LTC1266CS Linear Technology, LTC1266CS Datasheet - Page 12

LTC1266CS
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC1266CS
Description
IC REG CNTRLR N/PCH MOSFET16SOIC
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Type
Step-Down (Buck), Step-Up (Boost)r
Datasheet
1.LTC1266CSPBF.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of LTC1266CS
Internal Switch(s)
No
Synchronous Rectifier
Yes
Number Of Outputs
1
Voltage - Output
Adjustable
Current - Output
50mA
Frequency - Switching
400kHz
Voltage - Input
3.5 ~ 18 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
16-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Power - Output
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LTC1266CS
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1266CS#TR
Manufacturer:
PERICOMTECHNOLOGY
Quantity:
7 100
Part Number:
LTC1266CS#TR
Manufacturer:
LT/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1266CS-3.3
Manufacturer:
NEC
Quantity:
1 900
Part Number:
LTC1266CS-3.3
Manufacturer:
LT/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1266CS-5
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
12
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
LTC1266
LTC1266-3.3/LTC1266-5
series would normally be in continuous operation. The
output remains in regulation at all times. This minimum
capacitance requirement may be relaxed if Burst Mode
operation is disabled.
N-Channel vs P-Channel MOSFETs
The LTC1266 has the capability to drive either an
N-channel or a P-channel topside switch to give the user
more flexibility. N-channel MOSFETs are superior in per-
formance to P-channel due to their lower R
lower gate capacitance and are typically less expensive;
however, they do have a slightly more complicated gate
drive requirement and a more limited input voltage range
(see following sections).
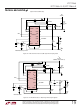
Driving P-Channel Topside MOSFETs
The P-channel topside switch circuit configuration is the
most straightforward due to the requirement of only one
supply voltage level. This is due to the negative gate
threshold of the P-channel MOSFET which allows the
MOSFET to be switched on and off by swinging the gate
between V
to ground to choose this operating mode. Normally, the
converter input (V
Pins 2 and 5 and can go as high as 20V. Pin 2 supplies the
high frequency current pulses to switch the MOSFETs and
should be decoupled with a 0.1 F to 1 F ceramic capaci-
tor. Pin 5 supplies most of the quiescent power to the rest
of the chip.
12
1000
800
200
600
400
IN
0
and ground. The phase invert (Pin 3) is tied
0
Figure 4. Minimum Value of C
IN
1
U
) is connected to the LTC1266 supply
(V
IN
– V
L = 25 H
R
L = 50 H
R
R
2
OUT
SENSE
SENSE
U
SENSE
) VOLTAGE (V)
L = 50 H
= 0.02
= 0.02
= 0.05
3
W
4
1266 F04
OUT
5
DS(ON)
U
and
Driving N-Channel Topside MOSFETs
Driving an N-channel topside MOSFET (PINV, Pin 3, tied to
PWR V
the gate voltage must be positive with respect to the
source to turn it on, which means that the gate voltage
must be higher than V
supply at least V
to boost the V
using a higher supply (see Figure 14) but if one is not
available, the bootstrap method can be used at the ex-
pense of an additional diode (see Figure 1). The bootstrap
works by charging the bootstrap capacitor to V
the off-time. During the on-time, the bottom plate of the
capacitor is pulled up to V
now twice V
Since the maximum allowable voltage at Pin 2 is 20V, the
Figure 1 bootstrap circuit limits V
higher V
charged to a voltage less than V
V
N-channel mode, internal circuitry limits the maximum
on-time to 60 s to guarantee start-up of the bootstrap
circuit. This maximum on-time reduces the maximum
duty cycle to:
which slightly increases the minimum input voltage at
which dropout occurs. However, because of the superior
on-conductance of the N-channel, the dropout perfor-
mance of an all N-channel regulator is still better (see
Figure 5) even with the duty cycle limitation, except at light
loads.
Low-Battery Comparator
The LTC1266 has an on-chip low-battery comparator
which can be used to sense a low-battery condition when
implemented as shown in Figure 6. The resistor divider
R1, R2 sets the comparator trip point as follows:
IN(MAX)
Max Duty Cycle =
V
TRIP
IN
IN
) is a little trickier than driving a P-channel since
= 20 – V
= 1.25 1 + R2
can be achieved if the bootstrap capacitor is
IN
IN
(plus any ringing on the switch node).
GS(ON)
to the proper level. The easiest method is
CAP
.
R1
60 s + t
above V
IN
. This requires either a second
60 s
IN
so that the voltage at Pin 2 is
IN
OFF
or a bootstrapping circuit
IN
to less than 10V. A
IN
, in which case
IN
during