MAX807NCPE Maxim Integrated, MAX807NCPE Datasheet - Page 15

MAX807NCPE
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX807NCPE
Description
Supervisory Circuits
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated
Series
MAX807L, MAX807M, MAX807Nr
Datasheet
1.MAX807MCWE-T.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of MAX807NCPE
Number Of Voltages Monitored
1
Monitored Voltage
4.575 V
Undervoltage Threshold
4.5 V
Overvoltage Threshold
4.65 V
Output Type
Active High, Active Low
Manual Reset
Resettable
Watchdog
Watchdog
Battery Backup Switching
Backup
Power-up Reset Delay (typ)
280 ms
Supply Voltage - Max
5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
Package / Case
PDIP N
Chip Enable Signals
Yes
Maximum Power Dissipation
842 mW
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
Power Fail Detection
Yes
Supply Current (typ)
70 uA
Supply Voltage - Min
0 V
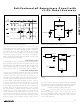
The backup battery may be disconnected while V
above the reset threshold, provided BATT is bypassed
with a 0.1µF capacitor to ground. No precautions are
necessary to avoid spurious reset pulses.
While issuing resets to the µP during power-up, power-
down, and brownout conditions, these supervisors are
relatively immune to short-duration negative-going V
transients (glitches). It is usually undesirable to reset
the µP when V
The Typical Operating Characteristics show Maximum
Transient Duration vs. Reset Comparator Overdrive, for
which reset pulses are not generated. The graph was
produced using negative-going V
5V and ending below the reset threshold by the magni-
tude indicated (reset comparator overdrive). The graph
shows the maximum pulse width that a negative-going
V
reset pulse to be issued. As the amplitude of the tran-
sient increases (i.e., goes farther below the reset
threshold), the maximum allowable pulse width
decreases.
Typically, a V
reset threshold and lasts for 3µs or less will not cause a
reset pulse to be issued.
Figure 15. Adding Hysteresis to the Power-Fail Comparator
CC
PFO
+5V
R2
R1
0V
transient may typically have without causing a
V IN
0V
V
V
TRIP
H
= 2.265 /
R3
= 2.265
TO µP
CC
CC
Negative-Going V
Full-Featured µP Supervisory Circuit with
Backup-Battery Replacement
experiences only small glitches.
R1 + R2
transient that goes 40mV below the
______________________________________________________________________________________
R1 + R2
C1*
R2
R2
||
||
R3
R3
PFI
PFO
V
L
V
MAX807
- 2.265 + 5 - 2.265 = 2.265
L
R1
CC
GND
+5V
V
V
CC
TRIP
V
IN
pulses, starting at
CC
V
H
R3
Transients
*OPTIONAL
R2
CC
CC
is
A 0.1µF bypass capacitor mounted close to the V
pin provides additional transient immunity.
To help the watchdog timer keep a closer watch on soft-
ware execution, you can use the method of setting and
resetting the watchdog input at different points in the
program, rather than “pulsing” the watchdog input high-
low-high or low-high-low. This technique avoids a “stuck”
loop where the watchdog timer continues to be reset
within the loop, keeping the watchdog from timing out.
Figure 16 shows an example flow diagram where the
I/O driving the watchdog input is set high at the begin-
ning of the program, set low at the beginning of every
subroutine or loop, then set high again when the pro-
gram returns to the beginning. If the program should
“hang” in any subroutine, the I/O is continually set low
and the watchdog timer is allowed to time out, causing
a reset or interrupt to be issued.
The V
the battery switchover comparator and should not
exceed 0.03V/µs. A standard rule for filter capacitance
on most regulators is on the order of 100µF per amp of
current. When the power supply is shut off or the main
battery is disconnected, the associated initial V
rate is just the inverse or 1A / 100µF = 0.01V/µs. The
V
tially, which more than satisfies the maximum fall-time
requirement.
Figure 16. Watchdog Flow Diagram
±1.5% Reset Accuracy
CC
fall rate decreases with time as V
CC
fall time is limited by the propagation delay of
Watchdog Software Considerations
OR PROGRAM LOOP,
SUBROUTINE
SET WDI
RETURN
START
Maximum V
HIGH
LOW
WDI
END
SET
CC
CC
falls exponen-
Fall Time
CC
fall
CC
15