PIC16LF1939-I/P Microchip Technology, PIC16LF1939-I/P Datasheet - Page 252

PIC16LF1939-I/P
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC16LF1939-I/P
Description
IC MCU 8BIT FLASH 40-DIP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® XLP™ 16Fr
Specifications of PIC16LF1939-I/P
Core Size
8-Bit
Program Memory Size
28KB (16K x 14)
Core Processor
PIC
Speed
32MHz
Connectivity
I²C, LIN, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, LCD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
36
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
256 x 8
Ram Size
1K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.8 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 14x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
40-DIP (0.600", 15.24mm)
Controller Family/series
PIC16LF
Eeprom Memory Size
256Byte
Ram Memory Size
1024Byte
Cpu Speed
32MHz
No. Of Timers
5
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC16LF1939-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
PIC16LF1939-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip
Quantity:
2 485
Company:
Part Number:
PIC16LF1939-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip
Quantity:
2 485
- Current page: 252 of 508
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
PIC16F193X/LF193X
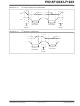
23.4.9
The 9th SCL pulse for any transferred byte in I
dedicated as an Acknowledge. It allows receiving
devices to respond back to the transmitter by pulling
the SDA line low. The transmitter must release control
of the line during this time to shift in the response. The
Acknowledge (ACK) is an active-low signal, pulling the
SDA line low indicated to the transmitter that the
device has received the transmitted data and is ready
to receive more.
The result of an ACK is placed in the ACKSTAT bit of
the SSPCON2 register.
Slave software, when the AHEN and DHEN bits are
set, allow the user to set the ACK value sent back to
the transmitter. The ACKDT bit of the SSPCON2 regis-
ter is set/cleared to determine the response.
Slave hardware will generate an ACK response if the
AHEN and DHEN bits of the SSPCON3 register are
clear.
There are certain conditions where an ACK will not be
sent by the slave. If the BF bit of the SSPSTAT register
or the SSPOV bit of the SSPCON1 register are set
when a byte is received.
When the module is addressed, after the 8th falling
edge of SCL on the bus, the ACKTIM bit of the
SSPCON3 register is set. The ACKTIM bit indicates
the acknowledge time of the active bus. The ACKTIM
Status bit is only active when the AHEN bit or DHEN
bit is enabled.
DS41364D-page 252
ACKNOWLEDGE SEQUENCE
2
C is
Preliminary
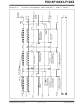
23.5
The MSSP Slave mode operates in one of four modes
selected in the SSPM bits of SSPCON1 register. The
modes can be divided into 7-bit and 10-bit Addressing
mode. 10-bit Addressing modes operate the same as
7-bit with some additional overhead for handling the
larger addresses.
Modes with Start and Stop bit interrupts operated the
same as the other modes with SSPIF additionally get-
ting set upon detection of a Start, Restart, or Stop
condition.
23.5.1
The SSPADD register (Register 23-6) contains the
Slave mode address. The first byte received after a
Start or Restart condition is compared against the
value stored in this register. If the byte matches, the
value is loaded into the SSPBUF register and an inter-
rupt is generated. If the value does not match, the
module goes idle and no indication is given to the soft-
ware that anything happened.
The SSP Mask register (Register 23-5) affects the
address matching process. See Section 23.5.9 “SSP
Mask Register” for more information.
23.5.1.1
In 7-bit Addressing mode, the LSb of the received data
byte is ignored when determining if there is an address
match.
23.5.1.2
In 10-bit Addressing mode, the first received byte is
compared to the binary value of ‘1 1 1 1 0 A9 A8 0’. A9
and A8 are the two MSb of the 10-bit address and
stored in bits 2 and 1 of the SSPADD register.
After the acknowledge of the high byte the UA bit is set
and SCL is held low until the user updates SSPADD
with the low address. The low address byte is clocked
in and all 8 bits are compared to the low address value
in SSPADD. Even if there is not an address match;
SSPIF and UA are set, and SCL is held low until
SSPADD is updated to receive a high byte again.
When SSPADD is updated the UA bit is cleared. This
ensures the module is ready to receive the high
address byte on the next communication.
A high and low address match as a write request is
required at the start of all 10-bit addressing communi-
cation. A transmission can be initiated by issuing a
Restart once the slave is addressed, and clocking in
the high address with the R/W bit set. The slave hard-
ware will then acknowledge the read request and pre-
pare to clock out data. This is only valid for a slave
after it has received a complete high and low address
byte match.
I
2
C
I
SLAVE MODE ADDRESSES
2
C Slave 7-bit Addressing Mode
Slave Mode Operation
I
2
C Slave 10-bit Addressing Mode
2009 Microchip Technology Inc.
Related parts for PIC16LF1939-I/P
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: