LM5080MM/NOPB National Semiconductor, LM5080MM/NOPB Datasheet - Page 7

LM5080MM/NOPB
Manufacturer Part Number
LM5080MM/NOPB
Description
IC CONTROLLER LOAD SHARE 8-MSOP
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM5080MMNOPB.pdf
(13 pages)
Specifications of LM5080MM/NOPB
Applications
Power Supplies, Converters, Controllers
Current - Supply
3.7mA
Voltage - Supply
3 V ~ 14 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-MSOP, Micro8™, 8-uMAX, 8-uSOP,
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
LM5080MM
LM5080MMTR
LM5080MMTR
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM5080MM/NOPB
Manufacturer:
TI/德州仪器
Quantity:
20 000
Operating Description
Identical regulators connected in parallel will theoretically
share the total load current equally. However, slight mis-
matches in the reference voltage or feedback dividers of
each regulator can cause significant imbalances in the load
current sharing. The LM5080 senses the load current of
each regulator with an external sense resistor and makes
adjustments to the regulator’s output voltage to achieve
nearly equal current sharing. There are four possible imple-
mentations for the LM5080:
Reference Adjust Mode achieves current sharing by adjust-
ing the regulator reference voltage by applying an error
current from the TRO transconductance amplifier to the trim
or adjust pin of the regulator.
Remote Sense Positive Mode achieves current sharing by
adjusting the positive remote sense pin of the power con-
verter with current supplied by the RSO buffer amplifier
output.
Remote Sense Negative Mode achieves current sharing by
adjusting the negative remote sense pin of the power con-
verter with current supplied by the RSO buffer amplifier
output.
Feedback Adjust Mode achieves current sharing by adjust-
ing the regulator feedback voltage by applying an error
current from the TRO transconductance amplifier to the
feedback resistor divider.
In each mode, the LM5080 combines the regulator’s load
current information with the total load information on the
share (SHR) bus to create an error current on the TRO
output which is proportional to the load current mismatch. In
the reference adjust or feedback adjust modes of operation,
the output of the current share amplifier (CSA) is fed directly
into the regulator reference or feedback divider. The RSO
buffer can optionally be used to boost the transconductance
of the CSA if needed. In the remote sense adjust modes, the
RSO and CSO pins are tied together which reconfigures the
CSA as a voltage error amplifier where the RSO buffer drives
the remote sense pins of the regulator directly.
Current Share Amplifier
The current share amplifier is a low input offset transconduc-
tance amplifier with inputs CSP and CSM and dual outputs,
TRO and CSO. The two outputs are identical except TRO is
current limited to approximately
maximum correction of the regulator reference in the trim
adjust and feedback adjust modes. The outputs can operate
down to 450 mV without saturating which allows the TRO
output to adjust reference voltages as low as 500 mV. A
capacitor from TRO to ground (CTRO) is used for frequency
compensation of the current share loop.
In the two remote sense adjust modes, the current share
amplifier is configured as a unity gain differential voltage
amplifier by tying RSO to CSO. A capacitor from TRO to
ground (CTRO) is used for frequency compensation of the
amplifier and the current share loop.
RSO Buffer
The RSO buffer is a low-offset unity-gain operational ampli-
fier that has different uses, depending on the mode of op-
eration. In the remote sense adjust modes, the RSO pin is
externally tied to the CSO pin to create a differential voltage
amplifier that can drive the 10Ω input impedance of the
remote sense pin of typical power converter modules. The
RSO buffer can source or sink 10mA at an output voltage as
±
10 µA in order to limit the
7
low as 20mV above ground. With RSO load resistors of 10Ω,
the buffer can drive up to 10nF without causing amplifier
instability. For RSO loads
this node is 500pF for stable operation. In the trim adjust and
feedback adjust modes, the RSO buffer can be configured
with external resistors to boost the CSA transconductance
which increases the current share loop gain.
CSP Mode Comparator
The LM5080 monitors CSP & CSM with the CSP mode
comparator and applies a 500 mV input offset on the RSO
buffer amplifier if CSP-CSM is less than 10% of VCC (which
indicates a remote sense application mode). This offset al-
lows the RSO output to swing within 10 mV of ground without
saturating the TRO output which drives the RSO buffer. In
the trim adjust and feedback adjust modes, the CSP pin is
left open. In this configuration CSP is internally biased such
that CSP - CSM = 0.2 x VCC resulting in the removal of the
500mV RSO buffer offset.
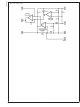
Reference Adjustment Operation
Mode
The reference adjust or trim adjust mode configuration is
shown in Figure 1. Typically only the current share amplifier
is used, however the RSO buffer can be optionally config-
ured for boosting the transconductance to increase the cur-
rent share loop gain (Figure 2). CSP is left open and CSM is
connected to a low side current sense resistor. The TRO
output is connected to the TRIM pin of the power converter
to inject a correction that adjusts the voltage regulator.
To understand the control loop, assume for a moment the
SHR pin is disconnected from the share bus. Since both
inputs to the current share amplifier are equal, the TRO
output current (IT) is zero and independent of the sense
resistor voltage (VRS). Hence the voltage regulation loop of
each converter is unaffected by the LM5080 when the SHR
bus is open. When the SHR pins are connected in a 2 supply
system, the transfer function between the sense resistor
voltages (VRS1 & VRS2) and the current injected into each
power converter TRIM pin (IT1 & IT2) are as follows:
where gm = current share amplifier transconductance
(8.7mA/V).
As long as the current sharing is equal (VRS1=VRS2), the
correction to the references (IT1 & IT2) will remain un-
changed. However, any difference between VRS1 and VRS2
will drive the TRIM pin currents in opposite polarities. As a
result the power converter output voltages will be adjusted to
force VRS1=VRS2. For 3 or more channels, the same aver-
aging concept is true; the injected currents (IT) will drive the
references such that the sense voltages are nearly identical.
A capacitor from TRO to ground (CTRO) sets the dominant
pole of the current share loop. The pole location is deter-
mined by gm, CTRO and the impedance of the regulator trim
pin. The current share loop frequency response does not
need to be fast and in fact should be less than or equal to
1/10th the regulator bandwidth. Since similar regulators will
have similar transient responses to a load step, the LM5080
only needs to correct the differences in each regulator’s
IT1 = 0.9 x gm x (VRS1 - VRS2)
IT2 = 0.9 x gm x (VRS2 - VRS1)
>
1 kΩ, max load capacitance on
www.national.com