ISL32457EIUZ-T7A Intersil, ISL32457EIUZ-T7A Datasheet - Page 12

ISL32457EIUZ-T7A
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL32457EIUZ-T7A
Description
RS-422/RS-485 Interface IC 60V OVP POLV -40+85 5V RS-485 1/2 DUP
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.ISL32450EIUZ-T7A.pdf
(21 pages)
Specifications of ISL32457EIUZ-T7A
Product Category
RS-422/RS-485 Interface IC
Rohs
yes
Data Rate
250 Kbps, 1 Mbps
Operating Supply Voltage
3.3 V to 5 V
Supply Current
4.5 mA
Operating Temperature Range
- 40 C to + 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
MSOP-8
Function
Transceiver
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Shutdown
Yes
Application Information
RS-485 and RS-422 are differential (balanced) data
transmission standards used for long haul or noisy environments.
RS-422 is a subset of RS-485, so RS-485 transceivers are also
RS-422 compliant. RS-422 is a point-to-multipoint (multidrop)
standard, which allows only one driver and up to 10 (assuming
one unit load devices) receivers on each bus. RS-485 is a true
multipoint standard, which allows up to 32 one unit load devices
(any combination of drivers and receivers) on each bus. To allow
for multipoint operation, the RS-485 specification requires that
drivers must handle bus contention without sustaining any
damage.
Another important advantage of RS-485 is the extended
common mode range (CMR), which specifies that the driver
outputs and receiver inputs withstand signals that range from
+12V to -7V. RS-422 and RS-485 are intended for runs as long as
4000 feet; thus, the wide CMR is necessary to handle ground
potential differences, as well as voltages induced in the cable by
external fields.
The ISL32450E, ISL32452E, ISL32453E, ISL32455E, ISL32457E
are a family of ruggedized RS-485 transceivers that improve on
the RS-485 basic requirements and therefore increases system
reliability. The CMR increases to ±20V, while the RS-485 bus pins
(receiver inputs and driver outputs) include fault protection
against voltages and transients up to ±60V. Additionally, the
±15kV to ±16.5kV built-in ESD protection complements the fault
protection.
Receiver (Rx) Features
These devices utilize a differential input receiver for maximum
noise immunity and common mode rejection. Input sensitivity is
better than ±200mV (3.3V operation), as required by the RS-422
and RS-485 specifications.
Receiver input (load) current surpasses the RS-422 specification
of 3mA, and is four times lower than the RS-485 “Unit Load (UL)”
requirement of 1mA maximum. Thus, these products are known
as “one-quarter UL” transceivers, and there can be up to 128 of
these devices on a network while still complying with the RS-485
loading specification.
The Rx functions with common mode voltages as great as ±20V,
making them ideal for industrial or long networks where induced
voltages are a realistic concern.
All the receivers include a “full fail-safe” function that guarantees
a high level receiver output if the receiver inputs are unconnected
(floating), shorted together, or connected to a terminated bus
with all the transmitters disabled (i.e., an idle bus).
Receivers easily meet the data rates supported by the
corresponding driver, and most receiver outputs are
three-statable via the active low RE input.
The Rx in the 250kbps and 1Mbps versions include noise filtering
circuitry to reject high frequency signals. The 1Mbps version
typically rejects pulses narrower than 50ns (equivalent to
20Mbps), while the 250kbps Rx rejects pulses below 150ns
(6.7Mbps).
ISL32450E, ISL32452E, ISL32453E, ISL32455E, ISL32457E
12
Driver (Tx) Features
The RS-485/RS-422 driver is a differential output device that
delivers at least 1.7V across a 54Ω load (RS-485), and at least 2V
across a 100Ω load (RS-422) with V
low propagation delay skew to maximize bit width and to
minimize EMI, and all drivers are three-statable via the active
high DE input.
The 250kbps and 1Mbps driver outputs are slew rate limited to
minimize EMI and to minimize reflections in unterminated or
improperly terminated networks.
High Overvoltage (Fault) Protection
Increases Ruggedness
NOTE: The available smaller pitch package (MSOP) may not meet the
creepage and clearance (C&C) requirements for ±60V levels. The user is
advised to determine his C&C requirements before selecting a package
type.
The ±60V (referenced to the IC GND) fault protection on the
RS-485 pins makes these transceivers some of the most rugged
on the market. This level of protection makes the ISL32450E,
ISL32452E, ISL32453E, ISL32455E, ISL32457E ideal for
applications in which power (e.g., 24V and 48V supplies) must be
routed in the conduit with the data lines and for outdoor applications
where large transients are likely to occur. When power is routed with
the data lines, even a momentary short between the supply and data
lines will destroy an unprotected device. The ±60V fault levels of this
family are at least four times higher than the levels specified for
standard RS-485 ICs. The ISL32450E, ISL32452E, ISL32453E,
ISL32455E, ISL32457E protection is active whether the Tx is
enabled or disabled, and even if the IC is powered down.
If transients or voltages (including overshoots and ringing)
greater than ±60V are possible, then additional external
protection is required. Use a protection device with the lowest
clamping voltage acceptable for the application, and remember
that TVS type devices typically clamp 5V to 10V above the
designated stand-off voltage (e.g., a “54V TVS” clamps between
60V and 66V).
Wide Common Mode Voltage (CMV) Tolerance
Improves Operating Range
RS-485 networks operating in industrial complexes or over long
distances are susceptible to large CMV variations. Either of these
operating environments may suffer from large node-to-node
ground potential differences or CMV pickup from external
electromagnetic sources, and devices with only the minimum
required +12V to -7V CMR may malfunction. The ISL32450E,
ISL32452E, ISL32453E, ISL32455E, ISL32457E extended ±20V
CMR allows for operation in environments that would overwhelm
lesser transceivers. Additionally, the Rx will not phase invert
(erroneously change state) even with CMVs of ±25V or
differential voltages as large as 40V.
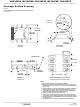
Cable Invert (Polarity Reversal) Function
With large node count RS-485 networks, it is common for some
cable data lines to be wired backwards during installation. When
this happens, the node is unable to communicate over the
network. Once a technician finds the miswired node, he must
then rewire the connector, which is time consuming.
CC
≥ 4.5V. The drivers feature
February 20, 2012
FN7921.0