26231941 Crouzet USA, 26231941 Datasheet - Page 20
26231941
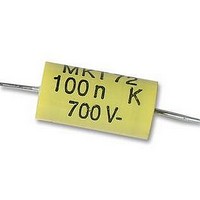
Manufacturer Part Number
26231941
Description
CAPACITOR, MOTOR MEDIUM TORQUE CAPACITOR, MOTOR MEDIUM TORQUE
Manufacturer
Crouzet USA
Datasheet
1.26231909.pdf
(196 pages)
Specifications of 26231941
Capacitance
0.1UF
Voltage Rating, Dc
700V
Capacitor Dielectric Type
POLYPROPYLENE
Tolerance,
10%
Tolerance, -
10%
Temp, Op. Max
85(DEGREE C)
Temp, Op. Min
0(DEGREE
- Current page: 20 of 196
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
1
20
➜ Temperature rise
The temperature rise of a motor is due to the difference between the
absorbed power and the output power of the motor. This difference is the
power loss.
Temperature rise is also related to the fact that power loss, in the form of
heat from the motor, is not rapidly absorbed by the ambient air (thermal
resistance). The thermal resistance of the motor can be greatly reduced
by ventilation.
Important
The nominal operating characteristics correspond to the voltage-
torque-speed characteristics required for continuous operation at
an ambient temperature of 20° C. Only intermittent duty is possible
outside these operating conditions : without exception, all checks
concerning extreme operating conditions must be performed in
the actual customer application conditions in order to ensure safe
operation.
D.C. motors are constructed to operate continuously within a range of
speeds near their no-load speed. This range of speeds is generally too
high for most applications. In order to reduce this speed, a full range of
geared motors is available, each with a series of gear ratios to suit most
speed requirements.
The complete range is suitable for a wide variety of applications.
➜ Gearbox characteristics
Our gearboxes have been designed for optimum performance and for
maximum life under normal operating conditions.
Their main characteristic is the capacity to withstand maximum design
torque with continuous duty.
The range of gearboxes shown in this catalogue can operate with
maximum torque of 0.5 to 6 N.m for long time periods. All values
previously stated are for standard products in normal operating
conditions, as specified.
In certain cases, these values may be increased if a shorter life is
required.
Please consult our Sales Office for further information.
Every gearbox has a torque limit, which is
If this torque is applied to the gearbox, it will cause severe damage.
➜ Gearbox construction
Motor and gearbox combinations
D.C. Motor
Gearbox case
the breaking torque
Motor shaft
Gearwheels
Output shaft
Bearing
➜ Selection of a geared motor
A geared motor is selected according to the required usable power
output.
A geared motor must have usable power equal to or greater than the
power required to rotate the load. It is selected by checking that the point
corresponding to the required operating conditions (torque and speed
output) is higher than the nominal torque versus speed curve of the
geared motor.
The required torque output of a geared motor must be within its maximum
recommended torque for continuous duty.
➜ Selecting the reduction gear ratio
Two selection criteria may be applied.
■
■
In order to avoid using numbers less than 1 where the reduction ratio is
concerned, the value 1/R is employed.
Due to the fact that it is always a reduction gear and not a «multiplier»
gear, there should be no ambiguity concerning the number used.
1/R =
P (useable)
W
The first criterion concerns the required speed output of the reduction
gear only. It is adequate for most applications and is easy to apply.
Given that :
The second criterion concerns the required usable power output of the
motor. The rotational speed of the motor is given by :
N
No = no-load speed of motor (rpm)
P
Cd = start-up torque of motor (Nm)
This gives the equation :
N = 1/2 (No +
R
= speed of motor (rpm)
= required output power (W)
Nb
N1
=
or
N1
Nb
=
1/R =
2
60
No
N1 = required speed of geared motor
Nb = basic nominal speed of motor
.M
Nm
2
N1
N
-
.n
4P
rpm
R =
A
) with A =
N1
N
30
Cd
No
Related parts for 26231941
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
SCREW SOCKET (OT08PC)
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PANEL PLATE FOR 813
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Controller; CTD46 Dual Display Temperature, 1/16 DIN, NEMA 4X, 110/220VAC
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1084
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1086
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1087
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1089
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1078
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1079
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:










