LM3916N National Semiconductor, LM3916N Datasheet - Page 9
LM3916N
Manufacturer Part Number
LM3916N
Description
IC DRIVER DOT BAR DISPLAY 18-DIP
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM3916N-1NOPB.pdf
(28 pages)
Specifications of LM3916N
Display Type
LED, LCD, Vacuum Fluorescent
Configuration
Dot/Bar Display
Digits Or Characters
10 Steps
Current - Supply
6.1mA
Voltage - Supply
3 V ~ 25 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
18-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Interface
-
Other names
*LM3916N
LM3916
LM3916
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM3916N
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LM3916N-1
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
2 100
Part Number:
LM3916N-1
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
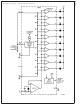
Mode Pin Functional Description
This pin actually performs two functions. Refer to the simpli-
fied block diagram below.
*High for bar
DOT OR BAR MODE SELECTION
The voltage at pin 9 is sensed by comparator C1, nominally
referenced to (V
pin 9 is above this level; otherwise it’s in dot mode. The
comparator is designed so that pin 9 can be left open circuit
for dot mode.
Taking into account comparator gain and variation in the
100 mV reference level, pin 9 should be no more than 20 mV
below V
open circuit) for dot mode. In most applications, pin 9 is
either open (dot mode) or tied to V
pin 9 should be connected directly to pin 3. Large currents
drawn from the power supply (LED current, for example)
should not share this path so that large IR drops are avoided.
+
for bar mode and more than 200 mV below V
Block Diagram of Mode Pin Function
+
−100 mV). The chip is in bar mode when
+
FIGURE 1. Cascading LM3914/15/16 Series in Dot Mode
(bar mode). In bar mode,
00797107
+
(or
9
DOT MODE CARRY
In order for display to make sense when multiple drivers are
cascaded in dot mode, special circuitry has been included to
shut off LED #10 of the first device when LED #1 of the
second device comes on. The connection for cascading in
dot mode has already been described and is depicted in
Figure 1.
As long as the input signal voltage is below the threshold of
the second driver, LED #11 is off. Pin 9 of driver #1 thus sees
effectively an open circuit so the chip is in dot mode. As soon
as the input voltage reaches the threshold of LED #11, pin 9
of driver #1 is pulled an LED drop (1.5V or more) below
V
enced 600 mV below V
which shuts off output transistor Q2, extinguishing LED #10.
V
very small current (less than 100 µA) that is diverted from
LED #9 does not noticeably affect its intensity.
An auxiliary current source at pin 1 keeps at least 100 µA
flowing through LED #11 even if the input voltage rises high
enough to extinguish the LED. This ensures that pin 9 of
driver #1 is held low enough to force LED #10 off when any
higher LED is illuminated. While 100 µA does not normally
produce significant LED illumination, it may be noticeable
when using high-efficiency LEDs in a dark environment. If
this is bothersome, the simple cure is to shunt LED #11 (and
LED #1) with a 10k resistor. The 1V 1R drop is more than the
900 mV worst case required to hold off LED #10 yet small
enough that LED #11 does not conduct significantly.
In some circuits a number of outputs on the higher device
are not used. Examples include the high resolution VU meter
and the expanded range VU meter circuits (see Typical
Applications). To provide the proper carry sense voltage in
dot mode, the LEDs of the higher driver IC are tied to V
through two series-connected diodes as shown in Figure 2.
Shunting the diodes with a 1k resistor provides a path for
driver leakage current.
LED
LED
. This condition is sensed by comparator C2, refer-
is sensed via the 20k resistor connected to pin 11. The
LED
. This forces the output of C2 low,
00797108
www.national.com
LED