26231941 Crouzet USA, 26231941 Datasheet - Page 97
26231941
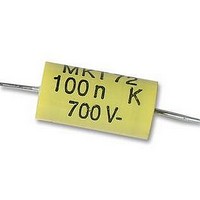
Manufacturer Part Number
26231941
Description
CAPACITOR, MOTOR MEDIUM TORQUE CAPACITOR, MOTOR MEDIUM TORQUE
Manufacturer
Crouzet USA
Datasheet
1.26231909.pdf
(196 pages)
Specifications of 26231941
Capacitance
0.1UF
Voltage Rating, Dc
700V
Capacitor Dielectric Type
POLYPROPYLENE
Tolerance,
10%
Tolerance, -
10%
Temp, Op. Max
85(DEGREE C)
Temp, Op. Min
0(DEGREE
- Current page: 97 of 196
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
By energising the electro-magnet with an AC current of frequency f, the
magnet will turn at a speed of f revolutions per second.
In these circumstances, a motor can start up in either direction. To
determine a particular direction, a mechanical device (anti-return)
is placed on the rotor to ensure that the motor operates only in the
direction required. There are several types of anti-return device which are
differentiated by the degree of the reverse rotation angle within which the
rotor can move.
Reversible
(Also called reversible synchronous motor)
Technology
Synchronous motors with a single-phase AC voltage and a permanent
magnet must have, for reverse operation, at least 2 stators and 2 coils.
Reverse operation can be achieved electrically using a single-pole switch.
A capacitor is used on reversible synchronous motors with 2 coils to
produce an electrical dephasing of 90° between the 2 coils. This creates a
circular revolving magnetic field. Component precision assures a perfectly
circular field and ensures silent motor operation.
➜ Wiring diagram for capacitor
The capacitor specification must be appropriate to each type of motor and
to the supply voltage. An incorrect capacitor may distort the magnetic field
and have detrimental effects on the reliability of the start-up of the motor
as well as on operational quality.
Coils
Pole pairs
Coil 1
Coil 2
Bronze sintered bearing
Rotor
The curve (motor reversing curve) below shows the limits within which the
motor will always start in relation to variation in supply voltage and the
capacitor values.
The zone within which the motor operates, ie. the area around the
nominal voltage of the capacitor, must be completely controlled by the
manufacturer.
Operating within this zone guarantees starting and operating in the
direction selected by the user.
As the diagram shows, we build our motors so that the operating zone
is as far as possible from the critical zones, whatever the nature of the
torque.
Boosted winding
Our experience in this area allows us, in certain cases and depending
on the precise specification, to operate outside this zone to produce a
higher torque and increase performance by between 30 and 80%. Please
consult us.
➜ Motor torque
2 types of torque can be distinguished.
Starting/running torque (or synchronisation torque)
This is the torque that a synchronous motor can develop both at
start-up and at synchronisation speed.
N.B:
In all technical data concerning geared motors in this catalogue, the
torque/speed curves indicate the value of the starting/running torque for
all the gearbox output speeds.
Stall torque (or desynchronisation torque)
This is the torque limit at which a synchronous motor loses its
synchronisation.
Maximum voltage
Minimum voltage
Ca : Starting/running torque
Minimum voltage of the capacitor
Nominal voltage of capacitor
Cd : Stall torque
Voltage
Zone within which the direction of the motor on starting
Zone within which the motor will not start
is not controllable
Safety zone
Speed of synchronisation
Torque
Maximum voltage of capacitor
Safety zone
Voltage of
capacitor
Speed
(rpm)
97
4
Related parts for 26231941
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
SCREW SOCKET (OT08PC)
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PANEL PLATE FOR 813
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Controller; CTD46 Dual Display Temperature, 1/16 DIN, NEMA 4X, 110/220VAC
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1084
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1086
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1087
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1089
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1078
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
11R1079
Manufacturer:
Crouzet USA
Datasheet:










