LTC1852 LINER [Linear Technology], LTC1852 Datasheet - Page 18

LTC1852
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC1852
Description
8-Channel, 10-Bit/12-Bit, 400ksps, Low Power, Sampling ADCs
Manufacturer
LINER [Linear Technology]
Datasheet
1.LTC1852.pdf
(24 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LTC1852CFW
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1852CFW#PBF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
1 689
Part Number:
LTC1852CFW#TRPBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LTC1852IFW
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1852IFW#PBF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
520
Part Number:
LTC1852IFW#PBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
LTC1852/LTC1853
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
appear on the data outputs; BUSY goes high releasing the
processor, and the processor takes RD ( = CONVST) back
high and reads the new conversion data.
In ROM mode, the processor takes RD ( = CONVST) low,
starting a conversion and reading the previous conversion
result. After the conversion is complete, the processor can
read the new result and initiate another conversion.
MODES OF OPERATION
Direct Address Mode
The simplest mode of operation is the Direct Address
mode. This mode is selected when both the M1 and M0
pins are low. In this mode, the address input pins directly
control the MUX and the confi guration input pins directly
control the input span. The address and confi guration
input pins are enabled when WR is low. WR can be tied
low if the pins will be constantly driven or the rising edge
of WR can be used to latch and hold the inputs for as long
as WR is held high.
Scan Mode
Scan mode is selected when M1 is low and M0 is high.
This mode allows the converter to scan through all of
the input channels sequentially and repeatedly without
the user having to provide an address. The address
input pins (A2 to A0) are ignored but the DIFF , PGA and
UNI/BIP pins are still enabled when WR is low. As in the
direct address mode, WR can be held low or the rising
edge of WR can be used to latch and hold the information
on these pins for as long as WR is held high. The DIFF
pin selects the scan pattern. If DIFF is held low, the scan
pattern will consist of all eight channels in succession,
single-ended relative to COM (CH0-COM, CH1-COM,
CH2-COM, CH3-COM, CH4-COM, CH5-COM, CH6-COM,
CH7-COM, repeat). At the maximum conversion rate the
throughput rate for each channel would be 400ksps/8 or
50ksps. If DIFF is held high, the scan pattern will consist
of four differential pairs (CH0-CH1, CH2-CH3, CH4-CH5,
CH6-CH7, repeat). At the maximum conversion rate, the
throughput rate for each pair would be 400ksps/4 or
100ksps. It is possible to drive the DIFF input pin while
the part is in Scan mode to achieve combinations of
18
single-ended and differential inputs. For instance, if the
A0
will consist of four single-ended inputs and two differential
pairs (CH0-COM single-ended, CH1-COM single-ended,
CH2-CH3 differential, CH4-COM single-ended, CH5-COM
single-ended, CH6-CH7 differential, repeat).
The scan counter is reset to zero whenever the M0 pin
changes state so that the fi rst conversion after M0 rises
will be MUX Address 000 (CH0-COM single-ended or CH0-
CH1 differential depending on the state of the DIFF pin).
A conversion is initiated by the falling edge of CONVST.
After each conversion, the address counter is advanced
(by one if DIFF is low, by two if DIFF is high) and the MUX
address for the present conversion is available on the ad-
dress output pins (DIFF
the conversion result.
Program/Readback Mode
The LTC1852 and LTC1853 include a sequencer that can
be programmed to run a sequence of up to 16 locations
containing a MUX address and input confi guration. The
MUX address and input confi guration for each location
are programmed using the DIFF , A2 to A0, UNI/BIP and
PGA pins and are stored in memory along with an end-of-
sequence (EOS) bit that is generated automatically. The
six input address and confi guration bits plus the EOS bit
can be read back by accessing the 7-bit readback status
word (S6-S0) through the data output pins. The sequencer
memory is a 16 × 7 block of memory represented by the
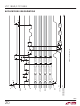
block diagram in Figure 10.
LOCATION 0000
LOCATION 0001
LOCATION 0010
LOCATION 1110
LOCATION 1111
OUT
pin is tied to the DIFF input pin, the scan pattern
Figure 10. Sequencer Memory Block Diagram
DIFF
•
•
•
A2
•
•
•
OUT
A1
, A2
•
•
•
OUT
A0
•
•
•
to A0
UNI/BIP
•
•
•
OUT
) along with
PGA
•
•
•
EOS
18523 F10
18523fa
•
•
•