lm5085sdx National Semiconductor Corporation, lm5085sdx Datasheet - Page 12

lm5085sdx
Manufacturer Part Number
lm5085sdx
Description
75v Constant On-time Pfet Buck Switching Controller
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.LM5085SDX.pdf
(22 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM5085SDX
Manufacturer:
TI/德州仪器
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
lm5085sdx/NOPB
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
6 855
www.national.com
For V
SHUTDOWN
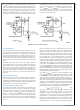
The LM5085 can be shutdown by grounding the RT pin (see
Figure 1). In this mode the PFET is held off, and the VCC
regulator is disabled. The internal operating current is re-
duced to the value shown in the graph “Shutdown current vs.
VIN”. The shutdown threshold at the RT pin is
≊
eration. The RT pin must not be forced high during normal
operation.
CURRENT LIMITING
The LM5085 current limiting operates by sensing the voltage
across either the R
on-time and comparing it to the voltage across the resistor
R
accurate and stable over temperature when a sense resistor
is used. The R
ation and a large temperature coefficient.
If the voltage across R
greater than the voltage across R
parator switches to turn off Q1. Current sensing is disabled
for a blanking time of
to prevent false triggering of the current limit comparator due
to leading edge current spikes. Because of the blanking time
and the turn-on and turn-off delays created by the PFET, the
on-time at the PGATE pin should not be set less than 150 ns.
An on-time shorter than that may prevent the current limit de-
tection circuit from properly detecting an over-current condi-
tion. The duration of the subsequent forced off-time is a
function of the input voltage and the voltage at the FB pin, as
shown in the graph “Off-time vs. V
than-normal forced off-time allows the inductor current to
decrease to a low level before the next on-time. This cycle-
by-cycle monitoring, followed by a forced off-time, provides
effective protection from output load faults over a wide range
of operating conditions.
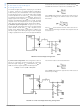
The voltage across the R
µA current sink at the ADJ pin. When using Q1’s R
sensing, the current at which the current limit comparator
switches is calculated from:
When using a sense resistor (R
rent limit comparator is calculated from:
50 mV of hysteresis. Releasing the pin enables normal op-
ADJ
(see Figure 2). The current limit function is much more
IN
= 48V and t
FIGURE 1. Shutdown Implementation
I
CL
DS(ON)
I
CL
= 40 µA x R
DS(ON)
= 40 µA x R
D
of a MOSFET has a wide process vari-
= 100 ns, the simplified equation is:
≊
100 ns at the beginning of the on-time
DS(ON)
of Q1, or a sense resistor, during the
ADJ
resistor is set by an internal 40
ADJ
of Q1, or the sense resistor, is
ADJ
SEN
/R
/R
ADJ
DS(ON)
) the threshold of the cur-
IN
SEN
, the current limit com-
and V
FB
”. The longer-
≊
30057724
0.73V, with
DS(ON)
(6)
(7)
for
12
When using equation 6 or 7, the tolerances for the ADJ pin
current sink and the offset of the current limit comparator
should be included to ensure the resulting minimum current
limit is not less than the required maximum switch current.
Simultaneously increasing the values of R
creases the effects of the current limit comparator offset, but
at the expense of higher power dissipation. When using a
sense resistor, the R
in the practical limitations of power dissipation and physical
size. For example, for a 10A current limit, setting R
0.005Ω results in a power dissipation as high as 0.5W. Cur-
rent sense connections to the R
be Kelvin connections to ensure accuracy.
The C
prevent unintended switching of the current limit comparator
due to input voltage transients. The recommended value for
C
CURRENT LIMIT OFF-TIME
When the current through Q1 exceeds the current limit thresh-
old, the LM5085 forces an off-time longer than the normal off-
time defined by Equation 1. See the graph “Off-Time vs. V
and V
lowing equation:
where V
FB pin at the time current limit was detected. This feature is
necessary to allow the inductor current to decrease sufficient-
ly to offset the current increase which occurred during the on-
time. During the on-time, the inductor current increases an
amount equal to:
During the off-time the inductor current decreases due to the
reverse voltage applied across the inductor by the output volt-
age, the freewheeling diode’s forward voltage (V
voltage drop due to the inductor’s series resistance (V
The current decrease is equal to:
The on-time in Equation 9 is shorter than the normal on-time
since the PFET is shut off when the current limit threshold is
crossed. If the off-time is not long enough, such that the cur-
rent decrease (Equation 10) is less than the current increase
(Equation 9), the current levels are higher at the start of the
next on-time. This results in a further decrease in on-time,
since the current limit threshold is crossed sooner. A balance
is reached when the current changes in Equations 9 and 10
are equal. The worst case situation is that of a direct short
circuit at the output terminals, where V
results in the largest current increase during the on-time, and
the smallest decrease during the off-time. The sum of the
diode’s forward voltage and the inductor’s ESR voltage must
be sufficient to ensure current runaway does not occur. Using
Equations 9 and 10, this requirement can be stated as:
ADJ
is 1000 pF.
FB
ADJ
”, or calculate the current limit off-time from the fol-
IN
capacitor filters noise from the ADJ pin, and helps
is the input voltage, and V
SEN
resistor value should be chosen with-
SEN
resistor, or to Q1, must
FB
OUT
is the voltage at the
ADJ
= 0 volts, as that
and R
FD
), and the
SEN
SEN
ESR
(10)
(11)
de-
(8)
(9)
IN
).
=