LMX2216M National Semiconductor, LMX2216M Datasheet - Page 9
LMX2216M
Manufacturer Part Number
LMX2216M
Description
IC AMP/MIXER LO NOISE 16-SOIC
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LMX2216M.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of LMX2216M
Current - Supply
6.5mA ~ 8mA
Frequency
100MHz ~ 2GHz
Gain
9dB ~ 10dB
Noise Figure
4.8dB ~ 6dB
P1db
-5dBm ~ -3dBm
Package / Case
16-SOIC (0.154", 3.90mm Width)
Rf Type
Cellular, WLAN, PCS, PHS, Cordless Phones
Test Frequency
2GHz
Voltage - Supply
2.85V ~ 3.15V
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
*LMX2216M
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LMX2216M
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Functional Description
THE LNA
The LNA is a common emitter stage with active feedback
This feedback network allows for wide bandwidth operation
while providing the necessary optimal input impedance for
low noise performance The power down feature is imple-
mented using a CMOS buffer and a power-down switch The
power down switch is implemented with CMOS devices
During power down the switch is open and only leakage
currents are drawn from the supply
THE MIXER
The mixer is a Gilbert cell architecture with the RF input
signal modulating the LO signal and single ended output
taken from the collector of one of the upper four transistors
The power down circuitry of the mixer is similar to that of the
LNA The power down switch is used to provide or cut off
bias to the Gilbert cell
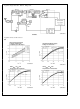
Typical Low Noise Amplifier
A typical low noise amplifier consists of an active amplifying
element and input and output matching networks The input
matching network is usually optimized for noise perform-
ance and the output matching network for gain The active
element is chosen such that it has the lowest optimal noise
figure F
figure of a linear two-port is a function of the source admit-
tance and can be expressed by
where G
F
e
G
MIN
G
ON
F
a
MIN
FIGURE 4 Typical LNA Structure
a
R
an intrinsic property of the device The noise
jB
n
a
jB
G
ON
G
R
G
n
e
e
e
(G
generator admittance presented to
the input of the two port
generator admittance at which op-
timum noise figure occurs
empirical constant relating the
sensitivity of the noise figure to
generator admittance
ON
b
G
G
)
2
a
(Continued)
(B
ON
b
TL W 11814 – 14
B
G
)
2
9
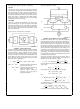
Typical Gilbert Cell
The Gilbert cell shown above is a circuit which multiplies
two input signals RF and LO The input RF voltage differen-
tially modulates the currents on the collectors of the transis-
tors Q1 and Q2 which in turn modulate the LO voltage by
varying the bias currents of the transistors Q3 Q4 Q5 and
Q6 Assuming that the two signals are small the result is a
product of the two signals producing at the output a sum
and difference of the frequencies of the two input signals If
either of these two signals are much larger than the thresh-
old voltage V
and higher order terms which are undesirable and may need
to be attenuated or filtered out
Analysis of the Gilbert cell shows that the output which is
the difference of the collector currents of Q3 and Q6 is
related to the two inputs by the equation
and the hyperbolic tangent function can be expressed as a
Taylor series
Assuming that the RF and LO signals are sinusoids
then
The lowest order term is a product of two sinusoids yielding
a sum of two sinusoids
one of which is the desired intermediate frequency signal
I
e
I
FIGURE 5 Typical Gilbert Cell Circuit Diagram
I
e
EE
I
EE
I
AB
C3
Bcos (
2
Acos (
b
T
cos ((
a
tanh(x)
I
the output will contain other mixing products
C6
V
V
LO
cos ((
RF
LO
RF
e
t
a
e
e
t
I
RF
a
EE
e
Acos (
Bcos (
LO
RF
a
x
RF
)
tanh
b
b
b
)
b
LO
x
B
3
3
3
3
RF
LO
A
3
) t
LO
cos
a
3
V
2V
cos
t
t
a
) t
RF
x
3
5
a
a
T
5
(
3
a
b
(
RF
LO
RF
LO
RF
t
RF
a
tanh
)
)
a
t
a
b
LO
LO
TL W 11814– 15
RF
)
)
V
LO
2V
a
LO
)
a
)
T