lm5085sdx National Semiconductor Corporation, lm5085sdx Datasheet - Page 13

lm5085sdx
Manufacturer Part Number
lm5085sdx
Description
75v Constant On-time Pfet Buck Switching Controller
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.LM5085SDX.pdf
(22 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM5085SDX
Manufacturer:
TI/德州仪器
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
lm5085sdx/NOPB
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
6 855
For t
node. To determine this time period add the “Minimum on-
time in current limit” specified in the Electrical Characteristics
(t
the PFET. For t
V
volts. When using the minimum or maximum limits of those
VCC REGULATOR
The VCC regulator provides a regulated voltage between the
VIN and the VCC pins to provide the bias and gate current for
the PFET gate driver. The 0.47 µF capacitor at the VCC pin
must be a low ESR capacitor, preferably ceramic as it pro-
vides the high surge current for the PFET’s gate at each turn-
on. The capacitor must be located as close as possible to the
VIN and VCC pins to minimize inductance in the PC board
traces.
Referring to the graph “VCC vs. VIN”, the voltage across the
VCC regulator (VIN – VCC) is equal to VIN until VIN reaches
approximately 8.5V. At higher values of VIN, the voltage at
the VCC pin is regulated at approximately 7.7V below VIN.
The VCC regulator has a maximum current capability of at
least 20 mA. The regulator is disabled when the LM5085 is
shutdown using the RT pin, or when the thermal shutdown is
activated.
PGATE DRIVER OUTPUT
The PGATE pin output swings between V
VCC pin voltage (Q1 on). The rise and fall times depend on
the PFET gate capacitance and the source and sink currents
provided by the internal gate driver. See the Electrical Chara-
teristics for the current capability of the driver.
P-CHANNEL MOSFET SELECTION
The PFET must be rated for the maximum input voltage, with
some margin above that to allow for transients and ringing
which can occur on the supply line and the switching node.
The gate-to-source voltage (V
PFET is 7.7 volts for VIN greater than 8.5V. However, if the
circuit is to be operated at lower values of VIN, the selected
PFET must be able to fully turn-on with a V
to VIN. The minimum input operating voltage for the LM5085
is 4.5V.
ON
IN
-4) to the difference of the turn-off and turn-on delays of
and V
ON
in Equation 11 use the minimum on-time at the SW
FB
”, or use Equation 8, where V
OFF
use the value in the graph “Off-Time vs.
GS
) normally provided to the
FB
IN
GS
(Q1 off) and the
is equal to zero
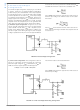
FIGURE 2. Current Limit Sensing
voltage equal
13
specifications to determine worst case situations, the toler-
ance of the minimum on-time (t
times (t
process and temperature variations. A device which has an
on-time at the high end of the range will have an off-time that
is at the high end of its range.
Similar to NFETs, the case or exposed thermal pad for a
PFET is electrically connected to the drain terminal. When
designing a PFET buck regulator the drain terminal is con-
nected to the switching node. This situation requires a trade-
off between thermal and EMI performance since increasing
the PC board area of the switching node to aid the PFET
power dissipation also increases radiated noise, possibly dis-
rupting the circuit operation. Typically the switching node area
is kept to a reasonable minimum and the PFET peak current
is derated to stay within the recommended temperature rating
of the PFET. The R
of the power dissipation in the PFET. However, PFETs with
very low R
PFET with a higher gate charge has a corresponding slower
switching speed, leading to higher switching losses and af-
fecting the PFET power dissipation.
If the PFET R
that it typically has a positive temperature coefficient. At 100°
C the R
at 25°C which could result in incorrect current limiting if not
accounted for when determining the value of the R
The PFET Total Gate Charge determines most of the power
dissipation in the LM5085 due to the repetitive charge and
discharge of the PFET’s gate capacitance by the gate driver
(powered from the VCC regulator). The LM5085’s internal
power dissipation can be calculated from the following:
where Q
datasheet, F
LM5085's operating current obtained from the graph "Input
Operating Current vs. V
specifications in the Electrical Characteristics table, the ap-
proximate junction temperature can be determined. If the
calculated junction temperature is near the maximum oper-
ating temperature of 125°C, either the switching frequency
DS(ON)
OFF(CL1)
G
is the PFET's Total Gate Charge obtained from its
DS(ON)
P
S
may be as much as 50% higher than the value
DISS
DS(ON)
is the switching frequency, and I
through t
usually have large values of gate charge. A
= V
DS(ON)
is used for current limit detection, note
IN
x ((Q
IN
OFF(CL4)
of the PFET determines a portion
". Using the Thermal Resistance
G
ON
x F
) track each other over the
-4) and the current limit off-
S
) + I
IN
)
www.national.com
ADJ
30057725
IN
resistor.
is the
(12)