GS82032A ETC1 [List of Unclassifed Manufacturers], GS82032A Datasheet

GS82032A
Available stocks
Related parts for GS82032A
GS82032A Summary of contents
Page 1
... Functional Description Applications The GS820E32 is a 2,097,152 bit high performance synchronous SRAM with a 2 bit burst address counter. Although of a type originally developed for Level 2 Cache applications supporting high performance CPU’s, the device now finds application in synchronous SRAM applications ranging from DSP main store to networking chip set support ...
Page 2
GS820E32 100 Pin TQFP and QFP Pinout 100 DDQ ...
Page 3
TQFP Pin Description Pin Location 37, 36 35, 34, 33, 32, 100, 99, 82, 81, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49 52, 53, 56, 57, 58, 59, 62, 63 68, 69, 72, 73, 74, 75, 78 ...
Page 4
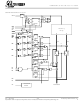
GS820E18/32/36 Block Diagram Register A0- LBO ADV CK ADSC ADSP Power Down ZZ Control Rev: 1.03 2/2000 Specifications ...
Page 5
Mode Pin Functions Mode Name Pin Name State Burst Order Control Output Register Control Power Down Control Note: There are pull up devices on LBO and FT pins and a pull down device on and ZZ pin, so those input ...
Page 6
Synchronous Truth Table Operation Address Used Deselect Cycle, Power Down Deselect Cycle, Power Down Deselect Cycle, Power Down Read Cycle, Begin Burst External Read Cycle, Begin Burst External Write Cycle, Begin Burst External Read Cycle, Continue Burst Read Cycle, Continue ...
Page 7
Simplified State Diagram Notes: 1. The diagram shows only supported (tested) synchronous state transitions. The diagram presumes G is tied Low. 2. The upper portion of the diagram assumes active use of only the Enable (E and that ADSP is ...
Page 8
Simplified State Diagram with G Notes: 1. The diagram shows supported (tested) synchronous state transitions plus supported transitions that depend upon the use Use of “Dummy Reads” (Read Cycles with G High) may be used to make ...
Page 9
Absolute Maximum Ratings ) (All voltages reference Symbol Description V Voltage on V Pins Voltage in V Pins DDQ DDQ V Voltage on Clock Input Pin CK V Voltage on I/O Pins I/O V ...
Page 10
... Junction to Ambient (at 200 lfm) Junction to Ambient (at 200 lfm) Junction to Case (TOP) Notes: 1. Junction temperature is a function of SRAM power dissipation, package thermal resistance, mounting board temperature, ambient. Temper- ature air flow, board density, and PCB thermal resistance. 2. SCMI G-38-87. 3. Average thermal resistance between die and top surface, MIL SPEC-883, Method 1012.1. ...
Page 11
AC Test Conditions Parameter Input high level Input low level Input slew rate Input reference level Output reference level Output load Notes: 1. Include scope and jig capacitance. 2. Test conditions as specified with output loading as shown in Fig. ...
Page 12
Operating Currents Parameter Test Conditions Device Selected; Operating All other inputs Current Output open Standby 0.2V DD Current Device Deselected; Deselect All other inputs Current Operating Currents Parameter Test ...
Page 13
AC Electrical Characteristics Parameter Symbol Clock Cycle Time Clock to Output Valid Pipeline Clock to Output Invalid Clock to Output in Low-Z Clock Cycle Time Clock to Output Valid Flow- Thru Clock to Output Invalid Clock to Output in Low-Z ...
Page 14
Write Cycle Timing Single Write ADSP ADSC ADV -An 0 WR1 Hi ...
Page 15
Flow Through Read Cycle Timing Single Read ADSP ADSC ADV -An RD1 tOLZ ...
Page 16
Flow Through Read-Write Cycle Timing Single Read ADSP ADSC ADV tS tH A0-An RD1 tOE G tKQ Hi-Z ...
Page 17
Pipelined DCD Read Cycle Timing Single Read ADSP ADSC ADV -An RD1 Hi-Z ...
Page 18
Pipelined DCD Read-Write Cycle Timing Single Read ADSP ADSC tS tH ADV RD1 ...
Page 19
... Dummy read cycles waste performance but their use usually assures there will be no bus contention in transitions from reads to writes or between banks of RAMs. DCD SRAMs do not waste bandwidth on dummy cycles and are logically simpler to manage in a multiple bank application (wait states need not be inserted at bank address boundary crossings) but greater care must be exercised to avoid excessive bus contention ...
Page 20
GS 820E32 Output Driver Characteristics 60 Pull Down Drivers -20 -40 Pull Up Drivers -60 -80 -0.5 0 0.5 3. Rev: 1.03 2/2000 Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation ...
Page 21
TQFPand QFP Package Drawing Symbol Description A1 A2 Body Thickness b c Lead Thickness D Terminal Dimension D1 Package Body E Terminal Dimension E1 Package Body Notes: 1. All dimensions are ...
Page 22
Org Part Number 64K x 32 GS820E32T-150 Pipeline/Flow Through 64K x 32 GS820E32T-138 Pipeline/Flow Through 64K x 32 GS820E32T-133 Pipeline/Flow Through 64K x 32 GS820E32T-4 Pipeline/Flow Through 64K x 32 GS820E32T-5 Pipeline/Flow Through 64K x 32 GS820E32T-6 Pipeline/Flow Through ...
Page 23
... Rev: 1.03 2/2000 Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com. Revisions • This was the first release of 2 Meg Burst Datasheets in the new format. Format They included information for the Fine Pitch BGA package. • Took out the Fine Pitch BGA information. ...