ATMEGA32-16PC Atmel, ATMEGA32-16PC Datasheet - Page 177

ATMEGA32-16PC
Manufacturer Part Number
ATMEGA32-16PC
Description
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ COM 40-DIP
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
AVR® ATmegar
Specifications of ATMEGA32-16PC
Core Processor
AVR
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
32
Program Memory Size
32KB (16K x 16)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
1K x 8
Ram Size
2K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Package / Case
40-DIP (0.600", 15.24mm)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
- Current page: 177 of 346
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
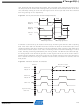
TWI Register
Description
TWI Bit Rate Register
– TWBR
TWI Control Register –
TWCR
2503Q–AVR–02/11
• Bits [7:0] – TWI Bit Rate Register
TWBR selects the division factor for the bit rate generator. The bit rate generator is a frequency
divider which generates the SCL clock frequency in the Master modes. See
Unit” on page 175
The TWCR is used to control the operation of the TWI. It is used to enable the TWI, to initiate a
master access by applying a START condition to the bus, to generate a receiver acknowledge,
to generate a stop condition, and to control halting of the bus while the data to be written to the
bus are written to the TWDR. It also indicates a write collision if data is attempted written to
TWDR while the register is inaccessible.
• Bit 7 – TWINT: TWI Interrupt Flag
This bit is set by hardware when the TWI has finished its current job and expects application
software response. If the I-bit in SREG and TWIE in TWCR are set, the MCU will jump to the
TWI Interrupt Vector. While the TWINT Flag is set, the SCL low period is stretched.
The TWINT Flag must be cleared by software by writing a logic one to it. Note that this flag is not
automatically cleared by hardware when executing the interrupt routine. Also note that clearing
this flag starts the operation of the TWI, so all accesses to the TWI Address Register (TWAR),
TWI Status Register (TWSR), and TWI Data Register (TWDR) must be complete before clearing
this flag.
• Bit 6 – TWEA: TWI Enable Acknowledge Bit
The TWEA bit controls the generation of the acknowledge pulse. If the TWEA bit is written to
one, the ACK pulse is generated on the TWI bus if the following conditions are met:
1. The device’s own slave address has been received.
2. A general call has been received, while the TWGCE bit in the TWAR is set.
3. A data byte has been received in Master Receiver or Slave Receiver mode.
By writing the TWEA bit to zero, the device can be virtually disconnected from the Two-wire
Serial Bus temporarily. Address recognition can then be resumed by writing the TWEA bit to one
again.
• Bit 5 – TWSTA: TWI START Condition Bit
The application writes the TWSTA bit to one when it desires to become a master on the Two-
wire Serial Bus. The TWI hardware checks if the bus is available, and generates a START con-
dition on the bus if it is free. However, if the bus is not free, the TWI waits until a STOP condition
Bit
Read/Write
Initial Value
Bit
Read/Write
Initial Value
TWBR7
TWINT
R/W
R/W
7
0
7
0
for calculating bit rates.
TWBR6
TWEA
R/W
R/W
6
0
6
0
TWBR5
TWSTA
R/W
R/W
5
0
5
0
TWBR4
TWSTO
R/W
R/W
4
0
4
0
TWBR3
TWWC
R/W
R
3
0
3
0
TWBR2
TWEN
R/W
R/W
2
0
2
0
TWBR1
R/W
R
1
0
1
–
0
ATmega32(L)
TWBR0
TWIE
R/W
R/W
0
0
0
0
“Bit Rate Generator
TWBR
TWCR
177
Related parts for ATMEGA32-16PC
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ 5V 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ 5V 40DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ 5V 44TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ IND 40-DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ IND 44-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 32KB FLASH 16MHZ 44TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 32KB FLASH 16MHZ 44QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 32K FLASH 16MHZ 44-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ COM 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ COM 44-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 32K 16MHZ IND 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet: