LMV932MA National Semiconductor, LMV932MA Datasheet - Page 13
LMV932MA
Manufacturer Part Number
LMV932MA
Description
OP AMP RRIO 1.8V DUAL, SOIC8, 932
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LMV932MA.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of LMV932MA
Op Amp Type
Low Voltage
No. Of Amplifiers
2
Bandwidth
1.5MHz
Slew Rate
0.42V/µs
Supply Voltage Range
1.8V To 5V
Amplifier Case Style
SOIC
No. Of Pins
8
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C To
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LMV932MA
Manufacturer:
nstion
Quantity:
39
Part Number:
LMV932MA
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LMV932MA/NOPB
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LMV932MAX
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LMV932MAX/NOPB
Manufacturer:
NS/TI
Quantity:
45
Part Number:
LMV932MAX/NOPB
Manufacturer:
TI/德州仪器
Quantity:
20 000
Application Note
INPUT AND OUTPUT STAGE
The rail-to-rail input stage of this family provides more flexi-
bility for the designer. The LMV931/LMV932/LMV934 use a
complimentary PNP and NPN input stage in which the PNP
stage senses common mode voltage near V
stage senses common mode voltage near V
from the PNP stage to NPN stage occurs 1V below V
both input stages have their own offset voltage, the offset of
the amplifier becomes a function of the input common mode
voltage and has a crossover point at 1V below V
This V
AC coupled signals if proper care is not taken. Large input
signals that include the V
tion in the output signal. One way to avoid such distortion is
to keep the signal away from the crossover. For example, in
a unity gain buffer configuration and with V
to-peak signal will contain input-crossover distortion while a
3V peak-to-peak signal centered at 1.5V will not contain input-
crossover distortion as it avoids the crossover point. Another
way to avoid large signal distortion is to use a gain of −1 circuit
which avoids any voltage excursions at the input terminals of
the amplifier. In that circuit, the common mode DC voltage
can be set at a level away from the V
small signals, this transition in V
OS
crossover point can create problems for both DC and
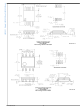
Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Range
Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Range
OS
crossover point will cause distor-
OS
shows up as a V
OS
cross-over point. For
S
= 5V, a 5V peak-
+
−
. The transition
and the NPN
+
.
20032636
20032638
+
. Since
CM
de-
13
pendent spurious signal in series with the input signal and can
effectively degrade small signal parameters such as gain and
common mode rejection ratio. To resolve this problem, the
small signal should be placed such that it avoids the V
crossover point. In addition to the rail-to-rail performance, the
output stage can provide enough output current to drive
600Ω loads. Because of the high current capability, care
should be taken not to exceed the 150°C maximum junction
temperature specification.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT CONSIDERATION
The LMV931/LMV932/LMV934 family has a complementary
bipolar input stage. The typical input bias current (I
The input bias current can develop a significant offset voltage.
This offset is primarily due to I
feedback resistor, R
100kΩ, then an offset voltage of 5mV will develop (V
R
1, cancels this effect. But the input offset current (I
contribute to an offset voltage in the same manner.
F
). Using a compensation resistor (R
Offset Voltage vs. Common Mode Range
F
. For example, if I
B
flowing through the negative
C
), as shown in
B
is 50nA and R
20032637
www.national.com
OS
B
) is 15nA.
OS
) will still
Figure
= I
F
B
OS
is
x