INA111_07 BURR-BROWN [Burr-Brown Corporation], INA111_07 Datasheet - Page 8

INA111_07
Manufacturer Part Number
INA111_07
Description
High Speed FET-Input INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
Manufacturer
BURR-BROWN [Burr-Brown Corporation]
Datasheet
1.INA111_07.pdf
(14 pages)
The INA111 exhibits approximately 6dB rise in gain at
2MHz in unity gain. This is a result of its current-feedback
topology and is not an indication of instability. Unlike an op
amp with poor phase margin, the rise in response is a
predictable +6dB/octave due to a response zero. A simple
pole at 700kHz or lower will produce a flat passband
response (see Input Filtering).
The INA111 provides excellent rejection of high frequency
common-mode signals. The typical performance curve,
“Common-Mode Rejection vs Frequency” shows this be-
havior. If the inputs are not properly balanced, however,
common-mode signals can be converted to differential sig-
nals. Run the V
other, from the source signal all the way to the input pins. If
possible use a ground plane under both input traces. Avoid
running other potentially noisy lines near the inputs.
NOISE AND ACCURACY PERFORMANCE
The INA111’s FET input circuitry provides low input bias
current and high speed. It achieves lower noise and higher
accuracy with high impedance sources. With source imped-
ances of 2k to 50k the INA114 may provide lower offset
voltage and drift. For very low source impedance ( 1k ),
the INA103 may provide improved accuracy and lower
noise.
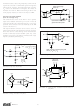
OFFSET TRIMMING
The INA111 is laser trimmed for low offset voltage and
drift. Most applications require no external offset adjust-
ment. Figure 2 shows an optional circuit for trimming the
output offset voltage. The voltage applied to Ref terminal is
summed at the output. Low impedance must be maintained
at this node to assure good common-mode rejection. The op
amp shown maintains low output impedance at high fre-
quency. Trim circuits with higher source impedance should
be buffered with an op amp follower circuit to assure low
impedance on the Ref pin.
FIGURE 2. Optional Trimming of Output Offset Voltage.
V
V
IN
IN
+
–
R
G
NOTE: (1) For wider trim range required
in high gains, scale resistor values larger
Adjustment Range
INA111
®
IN
±10mV
+
INA111
and V
Ref
IN
–
OPA177
V
connections directly adjacent each
O
10k
V+
V–
(1)
100
100
1/2 REF200
1/2 REF200
100µA
100µA
(1)
(1)
8
INPUT BIAS CURRENT RETURN PATH
The input impedance of the INA111 is extremely high—
approximately 10
the input bias current of both inputs. This input bias current
is typically less than 10pA. High input impedance means
that this input bias current changes very little with varying
input voltage.
Input circuitry must provide a path for this input bias current
if the INA111 is to operate properly. Figure 3 shows various
provisions for an input bias current path. Without a bias
current return path, the inputs will float to a potential which
exceeds the common-mode range of the INA111 and the
input amplifiers will saturate.
If the differential source resistance is low, the bias current
return path can be connected to one input (see the thermo-
couple example in Figure 3). With higher source impedance,
using two resistors provides a balanced input with possible
advantages of lower input offset voltage due to bias current
and better high-frequency common-mode rejection.
FIGURE 3. Providing an Input Common-Mode Current Path.
INPUT COMMON-MODE RANGE
The linear common-mode range of the input op amps of the
INA111 is approximately 12V (or 3V from the power
supplies). As the output voltage increases, however, the
linear input range will be limited by the output voltage swing
of the input amplifiers, A
is related to the output voltage of the complete amplifier—
see performance curve “Input Common-Mode Range vs
Output Voltage”.
Transducer
Crystal or
Thermocouple
Ceramic
1M
12
. However, a path must be provided for
1
and A
Center-tap provides
10k
bias current return.
1M
2
. The common-mode range
INA111
INA111
INA111