ISL3873BIK Intersil, ISL3873BIK Datasheet - Page 15

ISL3873BIK
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL3873BIK
Description
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.ISL3873BIK.pdf
(42 pages)
Specifications of ISL3873BIK
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Supplier Unconfirmed
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ISL3873BIK
Manufacturer:
ISL
Quantity:
62
Company:
Part Number:
ISL3873BIK
Manufacturer:
HOLTEK
Quantity:
487
Part Number:
ISL3873BIK
Manufacturer:
CONEXANT
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ISL3873BIK-TK
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
628
Company:
Part Number:
ISL3873BIKTK
Manufacturer:
Intersil
Quantity:
178
Part Number:
ISL3873BIKZ-TK
Manufacturer:
CONEXANT
Quantity:
20 000
USB Port
The USB interface implemented in the ISL3873B complies
with the Universal Serial Bus Specification Revision 1.1.
dated September 23, 1998, which is available from the USB
Implementers’ Forum at http://www.usb.org/.
The USB supports 4 endpoints.
• One Communications Class control endpoint for interface
• One Communications Class interrupt endpoint for
• Two Bulk endpoints for transfer of encapsulated NDIS
The USB along with USB support firmware provides an
alternate host interface for attaching an 802.11{b} WLAN
adapter to a host computer. This interface does not provide
“wireless USB” where USB packets are sent on the wireless
medium due to timing constraints in the USB protocol.
USB+ and USB- are the differential pair signals provided for
the user. These signals are capable of directly driving a USB
cable.
USB_DETECT is a 5V tolerant input to the ISL3873B device.
It is used to signal the MAC processor that a USB cable is
attached to the unit.
Complete details on the USB firmware for controlling this
port can be obtained by contacting the factory directly.
Power Sequencing
The ISL3873B provides a number of firmware controlled port
pins that are used for controlling the power sequencing and
other functions in the front end and baseband processor
components of the radio.
Packet transmission requires precise control of the radio.
Ideally, energy at the antenna ceases immediately after the
management;
signalling interrupts to the host; and,
functions to and from the host.
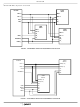
DEALLOCATE
HOST
ALLOCATE/
BUS
REQUEST
15
OFFSET CENTER
POST-WRITE
FID
DATA PORT
PRE-READ/
FIGURE 9. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF A BUFFER ACCESS PATH
BUFFER DESCRIPTOR
ACCESS (FIRMWARE)
OFFSET
BLOCK
ISL3873B
A
D
last symbol of information has been transmitted while
minimizing spurious radiation. To this end, the
transmit/receive switch is used to smoothly control the power
output. It's also important to apply appropriate modulation to
the PA while it is active to minimize radiation of CW signals.
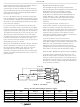
Signaling sequences for the beginning and end of normal
transmissions are illustrated in Figure 10. Table 1 lists
applicable delays associated with these control signals.
A transmission begins with PE2 and an internal signal
(TX_PE) to the Baseband processor as shown in Figure 10.
This enable activates the transmit state machine in the BBP
and the upconverter in the ISL3783. This starts the
modulated signal flowing to the PA which is turned on by
PA_PE once the drive signal is available. The PA power
ramps up and the power control loop becomes active and
stabilizes. Lastly, the transmit/receive switch is configured
for transmission via the differential pair TR_SW and
TR_SW_BAR. Delays for these signals related to the
initiation of transmission are referenced to PE2. The
switching of the T/R switch after the PA is enabled is done to
minimize RF spurious radiation. While it is not usual practice
to switch the T/R switch while RF is on, in this case it
suppresses spurious by employing the 20dB attenuation of
the switch until the PA turn-on or turn-off transients have died.
After the final data bit has been clocked out of the MAC it waits
for an internal control signal (TX_READY) from the Baseband
processor. This signals that the BBP has modulated the final
information-rich symbol. After allowing time for that symbol to
exit the antenna, the MAC de-asserts TR_SW and
TR_SW_BAR to shut off transmission and lowers PA_PE
followed by PE2 going high. Delays for these signals related to
the termination of transmission are referenced to the rising
edge of PE2. The baseband processor also internally extends
the transmission of data bits for a sufficient time to insure that it
outputs the final bits
FRAME BUFFER
VIRTUAL
HEADER
STATUS
DATA
.
MEMORY
BUFFER