TC9455N Toshiba Semiconductor, TC9455N Datasheet - Page 4

TC9455N
Manufacturer Part Number
TC9455N
Description
(TC9455 / TC9488) TOSHIBA CMOS Digital Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic
Manufacturer
Toshiba Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.TC9455N.pdf
(14 pages)
Operation
1. Oscillator circuit
2. Microphone amps
1.1
1.2
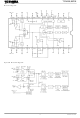
The TC9455F/N and TC9488F/N generate an internal system clock using the CR oscillator circuit.
Connecting a capacitance (C) of 68 pF and a resistance (R) of 5.6 kΩ sets the oscillator frequency to approx.
4 MHz and the sampling frequency to 32 kHz.
Varying the external capacitance enables the oscillator frequency and sampling frequency for the system
clock to be adjusted. Varying the system clock enables the delay time to be adjusted.
Figure 1 shows the CR oscillator circuit.
The IC incorporates microphone amps with auto level control (ALC).
The microphone amp gain is typically 36dB.
When a signal from 0 to −46dB is input, the ALC circuit can control the output signal level.
Changing the external capacitor connected to the ALC circuit to a resistor sets the ALC circuit to off.
Figure 2 shows the microphone amp circuit.
When C = 4.7 µF, the attack and release times are as follows:
Setting the capacitance (C) to a smaller value enables the
attack and release times to be adjusted. When the ALC circuit
is not used, change the capacitor (*1) to a resistor (approx. 10
kΩ), and connect to GND line.
At power on, while the capacitor is being charged, no sound is
output. So, use a capacitance of 4.7 µF or less.
Attack time = Approx. 29 ms
Release time = Approx. 1.6 s
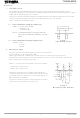
How to determine oscillator frequency (f)
f [MHz] = 1532/(C [pF] × R [kΩ])
Note 2: The oscillator frequency is a typical value (Ta =
How to determine sampling frequency (fs)
fs [kHz] = f/128
25°C). Set the resistance to between 4.7 kΩ and
6.8 kΩ.
= 1532/(68 × 5.6)
≈ 4.0 MHz (Note 2)
= 4.0/128
≈ 32 kHz
4
Microphone amp with ALC
CR Oscillator circuit
Figure 1
Figure 2
TC9455,88F/N
2002-02-05