S29GL512S10FHI010 Spansion, S29GL512S10FHI010 Datasheet

S29GL512S10FHI010
Specifications of S29GL512S10FHI010
Related parts for S29GL512S10FHI010
S29GL512S10FHI010 Summary of contents
Page 1
... Availability of this document is retained for reference and historical purposes only. Notice to Readers: This document states the current technical specifications regarding the Spansion product(s) described herein. Spansion Inc. deems the products to have been in sufficient production volume such that subsequent versions of this document are not expected to change. However, typographical or specification corrections, or modifications to the valid combinations offered may occur ...
Page 2
... The Advance Information designation indicates that Spansion Inc. is developing one or more specific products, but has not committed any design to production. Information presented in a document with this designation is likely to change, and in some cases, development on the product may discontinue. Spansion Inc. therefore places the following conditions upon Advance Information content: “ ...
Page 3
... Data# polling and toggle bits provide status – Unlock Bypass Program command reduces overall multiple-word programming time – CFI (Common Flash Interface) compliant: allows host system to identify and accommodate multiple flash devices Hardware Features – Advanced Sector Protection – ...
Page 4
... The RESET# pin may be tied to the system reset circuitry. A system reset would thus also reset the device, enabling the host system to read boot-up firmware from the Flash memory device. The device reduces power consumption in the standby mode when it detects specific voltage levels on CE# and RESET#, or when addresses have been stable for a specified period of time ...
Page 5
... Persistent Protection Mode Lock Bit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 7.15 Password Sector Protection 7.16 Password and Password Protection Mode Lock Bit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 7.17 64-bit Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 7.18 Persistent Protection Bit Lock (PPB Lock Bit 7.19 Secured Silicon Sector Flash Memory Region . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 7.20 Write Protect (WP 7.21 Hardware Data Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 8. Common Flash Memory Interface (CFI Command Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 9.1 Reading Array Data ...
Page 6
DQ7: Data# Polling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 7
Figures Figure 3.1 56-Pin Standard TSOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 8
Tables Table 7.1 Device Bus Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 9
Product Selector Guide 1.1 S29GL512N Part Number Speed Option Max. Access Time (ns) Max. CE# Access Time (ns) Max. Page access time (ns) Max. OE# Access Time (ns) 1.2 S29GL256N, S29GL128N Speed Option Max. Access Time (ns) Max. CE# ...
Page 10
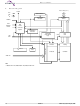
Block Diagram RY/BY RESET# WE# State WP#/ACC Control BYTE# Command Register CE# OE# V Detector CC A **–A0 Max Note ** A GL512N = A24, A GL256N = A23, A Max Max Max ...
Page 11
Connection Diagrams NC for S29GL128N A23 1 A22 2 A15 3 A14 4 A13 5 A12 6 A11 7 A10 A19 11 A20 12 WE# 13 RESET# 14 A21 15 WP#/ACC 16 RY/BY# 17 ...
Page 12
... Special Package Handling Instructions Special handling is required for Flash Memory products in molded packages (TSOP, BGA). The package and/or data integrity may be compromised if the package body is exposed to temperatures above 150°C for prolonged periods of time. 4. Pin Description A24–A0 25 Address inputs (512 Mb) A23– ...
Page 13
May 30, 2008 S29GL-N_00_B8 Figure 5.2 S29GL256N 24 A23–A0 DQ15–DQ0 CE# (A-1) OE# WE# WP#/ACC RESET RY/BY# BYTE# Figure 5.3 S29GL128N 23 A22–A0 DQ15–DQ0 CE# (A-1) OE# WE# WP#/ACC ...
Page 14
... S29GL512N 11 DEVICE NUMBER/DESCRIPTION S29GL128N, S29GL256N, S29GL512N 3.0 Volt-only, 512 Megabit ( 16-Bit/ 8-Bit) Page-Mode Flash Memory Manufactured on 110 nm MirrorBit process technology Valid Combinations Valid Combinations list configurations planned to be supported in volume for this device. Consult your local sales office to confirm availability of specific valid combinations and to check on newly released combinations ...
Page 15
Device Bus Operations This section describes the requirements and use of the device bus operations, which are initiated through the internal command register. The command register itself does not occupy any addressable memory location. The register is a latch ...
Page 16
The device remains enabled for read access until the command register contents are altered. See Reading Array Data on page 48 timing specifications and to table for ...
Page 17
... CMOS standby current (I greater. The RESET# pin may be tied to the system reset circuitry. A system reset would thus also reset the Flash memory, enabling the system to read the boot-up firmware from the Flash memory. Refer to the AC Characteristics tables for RESET# parameters and to diagram ...
Page 18
Output Disable Mode When the OE# input impedance state. Sector SA0 0 0 SA1 0 0 SA2 0 0 SA3 0 0 SA4 0 0 SA5 0 0 SA6 0 0 SA7 0 0 SA8 0 ...
Page 19
Sector SA44 0 0 SA45 0 0 SA46 0 0 SA47 0 0 SA48 0 0 SA49 0 0 SA50 0 0 SA51 0 0 SA52 0 0 SA53 0 0 SA54 0 0 SA55 0 0 SA56 0 0 ...
Page 20
Sector SA91 0 0 SA92 0 0 SA93 0 0 SA94 0 0 SA95 0 0 SA96 0 0 SA97 0 0 SA98 0 0 SA99 0 0 SA100 0 0 SA101 0 0 SA102 0 0 SA103 0 0 ...
Page 21
Sector SA138 0 1 SA139 0 1 SA140 0 1 SA141 0 1 SA142 0 1 SA143 0 1 SA144 0 1 SA145 0 1 SA146 0 1 SA147 0 1 SA148 0 1 SA149 0 1 SA150 0 1 ...
Page 22
Sector SA185 0 1 SA186 0 1 SA187 0 1 SA188 0 1 SA189 0 1 SA190 0 1 SA191 0 1 SA192 0 1 SA193 0 1 SA194 0 1 SA195 0 1 SA196 0 1 SA197 0 1 ...
Page 23
Sector SA232 0 1 SA233 0 1 SA234 0 1 SA235 0 1 SA236 0 1 SA237 0 1 SA238 0 1 SA239 0 1 SA240 0 1 SA241 0 1 SA242 0 1 SA243 0 1 SA244 0 1 ...
Page 24
Sector SA279 1 0 SA280 1 0 SA281 1 0 SA282 1 0 SA283 1 0 SA284 1 0 SA285 1 0 SA286 1 0 SA287 1 0 SA288 1 0 SA289 1 0 SA290 1 0 SA291 1 0 ...
Page 25
Sector SA326 1 0 SA327 1 0 SA328 1 0 SA329 1 0 SA330 1 0 SA331 1 0 SA332 1 0 SA333 1 0 SA334 1 0 SA335 1 0 SA336 1 0 SA337 1 0 SA338 1 0 ...
Page 26
Sector SA373 1 0 SA374 1 0 SA375 1 0 SA376 1 0 SA377 1 0 SA378 1 0 SA379 1 0 SA380 1 0 SA381 1 0 SA382 1 0 SA383 1 0 SA384 1 1 SA385 1 1 ...
Page 27
Sector SA420 1 1 SA421 1 1 SA422 1 1 SA423 1 1 SA424 1 1 SA425 1 1 SA426 1 1 SA427 1 1 SA428 1 1 SA429 1 1 SA430 1 1 SA431 1 1 SA432 1 1 ...
Page 28
Sector SA467 1 1 SA468 1 1 SA469 1 1 SA470 1 1 SA471 1 1 SA472 1 1 SA473 1 1 SA474 1 1 SA475 1 1 SA476 1 1 SA477 1 1 SA478 1 1 SA479 1 1 ...
Page 29
Sector SA0 0 0 SA1 0 0 SA2 0 0 SA3 0 0 SA4 0 0 SA5 0 0 SA6 0 0 SA7 0 0 SA8 0 0 SA9 0 0 SA10 0 0 SA11 0 0 SA12 0 0 ...
Page 30
Sector SA47 0 0 SA48 0 0 SA49 0 0 SA50 0 0 SA51 0 0 SA52 0 0 SA53 0 0 SA54 0 0 SA55 0 0 SA56 0 0 SA57 0 0 SA58 0 0 SA59 0 0 ...
Page 31
Sector SA94 0 1 SA95 0 1 SA96 0 1 SA97 0 1 SA98 0 1 SA99 0 1 SA100 0 1 SA101 0 1 SA102 0 1 SA103 0 1 SA104 0 1 SA105 0 1 SA106 0 1 ...
Page 32
Sector SA141 1 0 SA142 1 0 SA143 1 0 SA144 1 0 SA145 1 0 SA146 1 0 SA147 1 0 SA148 1 0 SA149 1 0 SA150 1 0 SA151 1 0 SA152 1 0 SA153 1 0 ...
Page 33
Sector SA188 1 0 SA189 1 0 SA190 1 0 SA191 1 0 SA192 1 1 SA193 1 1 SA194 1 1 SA195 1 1 SA196 1 1 SA197 1 1 SA198 1 1 SA199 1 1 SA200 1 1 ...
Page 34
Sector SA235 1 1 SA236 1 1 SA237 1 1 SA238 1 1 SA239 1 1 SA240 1 1 SA241 1 1 SA242 1 1 SA243 1 1 SA244 1 1 SA245 1 1 SA246 1 1 SA247 1 1 ...
Page 35
Sector SA0 0 0 SA1 0 0 SA2 0 0 SA3 0 0 SA4 0 0 SA5 0 0 SA6 0 0 SA7 0 0 SA8 0 0 SA9 0 0 SA10 0 0 SA11 0 0 SA12 0 0 ...
Page 36
Sector SA46 0 SA47 0 SA48 0 SA49 0 SA50 0 SA51 0 SA52 0 SA53 0 SA54 0 SA55 0 SA56 0 SA57 0 SA58 0 SA59 0 SA60 0 SA61 0 SA62 0 SA63 0 SA64 1 SA65 ...
Page 37
Sector SA93 1 0 SA94 1 0 SA95 1 0 SA96 1 1 SA97 1 1 SA98 1 1 SA99 1 1 SA100 1 1 SA101 1 1 SA102 1 1 SA103 1 1 SA104 1 1 SA105 1 1 ...
Page 38
... To access the autoselect codes in-system, the host system can issue the autoselect command via the command register, as shown in require V . Refer to the ID Table 7.5 Autoselect Codes (High Voltage Method) Description CE# OE# WE# Manufacturer ID Spansion Product Cycle 1 Cycle Cycle 3 Cycle 1 Cycle Cycle 3 Cycle 1 ...
Page 39
... Persistent Sector Protection Mode into the Password Protection Mode. The device is shipped with all sectors unprotected. The factory offers the option of programming and protecting sectors at the factory prior to shipping the device through the ExpressFlash™ Service. Contact your sales representative for details. ...
Page 40
Secured Silicon Sector Protection allows the user to lock the Secured Silicon Sector area Persistent Protection Mode Lock Bit allows the user to set the device permanently to operate in the Persistent Protection Mode Password Protection Mode Lock Bit allows ...
Page 41
... PPB Erase” command. The “All PPB Erase” command preprograms all PPB bits prior to PPB erasing. All PPB bits erase in parallel, unlike programming where individual PPB bits are programmable. The PPB bits have the same endurance as the flash memory. Programming the PPB bit requires the typical word programming time without utilizing the Write Buffer. ...
Page 42
... If they match, the PPB Lock Bit is cleared to the unfreezed state, and the PPB bits can be altered. If they do not match, the flash device does nothing. There is a built-in 2 µs delay for each password check after the valid 64-bit password is entered for the PPB Lock Bit to be cleared to the “ ...
Page 43
... Secured Silicon Sector Flash Memory Region The Secured Silicon Sector feature provides a Flash memory region that enables permanent part identification through an Electronic Serial Number (ESN). The Secured Silicon Sector is 256 bytes in length, and uses a Secured Silicon Sector Indicator Bit (DQ7) to indicate whether or not the Secured Silicon Sector is locked when shipped from the factory ...
Page 44
... ESN at addresses 000000h–000007h. Please contact your sales representative for details on ordering ESN Factory Locked devices. Customers may opt to have their code programmed by the factory through the ExpressFlash service (Express Flash Factory Locked). The devices are then shipped from the factory with the Secured Silicon Sector permanently locked ...
Page 45
... Software support can then be device-independent, JEDEC ID-independent, and forward- and backward-compatible for the specified flash device families. Flash vendors can standardize their existing interfaces for long-term compatibility. This device enters the CFI Query mode when the system writes the CFI Query command, 98h, to address 55h, any time the device is ready to read array data ...
Page 46
... N Device Size = 2 4Eh 0019h 1A = 512 Mb 256 Mb 128 Mb 0018h 50h 0002h Flash Device Interface description (refer to CFI publication 100) 52h 0000h 54h 0005h Max. number of byte in multi-byte write = 2 56h 0000h (00h = not supported) Number of Erase Block Regions within device (01h = uniform device, 02h = ...
Page 47
Addresses (x16) Addresses (x8) 40h 41h 42h 43h 44h 45h 46h 47h 48h 49h 4Ah 4Bh 4Ch 4Dh 4Eh 4Fh 50h May 30, 2008 S29GL-N_00_B8 Table 8.4 Primary Vendor-Specific Extended Query ...
Page 48
Command Definitions Writing specific address and data commands or sequences into the command register initiates device operations. Table 9.1 on page 60 Writing incorrect address and data values or writing them in the improper sequence may place the device ...
Page 49
... See also “Secured Silicon Sector Flash Memory Region” for further information. Note that the ACC function and unlock bypass modes are not available when the Secured Silicon Sector is enabled. ...
Page 50
... Once the specified number of write buffer locations have been loaded, the system must then write the Program Buffer to Flash command at the sector address. Any other address and data combination aborts the Write Buffer Programming operation. The device then begins programming. Data polling should be used while monitoring the last address location loaded into the write buffer ...
Page 51
... Write buffer programming is allowed in any sequence. Note that the Secured Silicon sector, autoselect, and CFI functions are unavailable when a program operation is in progress. This flash device is capable of handling multiple write buffer programming operations on the same write buffer address range without intervening erases ...
Page 52
... Sector Address Write first address/data Yes Abort Write to Yes Buffer Operation? No (Note 1) Write next address/data pair Write program buffer to flash sector address Read DQ15 - DQ0 at Last Loaded Address Yes DQ7 = Data DQ1 = 1? DQ5 = 1? Yes Yes Read DQ15 - DQ0 with ...
Page 53
Note See Table 9.1 on page 60 and 9.6 Program Suspend/Program Resume Command Sequence The Program Suspend command allows the system to interrupt a programming operation or a Write to Buffer programming operation so that data can be read from ...
Page 54
Chip Erase Command Sequence Chip erase is a six bus cycle operation. The chip erase command sequence is initiated by writing two unlock cycles, followed by a set-up command. Two additional unlock write cycles are then followed by the ...
Page 55
Sector Erase Command Sequence Sector erase is a six bus cycle operation. The sector erase command sequence is initiated by writing two unlock cycles, followed by a set-up command. Two additional unlock cycles are written, and are then followed ...
Page 56
... The Lock Register Command Set Exit command must be issued after the execution of the commands to reset the device to read mode. Otherwise the device hangs. If this happens, the flash device must be reset. Please refer to RESET# for more information important to note that the device is in either Persistent Protection mode or Password Protection mode depending on the mode selected prior to the device hang ...
Page 57
Password Protection Command Set Definitions The Password Protection Command Set permits the user to program the 64-bit password, verify the programming of the 64-bit password, and then later unlock the device by issuing the valid 64-bit password. The Password ...
Page 58
... PPB bits. The device preprograms all PPB bits prior to erasing when issuing the All PPB Erase command. Also note that the total number of PPB program/erase cycles has the same endurance as the flash memory array. PPB Status Read Command The programming state of the PPB for a given sector can be verified by writing a PPB Status Read Command to the device ...
Page 59
Volatile Sector Protection Command Set The Volatile Sector Protection Command Set permits the user to set the Dynamic Protection Bit (DYB) to the protected state, clear the Dynamic Protection Bit (DYB) to the unprotected state, and read the logic ...
Page 60
... The data is 00h for an unprotected sector and 01h for a protected sector. PPB Status Read provides the same data but in inverted form. 10. If DQ7 = 1, region is factory serialized and protected. If DQ7 = 0, region is unserialized and unprotected when shipped from factory. See Flash Memory Region on page 43 for more information. ...
Page 61
Command Sequence (Notes) Command Set Entry (5) 3 Lock Program (6) 2 Register Read (6) 1 Bits Command Set Exit (7) 2 Command Set Entry (5) 3 Program (8) 2 Password Read (9) 4 Protection Unlock (10) 7 Command Set ...
Page 62
... The data is 00h for an unprotected sector and 01h for a protected sector. PPB Status Read provides the same data but in inverted form. 10. If DQ7 = 1, region is factory serialized and protected. If DQ7 = 0, region is unserialized and unprotected when shipped from factory. See Flash Memory Region on page 43 for more information. ...
Page 63
Command Sequence (Notes) Command Set Entry (5) 3 Lock Program (6) 2 Register Read (6) 1 Bits Command Set Exit (7) 2 Command Set Entry (5) 3 Program (8) 2 Read (9) 8 Password Protection 1 Unlock (10) 1 Command ...
Page 64
Write Operation Status The device provides several bits to determine the status of a program or erase operation: DQ2, DQ3, DQ5, DQ6, and DQ7. Table 10.1 on page 68 and DQ6 each offer a method for determining whether a ...
Page 65
Notes Valid address for programming. During a sector erase operation, a valid address is any sector address within the sector being erased. During chip erase, a valid address is any non-protected sector address. 2. DQ7 should be ...
Page 66
The system can use DQ6 and DQ2 together to determine whether a sector is actively erasing or is erase- suspended. When the device is actively erasing (that is, the Embedded Erase algorithm is in progress), DQ6 toggles. When the device ...
Page 67
DQ2: Toggle Bit II The Toggle Bit II on DQ2, when used with DQ6, indicates whether a particular sector is actively erasing (that is, the Embedded Erase algorithm is in progress), or whether that sector is erase-suspended. Toggle Bit ...
Page 68
DQ3: Sector Erase Timer After writing a sector erase command sequence, the system may read DQ3 to determine whether or not erasure has begun. (The sector erase timer does not apply to the chip erase command.) If additional sectors ...
Page 69
Absolute Maximum Ratings Storage Temperature, Plastic Packages Ambient Temperature with Power Applied Voltage with Respect to Ground: V (Note and ACC (Note 2) All other pins (Note 1) Output Short Circuit Current Notes 1. ...
Page 70
DC Characteristics 13.1 CMOS Compatible Parameter Parameter Description Symbol I Input Load Current Input Load Current LIT I Output Leakage Current Active Read Current CC1 Intra-Page Read Current CC2 CC ...
Page 71
Test Conditions Note Diodes are IN3064 or equivalent Output Load Output Load Capacitance, C (including jig capacitance) Input Rise and Fall Times Input Pulse Levels Input timing measurement reference levels (See Note) Output timing measurement reference levels Note If ...
Page 72
AC Characteristics 15.1 Read-Only Operations Parameter JEDEC Std Read Cycle Time AVAV Address to Output Delay AVQV ACC t t Chip Enable to Output Delay ELQV CE t Page Access Time PACC t t ...
Page 73
Amax-A2 A2-A0* Data Bus CE# OE# Note * Figure shows word mode. Addresses are A2–A-1 for byte mode. 15.2 Hardware Reset (RESET#) Parameter JEDEC Std. RESET# Pin Low (During Embedded Algorithms Ready Read Mode RESET# Pin Low (NOT ...
Page 74
RY/BY# CE#, OE# RESET# RY/BY# CE#, OE# RESET Figure 15.3 Reset Timings Ready Reset Timings NOT during Embedded Algorithms Reset Timings during Embedded Algorithms t ...
Page 75
Erase and Program Operations Parameter JEDEC Std Write Cycle Time AVAV Address Setup Time AVWL AS Address Setup Time to OE# low during toggle bit t ASO polling t t Address Hold Time WLAX ...
Page 76
Addresses CE# OE# WE# Data RY/BY Notes program address program data Illustration shows device in word mode ACC Notes 1. Not 100% tested. 2. ...
Page 77
Addresses CE# OE# WE# Data RY/BY Notes sector address (for Sector Erase Valid Address for reading status data (see 2. These waveforms are for the word mode. Addresses CE OE# ...
Page 78
Addresses CE# WE# OE# Valid Data DQ2 and DQ6 RY/BY# Notes VA = Valid address; not required for DQ6. Illustration shows first two status cycle after command sequence, last status read cycle, and array data read cycle Enter Erase Embedded ...
Page 79
Alternate CE# Controlled Erase and Program Operations: S29GL128N, S29GL256N, S29GL512N Parameter JEDEC Std Write Cycle Time AVAV Address Setup Time AVWL AS T Address Setup Time to OE# low during toggle bit polling ASO ...
Page 80
Figure 15.10 Alternate CE# Controlled Write (Erase/Program) Operation Timings Addresses WE# OE# CE# Data RESET# RY/BY# Notes 1. Figure indicates last two bus cycles of a program or erase operation program address sector address, PD ...
Page 81
Erase And Programming Performance Parameter Sector Erase Time Chip Erase Time Total Write Buffer Programming Time Total Accelerated Effective Write Buffer Programming Time (Note 3) Chip Program Time Notes 1. Typical program and erase times assume the following conditions: ...
Page 82
Physical Dimensions 18.1 TS056—56-Pin Standard Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP) PACKAGE TS 56 JEDEC MO-142 (B) EC SYMBOL MIN. NOM. MAX. A --- --- 1.20 A1 0.05 --- 0.15 A2 0.95 1.00 1.05 b1 0.17 0.20 0.23 b 0.17 ...
Page 83
LAA064—64-Ball Fortified Ball Grid Array (FBGA) PACKAGE LAA 064 JEDEC N/A 13. 11.00 mm PACKAGE SYMBOL MIN NOM A --- --- A1 0.40 --- A2 0.60 --- D 13.00 BSC. E 11.00 BSC. D1 7.00 BSC. E1 ...
Page 84
Advance Information on S29GL-P Hardware Reset (RESET#) and Power- up Sequence Parameter JEDEC Std. RESET# Pin Low (During Embedded Algorithms Ready Read Mode or Write mode RESET# Pin Low (NOT During Embedded Algorithms) t Ready to Read ...
Page 85
Parameter Reset Low Time from Rising Edge VCS Edge of RESET# Reset Low Time from Rising Edge VIOS Edge of RESET# t Reset High Time Before Read RH Notes 1. V < ...
Page 86
Advance Information on S29GL MirrorBit Hardware Reset (RESET#) and Power-up Sequence Parameter t RESET# Low to CE# Low RPH t RESET# Pulse Width RP t Time between RESET# (high) and CE# (low) RH Note CE#, OE# and ...
Page 87
Revision History 21.1 Revision A (September 2, 2003) Initial Release. 21.2 Revision A1 (October 16, 2003) Global Added LAA064 package. Distinctive Characteristics, Performance Characteristics Clarified fifth bullet information. Added RTSOP to Package Options. Distinctive Characteristics, Software and Hardware Features ...
Page 88
Revision A2 (January 22, 2004) Lock Register Corrected and added new text for Secured Silicon Sector Protection Bit, Persistent Protection Mode Lock Bit, and Password Protection Mode Lock Bit. Persistent Sector Protection Persistent Protection Bit (PPB): Added the second ...
Page 89
Revision A4 (May 13, 2004) Global Removed references to RTSOP. Distinctive Characteristics Removed 16-word/32-byte page read buffer from Performance Characteristics. Changed Low power consumption typical active read current and removed 10 mA typical intrapage active read ...
Page 90
Figure Read Operation Timings Added t to figure. CEH Figure Page Read Timings Change A1-A0 to A2-A0. Erase and Program Operations Updated t and t WHWH1 Figure Chip/Sector Erase Operation Timings Changed 5555h to 55h and 3030h to 30h. Figure ...
Page 91
Erase and Program Operations Created a family table. Alternate CE# Controlled Erase and Program Operations Created a family table. Erase and Programming Performance Created a family table. 21.7 Revision A6 (January 24, 2005) Global Updated access times for S29GL512N. Product ...
Page 92
... Corrected bit range values for A22–A16. Persistent Protection Bit (PPB) Corrected typo in second sentence, second paragraph. Secured Silicon Sector Flash Memory Region Deleted note at end of second paragraph. Customer Lockable: Secured Silicon Sector NOT Programmed or Protected At the Factory Modified 1st bullet text. ...
Page 93
Write Buffer Programming Deleted note from eighth paragraph. Program Suspend/Program Resume Command Sequence Corrected typos in first paragraph. Lock Register Command Set Definitions Modified fifth paragraph. Volatile Sector Protection Command Set Modified fourth paragraph. Sector Protection Commands (x16) table Changed ...
Page 94
Revision B6 (November 8, 2007) Advance Information on S29GL-R 65nm MirrorBit Hardware Reset (RESET#) and Power-up Sequence Added advanced information 21.18 Revision B7 (February 12, 2008) Erase And Programming Performance Chip Program Time: removed comment Advance Information on S29GL-R ...
Page 95
... Please note that Spansion will not be liable to you and/or any third party for any claims or damages arising in connection with above-mentioned uses of the products. Any semiconductor devices have an inherent chance of failure ...