MAX97000EVKIT+ Maxim Integrated Products, MAX97000EVKIT+ Datasheet - Page 22

MAX97000EVKIT+
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX97000EVKIT+
Description
KIT EVALUATION FOR MAX97000
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Specifications of MAX97000EVKIT+
Description/function
Audio Amplifiers
Operating Supply Voltage
2.7 V to 5.5 V
Product
Audio Development Tools
Supply Current
1 A
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With/related Products
MAX97000
Audio Subsystem with Mono Class D
Speaker and Class H Headphone Amplifier
conserving board space, reducing cost, and improving
the frequency response of the headphone amplifier.
See the Output Power vs. Load Resistance graph in
the Typical Operating Characteristics for details of the
possible capacitor sizes. There is a low DC voltage on
the amplifier outputs due to amplifier offset. However,
the offset of the MAX97000 is typically Q0.15mV, which,
when combined with a 32I load, results in less than 5FA
of DC current flow to the headphones.
In addition to the cost and size disadvantages of
the DC-blocking capacitors required by conventional
headphone amplifiers, these capacitors limit the ampli-
fier’s low-frequency response and can distort the audio
signal. Previous attempts at eliminating the output-cou-
pling capacitors involved biasing the headphone return
(sleeve) to the DC bias voltage of the headphone ampli-
fiers. This method raises some issues:
•
•
•
The MAX97000’s dual-mode charge pump generates
both the positive and negative power supply for the
headphone amplifier. To maximize efficiency, both the
charge pump’s switching frequency and output voltage
change based on signal level.
When the input signal level is less than 10% of VDD,
the switching frequency is reduced to a low rate. This
minimizes switching losses in the charge pump. When
the input signal exceeds 10% of VDD, the switching fre-
quency increases to support the load current.
For input signals below 25% of VDD, the charge pump
generates Q(VDD/2) to minimize the voltage drop across
the amplifier’s power stage and thus improve efficiency.
Input signals that exceed 25% of VDD cause the charge
pump to output QVDD. The higher output voltage allows
for full output power from the headphone amplifier.
22
The sleeve is typically grounded to the chassis.
Using the midrail biasing approach, the sleeve must
be isolated from system ground, complicating prod-
uct design.
During an ESD strike, the amplifier’s ESD structures
are the only path to system ground. Thus, the ampli-
fier must be able to withstand the full energy from an
ESD strike.
When using the headphone jack as a line out to
other equipment, the bias voltage on the sleeve may
conflict with the ground potential from other equip-
ment, resulting in possible damage to the amplifiers.
Charge Pump
To prevent audible gliches when transitioning from the
Q(VDD/2) output mode to the QVDD output mode, the
charge pump transitions very quickly. This quick change
draws significant current from VDD for the duration of
the transition. The bypass capacitor on VDD supplies the
required current and prevents droop on VDD.
The charge pump’s dynamic switching mode can be
turned off through the I
can then be forced to output either Q(VDD/2) or QVDD
regardless of input signal level.
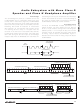
A Class H amplifier uses a Class AB output stage with
power supplies that are modulated by the output signal.
In the case of the MAX97000, two nominal power-supply
differentials of 1.8V (+0.9V to -0.9V) and 3.6V (+1.8V
to -1.8V) are available from the charge pump. Figure 7
shows the operation of the output-voltage-dependent
power supply.
To minimize power consumption when using the head-
phone amplifier, enable the low-power mode. In this
mode, the headphone mixers and volume control are
bypassed and shut down.
The MAX97000 uses a slave address of 0x9A or
1001101RW. The address is defined as the 7 most
significant bits (MSBs) followed by the read/write bit.
Set the read/write bit to 1 to configure the MAX97000 to
read mode. Set the read/write bit to 0 to configure the
MAX97000 to write mode. The address is the first byte
of information sent to the MAX97000 after the START (S)
condition.
Figure 7. Class H Operation
V
V
-0.9V
-1.8V
TH_H
TH_L
1.8V
0.9V
HPVDD
HPVSS
2
C interface. The charge pump
I
32ms
32ms
2
C Slave Address
Class H Operation
Low-Power Mode
OUTPUT
VOLTAGE