ISL32457EIUZ-T7A Intersil, ISL32457EIUZ-T7A Datasheet - Page 13

ISL32457EIUZ-T7A
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL32457EIUZ-T7A
Description
RS-422/RS-485 Interface IC 60V OVP POLV -40+85 5V RS-485 1/2 DUP
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.ISL32450EIUZ-T7A.pdf
(21 pages)
Specifications of ISL32457EIUZ-T7A
Product Category
RS-422/RS-485 Interface IC
Rohs
yes
Data Rate
250 Kbps, 1 Mbps
Operating Supply Voltage
3.3 V to 5 V
Supply Current
4.5 mA
Operating Temperature Range
- 40 C to + 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
MSOP-8
Function
Transceiver
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Shutdown
Yes
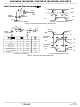
The ISL32457E simplifies this task by including a cable invert pin
(INV) that allows the technician to invert the polarity of the Rx
input and the Tx output pins simply by moving a jumper to
change the state of the invert pin. When the invert pin is low, the
IC operates like any standard RS-485 transceiver, and the bus
pins have their normal polarity definition of A and Y as
noninverting and B and Z as inverting. With the invert pin high,
the corresponding bus pins reverse their polarity, so B and Z
become noninverting, and A and Y become inverting.
Intersil’s unique cable invert function is superior to that found on
competing devices, because the Rx full fail-safe function is
maintained, even when the Rx polarity is reversed. Competitor
devices implement the Rx invert function simply by inverting the
Rx output. This means that with the Rx inputs floating or shorted
together, the Rx appropriately delivers a logic 1 in normal
polarity, but outputs a logic low when the IC is operated in the
inverted mode. Intersil’s innovative Rx design guarantees that,
with the Rx inputs floating or shorted together (V
output remains high, regardless of the state of the invert pin.
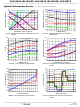
Data Rate, Cables, and Terminations
RS-485/RS-422 are intended for network lengths up to 4000ft,
but the maximum system data rate decreases as the
transmission length increases. Devices operating at 1Mbps can
operate at full data rates with lengths up to 800ft (244m). Jitter
is the limiting parameter at this faster data rate, so employing
encoded data streams (e.g., Manchester coded or Return-to-Zero)
may allow increased transmission distances. The slow versions
can operate at 115kbps or less at the full 4000ft (1220m)
distance, or at 250kbps for lengths up to 3000ft (915m). DC
cable attenuation is the limiting parameter, so using better
quality cables (e.g., 22 AWG) may allow increased transmission
distance.
Twisted pair is the cable of choice for RS-485/RS-422 networks.
Twisted pair cables tend to pick up noise and other
electromagnetically induced voltages as common mode signals,
which are effectively rejected by the differential receivers in
these ICs.
Short networks using the 250kbps versions need not be
terminated; however, terminations are recommended unless
power dissipation is an overriding concern.
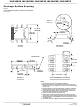
In point-to-point or point-to-multipoint (single driver on bus like
RS-422) networks, the main cable should be terminated in its
characteristic impedance (typically 120Ω) at the end farthest
from the driver. In multi-receiver applications, stubs connecting
receivers to the main cable should be kept as short as possible.
Multipoint (multi-driver) systems require that the main cable be
terminated in its characteristic impedance at both ends. Stubs
connecting a transceiver to the main cable should be kept as
short as possible.
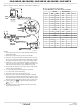
Built-In Driver Overload Protection
As stated previously, the RS-485 specification requires that
drivers survive worst-case bus contentions undamaged. These
transceivers meet this requirement via driver output short-circuit
current limits and on-chip thermal shutdown circuitry.
The driver output stages incorporate a double fold-back
short-circuit current limiting scheme, which ensures that the
ISL32450E, ISL32452E, ISL32453E, ISL32455E, ISL32457E
13
ID
= 0V), the Rx
output current never exceeds the RS-485 specification, even at
the common mode and fault condition voltage range extremes.
The first fold-back current level (≈83mA) is set to ensure that the
driver never folds back when driving loads with common mode
voltages up to ±20V. The very low second fold-back current
setting (≈13mA) minimizes power dissipation if the Tx is enabled
when a fault occurs.
In the event of a major short-circuit condition, devices also include
a thermal shutdown feature that disables the drivers whenever the
die temperature becomes excessive. This eliminates the power
dissipation, allowing the die to cool. The drivers automatically
re-enable after the die temperature drops about +15°C. If the
contention persists, the thermal shutdown/re-enable cycle repeats
until the fault is cleared. Receivers stay operational during thermal
shutdown.
Low Power Shutdown Mode
These BiCMOS transceivers all use a fraction of the power
required by competitive devices, but they (excluding ISL32457E)
also include a shutdown feature that reduces the already low
quiescent I
whenever the receiver and driver are simultaneously disabled
(RE = V
Disabling both the driver and the receiver for less than 60ns
guarantees that the transceiver will not enter shutdown.
Note that receiver and driver enable times increase when the
transceiver enables from shutdown. Refer to Notes 12, 13, 14,
15 and 16, at the end of the “Electrical Specification” table on
page 9, for more information.
CC
and DE = GND) for a period of at least 600ns.
CC
to a 10µA trickle. These devices enter shutdown
February 20, 2012
FN7921.0