upd17225 Renesas Electronics Corporation., upd17225 Datasheet

upd17225
Available stocks
Related parts for upd17225
upd17225 Summary of contents
Page 1
PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 4-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLER FOR SMALL GENERAL-PURPOSE INFRARED DESCRIPTION PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 (hereafter called PD17225 subseries) are 4-bit single-chip microcontrollers for small general-purpose infrared remote control transmitters. It employs a 17K architecture of general-purpose register type ...
Page 2
APPLICATION Preset remote controllers, toys, portable systems, etc. ORDERING INFORMATION Part Number PD17225CT- 28-pin plastic shrink DIP (400 mil) PD17225GT- 28-pin plastic SOP (375 mil) PD17225MC- -5A4 30-pin plastic shrink SOP (300 mil) PD17226CT- 28-pin plastic shrink DIP (400 mil) ...
Page 3
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW) • 28-pin plastic SOP (375 mil) PD17225GT- , 17226GT- , 17227GT- • 28-pin plastic shrink DIP (400 mil) PD17225CT- , 17226CT- , 17227CT- P0D 2 P0D 3 INT P0E 0 P0E 1 P0E 2 P0E 3 ...
Page 4
SOP (300 mil) PD17225MC- -5A4, PD17226MC- P0D 2 P0D 3 INT P0E 0 P0E 1 P0E 2 P0E 3 REM OUT X IN GND RESET WDOUT IC1 GND : Ground IC1, IC2 : ...
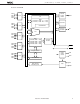
Page 5
BLOCK DIAGRAM P0A 0 P0A 1 P0A P0A 2 P0A 3 P0B 0 P0B 1 P0B P0B 2 P0B 3 P0C 0 P0C 1 P0C P0C 2 P0C 3 PD17225 : 2048 PD17226 : 4096 PD17227 : 6144 P0D PD17228 ...
Page 6
PIN FUNCTIONS ........................................................................................................................... 1.1 Pin Function List ................................................................................................................................ 1.2 Input/Output Circuits ......................................................................................................................... 1.3 Processing of Unused Pins .............................................................................................................. 2. MEMORY SPACE ......................................................................................................................... 2.1 Program Counter (PC) ....................................................................................................................... 2.2 Program Memory (ROM) ................................................................................................................... 2.3 Stack ................................................................................................................................................... 2.4 Data Memory (RAM) ...
Page 7
STANDBY FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................................ 8.1 HALT Mode ......................................................................................................................................... 8.2 HALT Instruction Execution Conditions .......................................................................................... 8.3 STOP Mode ......................................................................................................................................... 8.4 STOP Instruction Execution Conditions ......................................................................................... 8.5 Releasing Standby Mode .................................................................................................................. 9. RESET ........................................................................................................................................... 9.1 Reset by Reset Signal Input ............................................................................................................. 9.2 ...
Page 8
PIN FUNCTIONS 1.1 Pin Function List Pin No. Symbol 15 (16) P0A 0 4-bit CMOS input port with pull-up resistor. 16 (17) P0A 1 Can be used for key return input of key matrix. When at least 17 (18) ...
Page 9
Input/Output Circuits The equivalent input/output circuit for each PD17225 pin is shown below. (1) P0A, P0B V DD Input buffer (2) P0C, P0D Output data latch (3) P0E Pull-up data register Output data latch output disable Selector Input buffer ...
Page 10
Processing of Unused Pins Process the unused pins as follows: Table 1-1. Processing of Unused Pins Pin P0A -P0A 0 3 P0B -P0B 0 3 P0C -P0C 0 3 P0D -P0D 0 3 P0E -P0E 0 3 REM INT ...
Page 11
MEMORY SPACE 2.1 Program Counter (PC) The program counter (PC) specifies an address of the program memory (ROM). The program counter is an 11/12/13-bit binary counter as shown in Figure 2-1. Its contents are initialized to address 0000H at ...
Page 12
Figure 2-2. Program Memory Map Address 16 bits Reset start address Basic interval timer interrupt vector External input (INT) interrupt vector ...
Page 13
Stack A stack is a register to save a program return address and the contents of system registers (to be described later) when a subroutine is called or when an interrupt is accepted. 2.3.1 Stack configuration Figure 2-3 shows ...
Page 14
Function of stack The address stack register stores a return address when the subroutine call instruction or table reference instruction (first instruction cycle) is executed or when an interrupt is accepted. It also stores the contents of the address ...
Page 15
Data Memory (RAM) Data memory (random access memory) stores data for operations and control. It can be read-/write-accessed by instructions. 2.4.1 Memory configuration Figure 2-4 shows the configuration of the data memory (RAM). The data memory consists of two ...
Page 16
General-purpose data memory The general-purpose data memory area is an area of the data memory excluding the system register area, and the port register area. This memory area has a total of 223 nibbles (111 nibbles in BANK0 and ...
Page 17
System registers (SYSREG) The system registers are registers that are directly related to control of the CPU. These registers are mapped to addresses 74H-7FH on the data memory and can be referenced regardless of bank specification. The system registers ...
Page 18
General register (GR) A general register is a 16-word register on the data memory and used for arithmetic operations and transfer of data to and from the data memory. (1) Configuration of general register Figure 2-6 shows the configuration ...
Page 19
Data buffer (DBF) The data buffer on the addresses 0CH to 0FH of data memory is used for data transfer to and from peripheral hardware and for storage of data during table reference. (1) Functions of the data buffer ...
Page 20
Table 2-2. Relations between Hardware Peripherals and Data Buffer Hardware Peripherals Name 8-Bit Timer 8-bit counter 8-bit modulo register Remote Controller NRZ low-level Carrier Generator timer modulo register NRZ high-level timer modulo register Address Register Address register Notes 1. In ...
Page 21
Note on using data buffer When transferring data to/from the peripheral hardware via the data buffer, the unused peripheral addresses, write-only peripheral registers (only when executing PUT), and read-only peripheral registers (only when executing GET) must be handled as ...
Page 22
Register File (RF) The register file mainly consists of registers that set the conditions of the peripheral hardware. These registers can be controlled by dedicated instructions PEEK and POKE, and the embedded macro instructions of RA17K, SETn, CLRn, and ...
Page 23
Control registers The control registers consists of a total of 64 nibbles ( bits) of the addresses 00H-3FH of the register file. Of these, however, only 14 nibbles are actually used. The remaining 50 nibbles are unused ...
Page 24
Symbol definition of register file An error occurs if a register file address is directly specified as a numeral by the operand “rf” of the “PEEK WR, rf” or “POKE rf, WR” instruction if the 17K Series Assembler (RA17K) ...
Page 25
PORTS 3.1 Port 0A (P0A -P0A ) 0 3 This is a 4-bit input port. Data is read through port register P0A (address 70H). This port is a CMOS input port with a pull-up resistor, and can be used ...
Page 26
INT Pin This pin inputs an external interrupt request signal. At either the rising or falling edge of the signal input to this pin, the IRQ flag (RF: address 3EH, bit 0) is set. The status of this pin ...
Page 27
Switching Bit I/O The I/O which can be set in the input or output mode in bit units is called a bit I/O. P0E is a bit I/O port, which can be set in the input or output mode ...
Page 28
Specifying Pull-up Resistor Connection Whether or not a pull-up resistor is connected to port P0E can be specified by the following registers of the register file in 1-bit units when the port is in the input mode 3 2 ...
Page 29
CLOCK GENERATOR CIRCUIT 4.1 Instruction Execution Time (CPU Clock) Selection The PD17225 is equipped with a clock oscillator that supplies clocks to the CPU and hardware peripherals. Instruction execution time can be changed in two steps (ordinary mode and ...
Page 30
TIMER AND REMOTE CONTROLLER CARRIER GENERATOR CIRCUIT The PD17225 is equipped with the 8-bit timer which is mainly used to generate the leader pulse of the remote controller signal, and to output codes. 5.1 Configuration of 8-bit Timer ...
Page 31
Figure 5-1. Configuration of 8-bit Timer and Remote Controller Carrier Generator Circuit TMEN TMRES /256 X Selector 7-bit counter X Comparator bit 7 7-bit modulo register NRZLTMM ...
Page 32
Function of 8-bit Timer (with modulo function TMEN TMRES TMCK1 TMCK0 Notes 1. When the STOP mode is released, bit 3 must be set. 2. Bit write-only bit. NRZLTMM ...
Page 33
Carrier Generator Circuit for Remote Controller PD17225 is provided with a carrier generator circuit for the remote controller. The remote controller carrier generator circuit consists of a 7-bit counter, NRZ high-level timer modulo register (NRZHTMM), and NRZ low-level timer ...
Page 34
When bit 7 of NRZLTMM is 0 (carrier output) NRZ REM MAX. 500 ns (delay Note Value when (TMCK1, TMCK0) When (TMCK1, TMCK0) = (1, 1), the value differs depending on how NRZ is manipulated. If NRZ is ...
Page 35
Setting carrier frequency and duty factor Where the system clock frequency is f (division ratio /( divided into m:n and is set in the modulo registers as follows: High-level period set value = ...
Page 36
Countermeasures against noise during transmission (carrier output) When a signal is transmitted from the transmitter of a remote controller, a peak current of 0 may flow through the infrared LED. Since two batteries are usually used ...
Page 37
BASIC INTERVAL TIMER/WATCHDOG TIMER The basic interval timer has a function to generate the interval timer interrupt signal and watchdog timer reset signal. 6.1 Source Clock for Basic Interval Timer The system clock ( divided, to generate ...
Page 38
WDTRES BTMCK BTMRES Note Bits 1 and 3 are write-only bits. 38 PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 0 Address On reset R/W Note 03H 0H R/W BTMRES Basic Interval Timer Reset 0 Data read out ...
Page 39
Operation Timing for Watchdog Timer The basic interval timer can be used as a watchdog timer. Unless the watchdog timer is reset within a fixed time is reset therefore necessary to reset through programming the watchdog timer ...
Page 40
INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS 7.1 Interrupt Sources PD17225 is provided with three interrupt sources. When an interrupt has been accepted, the program execution automatically branches to a predetermined address, which is called a vector address. A vector address is assigned to ...
Page 41
Hardware of Interrupt Control Circuit This section describes the flags of the interrupt control circuit. (1) Interrupt request flag and interrupt enable flag The interrupt request flag (IRQ cleared to 0 when the interrupt processing is excuted. An interrupt ...
Page 42
IEG This pin selects the interrupt edge to be detected on the INT pin. When this flag is “0”, the interrupt is detected at the rising edge; when it is “1”, the interrupt is detected at the falling edge. ...
Page 43
IRQ This is an interrupt request flag that indicates the interrupt request status. When an interrupt request is generated, this flag is set to “1”. When the interrupt has been accepted, the interrupt request flag is reset to “0”. ...
Page 44
Interrupt Sequence If IRQ flag is set to “1” when IP flag is “1”, interrupt processing is started after the instruction cycle of the instruction executed when IRQ flag was set has ended. Since the MOVT instruction, EI instruction, ...
Page 45
Returning from interrupt processing routine To return from an interrupt processing routine, use the RETI instruction. Then the following processing is executed within an instruction cycle. To enable an interrupt after the processing of an interrupt has been finished, ...
Page 46
STANDBY FUNCTIONS PD17225 is provided with HALT and STOP modes as standby functions. By using the standby function, current consumption can be reduced. In the HALT mode, the program is not executed, but the system clock f tained, until ...
Page 47
Table 8-2. Operations After HALT Mode Release (2/2) (b) HALT 02H HALT Mode Released by: Interrupt Status 8-Bit Timer 8.2 HALT Instruction Execution Conditions The HALT instruction can be executed, only under special conditions, as shown in Table 8-3, to ...
Page 48
STOP Mode In the STOP mode, the system clock (f X consumption. To set the STOP mode, use the STOP instruction. The STOP mode releasing condition can be specified by the STOP instruction operand, as shown in Table 8-4. ...
Page 49
STOP Instruction Execution Conditions The STOP instruction can be executed, only under special conditions, as shown in Table 8-5, to prevent the program from hang-up. If the conditions in Table 8-5 are not satisfied, the STOP instruction is treated ...
Page 50
RESET 9.1 Reset by Reset Signal Input When a low-level signal more than input to the RESET pin, PD17225 is reset. When the system is reset, the oscillator circuit remains in the HALT mode and then ...
Page 51
Reset by Stack Pointer (Connect RESET and WDOUT pins) When the value of the stack pointer reaches during program execution, a low level is output to the WDOUT pin, and the program counter is reset to ...
Page 52
LOW-VOLTAGE DETECTOR CIRCUIT (CONNECT RESET AND WDOUT PINS) The low-voltage detector circuit outputs a low level from the WDOUT pin for initialization (reset) to prevent program hang-up that may take place when the batteries are replaced, if the circuit ...
Page 53
ASSEMBLER RESERVED WORDS 11.1 Mask Option Directives When developing the PD17225 program, mask options must be specified by using mask option directives in the program. The RESET pin for PD17225 requires a mask option to be specified. 11.1.1 OPTION ...
Page 54
Table 11-1. Mask Option Definition Directives Name Directive Operands 1st Operand RESET OPTRES 1 Mask option of RESET PULLUP (w/pull-up resistor) OPEN (w/o pull-up resistor) POC OPTPOC 1 USEPOC (low-voltage detector circuit provided) NOUSEPOC (low-voltage detector circuit not provided) 11.2 ...
Page 55
Table 11-2. Reserved Symbols (1/2) Symbol Name Attribute Value DBF3 MEM 0.0CH DBF2 MEM 0.0DH DBF1 MEM 0.0EH DBF0 MEM 0.0FH AR3 MEM 0.74H AR2 MEM 0.75H AR1 MEM 0.76H AR0 MEM 0.77H WR MEM 0.78H BANK MEM 0.79H IXH ...
Page 56
Table 11-2. Reserved Symbols (2/2) Symbol Name Attribute Value P0E0 FLG 0.6FH.0 P0E1 FLG 0.6FH.1 P0E2 FLG 0.6FH.2 P0E3 FLG 0.6FH.3 SP MEM 0.81H SYSCK FLG 0.82H.0 WDTRES FLG 0.83H.3 BTMCK FLG 0.83H.2 BTMRES FLG 0.83H.1 INT FLG 0.8FH.0 NRZBF ...
Page 57
PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 Data Sheet U12643EJ2V0DS00 57 ...
Page 58
Column 0 Address Row Address Bit 3 Bit Bit 1 Bit 0 Bit 3 0 Bit Bit 1 0 Bit 0 NRZBF Bit 3 Bit 2 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Bit 3 Bit ...
Page 59
Figure 11-1. Register Files (2/2) Column Address Row Address Bit 3 Bit 2 0 Bit 1 Bit 0 Bit 3 Bit 2 1 Bit 1 Bit 0 Bit 3 Bit 2 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Bit ...
Page 60
INSTRUCTION SET 12.1 Instruction Set Outline BIN. HEX ADD SUB ADDC SUBC 0 ...
Page 61
Legend AR : Address register ASR : Address stack register specified by stack pointer addr : Program memory address (low-order 11 bits) BANK : Bank register CMP : Compare register CY : Carry flag DBF : Data buffer h ...
Page 62
List of Instruction Sets Group Mnemonic Operand r, m (r) ADD m, #n4 ( (r) Addition ADDC m, #n4 ( INC (r) SUB m, #n4 (m) Subtraction r, m (r) SUBC ...
Page 63
Group Mnemonic Operand PUSH AR SP POP AR AR PEEK WR Transfer POKE rf, WR (rf) GET DBF, p (DBF) PUT p, DBF (p) addr Note Branch BR @AR PC addr SP PC CALL @AR SP Subroutine PC ...
Page 64
PD17228 Operand addr 12.4 Assembler (RA17K) Built-In Macro Instruction Legend flag n : FLG type symbol n : Bit number < > : Contents in < > can be omitted Mnemonic Operand Built-in SKTn flag ...
Page 65
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS Absolute Maximum Ratings ( Item Symbol Supply Voltage V DD Input Voltage V I Output Voltage V O Note High-Level Output Current I OH Note Low-Level Output Current I OL Operating Temperature T ...
Page 66
Recommended Operating Ranges (T Item Symbol Supply Voltage V DD1 V DD2 V DD3 V DD4 Oscillation Frequency f X Operating Temperature T A Note Low-Voltage Detector Circuit T CY (Mask Option) Note Reset if the status ...
Page 67
System Clock Oscillator Characteristics (T Recommended Resonator Constants Ceramic resonator OUT Notes 1. The oscillation frequency only indicates the oscillator characteristics. 2. The oscillation stabilization time is necessary for oscillation to be stabilized, after V STOP mode ...
Page 68
Main System Clock: Ceramic Resonator (T Manufacturer Part Number Murata Mfg. Co., Ltd. CSA2.00MG CSA3.00MG CSA4.00MG CSA6.00MG CSA8.00MTZ TDK Corp. CCR1000K2 CCR4.0MC3 CCR6.0MC3 CCR8.0MC5 FCR4.0MC5 FCR6.0MC5 Matsushita Electronic EF0EC2004A4 Components Co., Ltd. EF0EC3004A4 EF0EC4004A4 EF0EC6004A4 EF0EC8004A4 Toko Ceramic Co., Ltd. ...
Page 69
DC Characteristics (T = – Item Symbol High-Level Input Voltage V IH1 V IH2 Low-Level Input Voltage V IL1 V IL2 V IL3 High-Level Input Leakage I LIH Current Low-Level Input Leakage I LIL1 Current ...
Page 70
AC Characteristics (T = – Item Symbol Note CPU Clock Cycle Time t CY1 (Instruction Execution Time) t CY2 INT High/Low Level Width t t INTH, INTL RESET Low Level Width t RSL Note The ...
Page 71
APPLICATION CIRCUIT EXAMPLE P0D 2 1 P0D 3 2 INT 3 P0E 0 4 P0E 1 5 P0E 2 6 P0E 3 7 REM OUT 10 4 MHz GND ...
Page 72
PACKAGE DRAWINGS 28 PIN PLASTIC SHRINK DIP (400 mil NOTES 1) Each lead centerline is located within 0.17 mm (0.007 inch) of its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition. 2) Item "K" to ...
Page 73
PLASTIC SOP (375 mil NOTE Each lead centerline is located within 0. its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition. PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 15 detail of ...
Page 74
PIN PLASTIC SSOP (300 mil NOTE Each lead centerline is located within 0. its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition. 74 PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 16 detail of ...
Page 75
RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS For the PD17225 soldering must be performed under the following conditions. For details of recommended conditions for surface mounting, refer to information document "Semiconductor Device Mounting Technology Manual" (C10535E). For other soldering methods, please consult with ...
Page 76
APPENDIX A. DIFFERENCES AMONG PD17P218 is equipped with PROM to which data can be written by the user instead of the internal mask ROM (program memory) of the PD17228. Table A-1 shows the differences between the PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 ...
Page 77
PD17225, 17226, 17227, 17228 Data Sheet U12643EJ2V0DS00 77 ...
Page 78
APPENDIX B. FUNCTIONAL COMPARISON OF Product Name PD17201A Item ROM Capacity (Bit) 3072 RAM Capacity (Bit) LCD Controller/Driver 136 segments max. Infrared Remote Controller LED output is high-active LED output Carrier Generator (REM) I/O Ports External Interrupt (INT) (rising-edge detection) ...
Page 79
PD17225 PD17226 PD17227 PD17228 2048 16 4096 16 6144 16 8192 111 4 223 4 Not provided Provided (without LED output) 20 pins 1 pin (rising edge, falling edge detection) Not provided 2 channels 8-bit timer Basic interval timer Provided ...
Page 80
APPENDIX C. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS To develop the programs for the PD17225 subseries, the following development tools are available: Hardware Name IE-17K and IE-17K-ET are the in-circuit emulators used in common with the 17K series In-Circuit Emulator microcontroller. IE-17K, Note 1 ...
Page 81
Software Name Outline 17K Assembler The RA17K is an assembler com- (RA17K) mon to the 17K series products. When developing the program of devices, RA17K is used in combination with a device file (AS17225). 17K Series The emlC-17K is a ...
Page 82
NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES 1 PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD FOR SEMICONDUCTORS Note: Strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of the gate oxide and ultimately degrade the device operation. electricity as much as possible, and quickly ...
Page 83
Regional Information Some information contained in this document may vary from country to country. Before using any NEC product in your application, please contact the NEC office in your country to obtain a list of authorized representatives and distributors. They ...
Page 84
SIMPLEHOST are trademarks of NEC Corporation. Windows is either a registered trademark or a trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. PC/ trademark of IBM Corporation. The export of this product from ...