LTC3127EDD LINER [Linear Technology], LTC3127EDD Datasheet - Page 9

LTC3127EDD
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC3127EDD
Description
1A Buck-Boost DC/DC Converter with Programmable Input Current Limit
Manufacturer
LINER [Linear Technology]
Datasheet
1.LTC3127EDD.pdf
(20 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LTC3127EDD
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
LTC3127EDD
Manufacturer:
LINEAR
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LTC3127EDD#PBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
The LTC3127 is an average input current controlled buck-
boost DC/DC converter offered in both a thermally enhanced
3mm × 3mm DFN package and a thermally enhanced 12-
lead MSOP package. The buck-boost converter utilizes a
proprietary switching algorithm which allows its output
voltage to be regulated above, below or equal to the input
voltage. The low R
switches efficiently provide high frequency PWM control.
High efficiency is achieved at light loads when Burst Mode
operation is commanded.
PWM Mode Operation
The LTC3127 uses fixed frequency, average input cur-
rent PWM control. The MODE pin can be used to select
automatic Burst Mode operation (MODE connected to
V
continuous conduction operation for low noise applications
(MODE grounded).
A proprietary switching algorithm allows the converter
to switch between buck, buck-boost and boost modes
without discontinuity in inductor current or loop charac-
teristics. The switch topology for the buck-boost converter
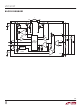
is shown in Figure 1.
When the input voltage is significantly greater than the
output voltage, the buck-boost converter operates in
buck mode. Switch D turns on continuously and switch C
remains off. Switches A and B are pulse width modulated
to produce the required duty cycle to support the output
regulation voltage. As the input voltage decreases, switch
A remains on for a larger portion of the switching cycle.
When the duty cycle reaches approximately 85%, the
switch pair AC begins turning on for a small fraction of the
switching period. As the input voltage decreases further,
operaTion
IN
) or to disable Burst Mode operation and select forced
DS(ON)
, low gate charge synchronous
LTC3127
Figure 1. Buck-Boost Switch Topology
V
IN
A
PGND
SW1
B
L
the AC switch pair remains on for longer durations and
the duration of the BD phase decreases proportionally. As
the input voltage drops below the output voltage, the AC
phase will eventually increase to the point that there is no
longer any BD switching. At this point, switch A remains
on continuously while switch pair CD is pulse width modu-
lated to obtain the desired output voltage. At this point,
the converter is operating solely in boost mode.
This switching algorithm provides a seamless transition
between operating modes and eliminates discontinuities
in average inductor current, inductor current ripple, and
loop transfer function throughout all three operational
modes. These advantages result in increased efficiency
and stability in comparison to the traditional 4-switch
buck-boost converter. In forced PWM mode operation,
the inductor is forced to have continuous conduction.
This allows for a constant switching frequency and better
noise performance.
Error Amplifier and Compensation
The buck-boost converter utilizes two control loops. The
outer voltage loop determines the amount of current re-
quired to regulate the output voltage. The voltage loop is
externally compensated and can be configured with either
integral compensation or proportional control. The inner
current loop is internally compensated and forces the input
current to equal the commanded current.
When V
dominant pole of the output capacitor is used to ensure
stability with a minimum of 1000µF of capacitance on the
output when a 499k resistor is used. There is no maximum
capacitance limitation with proportional compensation.
PGND
C
SW2
C
D
is compensated via proportional control, the
V
OUT
3127 F01
LTC3127
3127f