Figure 27. The AD544 has been designed for fast settling to 0.01%, however, feedback components, cir- cuit layout and circuit design must be carefully considered to obtain optimum settling time. Figure 26. Settling Characteristic Detail– ...
Page 8
... AD542/AD544/AD547 BiFET Application Hints APPLICATION NOTES The BiFET series was designed for high performance op amp applications that require true dc precision. To capitalize on all of the performance available from the BiFETs there are some practical error sources that should be considered. The bias currents of JFET input amplifiers double with every 10 C increase in chip temperature ...
Page 9
... V analog input, the circuit can perform a 4-quadrant multiplying function. Figure 32a. AD544 Used as DAC Output Amplifiers The photos exhibit the response to a step input at V 32b is the large signal response and Figure 32c is the small sig- nal response ...
Page 10
... AD542/AD544/AD547 This particular log ratio circuit is free from the dynamic prob- lems that plague many other log circuits. The –3 dB bandwidth is 50 kHz over the top 3 decades, 100 nA to 100 A, and de- creases smoothly at lower input levels. This circuit needs no ad- ditional frequency compensation for stable operation from input current sources, such as photodiodes, that may have 100 pF of shunt capacitance ...
Page 11
... REV. B OUTLINE DIMENSIONS Dimensions shown in inches and (mm). TO-99 (H-08A) –11– AD542/AD544/AD547 ...
Page 12
–12– ...