MAX9700BEBC-T Maxim Integrated, MAX9700BEBC-T Datasheet - Page 11

MAX9700BEBC-T
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX9700BEBC-T
Description
Audio Amplifiers
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated
Datasheet
1.MAX9700BEUB-T.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of MAX9700BEBC-T
Output Type
1-Channel Mono
Output Power
1.6 W x 1 at 6 Ohms
Thd Plus Noise
0.01 % at 8 Ohms at 125 mW
Operating Supply Voltage
3 V, 5 V
Maximum Power Dissipation
484 mW
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
UCSP
Audio Load Resistance
16 Ohms
Common Mode Rejection Ratio (min)
72 dB (Typ)
Input Signal Type
Differential
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Output Signal Type
Differential
Supply Type
Single
Supply Voltage - Max
5.5 V
Supply Voltage - Min
2.5 V
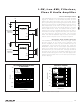
Figure 3. MAX9700 EMI Spectrum
The MAX9700 has a shutdown mode that reduces power
consumption and extends battery life. Driving SHDN low
places the MAX9700 in a low-power (0.1µA) shutdown
mode. Connect SHDN to V
The MAX9700 features comprehensive click-and-pop
suppression that eliminates audible transients on start-
up and shutdown. While in shutdown, the H-bridge is in
a high-impedance state. During startup or power-up,
the input amplifiers are muted and an internal loop sets
the modulator bias voltages to the correct levels, pre-
venting clicks and pops when the H-bridge is subse-
quently enabled. For 35ms following startup, a soft-start
function gradually unmutes the input amplifiers.
Traditional class D amplifiers require an output filter to
recover the audio signal from the amplifier’s output. The
filters add cost, increase the solution size of the amplifi-
er, and can decrease efficiency. The traditional PWM
scheme uses large differential output swings (2 x V
peak-to-peak) and causes large ripple currents. Any
parasitic resistance in the filter components results in a
loss of power, lowering the efficiency.
The MAX9700 does not require an output filter. The
device relies on the inherent inductance of the speaker
coil and the natural filtering of both the speaker and the
human ear to recover the audio component of the
square-wave output. Eliminating the output filter results
in a smaller, less costly, more efficient solution.
50.0
45.0
40.0
35.0
30.0
25.0
20.0
15.0
10.0
30.0
60.0
80.0 100.0 120.0 140.0 160.0 180.0
Applications Information
______________________________________________________________________________________
Click-and-Pop Suppression
FREQUENCY (MHz)
DD
for normal operation.
Filterless Operation
200.0
220.0
240.0 260.0
Shutdown
280.0 300.0
DD
1.2W, Low-EMI, Filterless,
Class D Audio Amplifier
Figure 4. MAX9700 Outputs with No Input Signal
Figure 5. MAX9700 Efficiency vs. Class AB Efficiency
Because the frequency of the MAX9700 output is well
beyond the bandwidth of most speakers, voice coil
movement due to the square-wave frequency is very
small. Although this movement is small, a speaker not
designed to handle the additional power can be dam-
aged. For optimum results, use a speaker with a series
inductance >10µH. Typical 8Ω speakers exhibit series
inductances in the 20µH to 100µH range.
Unlike a class AB amplifier, the output offset voltage of
a class D amplifier does not noticeably increase quies-
cent current draw when a load is applied. This is due to
V OUT+ - V OUT- = 0V
V IN = 0V
OUT+
OUT-
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0
EFFICIENCY vs. OUTPUT POWER
Power-Conversion Efficiency
0.1
MAX9700
0.2
OUTPUT POWER (W)
0.3
CLASS AB
0.4
0.5
V
f = 1kHz
R
DD
L
- 8Ω
= 3.3V
0.6
0.7
11