TN1112 LATTICE [Lattice Semiconductor], TN1112 Datasheet

TN1112
Related parts for TN1112
TN1112 Summary of contents
Page 1
... The specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice. www.latticesemi.com Input Hysteresis in Lattice CPLD and Cin 20 HCout 21 Cin 20 HCout 21 Cin 20 Input Series Resistor t RISE — <54ns 100 Ω 65ns 470 Ω 500ns 680 Ω >15ms 1 FPGA Devices Technical Note TN1112 59 Cout 59 Cout 59 Cout t FALL <56ns 63ns 470ns >15ms tn1112_01.1 ...
Page 2
Lattice Semiconductor Test Device: ispMACH 4128V I/O Standard: LVCMOS 3.3V with input bus-hold latch turned on Temperature: Room temperature External Input Input Series Circuit Resistor None 100 Ω Method 1 4.7K Ω 100 Ω Method 2 100 Ω Method 3 ...
Page 3
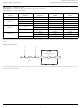
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 5. Input Measured at Point A Figure 6. Zoomed View of Rising Edge of Figure 5 Lattice CPLD and FPGA Devices 3 Input Hysteresis in ...
Page 4
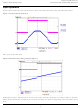
Lattice Semiconductor Input Hysteresis Figure 7 demonstrates the input signal with slow ramp rate virtually follow the ramp rate of MachXO output. Figure 7. Input measured at Point B Note “jump” at transition point. Figure 8. Zoomed View of Rising ...
Page 5
Lattice Semiconductor With a fast slew rate input, the signal will stay around the threshold region for a short time. With a slower signal, which stays in the threshold region for a long time, the noise will have more time ...
Page 6
Lattice Semiconductor Technical Support Assistance Hotline: 1-800-LATTICE (North America) +1-503-268-8001 (Outside North America) e-mail: techsupport@latticesemi.com Internet: www.latticesemi.com Revision History Date April 2006 September 2006 Version 01.0 Initial release. 01.1 Waveforms updated. Detailed explanation added. 6 Input Hysteresis in Lattice CPLD ...