ADSP-21160NCB-100 Analog Devices Inc, ADSP-21160NCB-100 Datasheet

ADSP-21160NCB-100
Specifications of ADSP-21160NCB-100
Available stocks
Related parts for ADSP-21160NCB-100
ADSP-21160NCB-100 Summary of contents
Page 1
... Analog Devices. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. FEATURES 100 MHz (10 ns) core instruction rate (ADSP-21160N) Single-cycle instruction execution, including SIMD opera- tions in both computational units Dual data address generators (DAGs) with modulo and bit- ...
Page 2
... Multiprocessing support provides Glueless connection for scalable DSP multiprocessing architecture Distributed on-chip bus arbitration for parallel bus con- nect ADSP-21160x processors plus host 6 link ports for point-to-point connectivity and array multiprocessing Serial ports provide Two synchronous serial ports with companding hardware ...
Page 3
... TABLE OF CONTENTS Summary ............................................................... 1 Features ................................................................. 1 Table of Contents .................................................... 3 Revision History ...................................................... 3 General Description ................................................. 4 ADSP-21160x Family Core Architecture .................... 4 Memory and I/O Interface Features ........................... 5 Development Tools ............................................... 8 Designing an Emulator-Compatible DSP Board (Target) 10 Additional Information ......................................... 10 Pin Function Descriptions ........................................ 11 Specifications ......................................................... 15 Operating Conditions—ADSP-21160M .................... 15 Electrical Characteristics—ADSP-21160M ................. 16 Operating Conditions—ADSP-21160N ..................... 17 REVISION HISTORY 2/10— ...
Page 4
... The ADSP-21160x introduces single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) processing. Using two computational units (ADSP-2106x SHARC DSPs have one), the ADSP-21160x can double performance versus the ADSP-2106x on a range of DSP algorithms. Fabricated in a state-of-the-art, high speed, low power CMOS process, the ADSP-21160N has instruction cycle time. ...
Page 5
... CS which the data memory (DM) bus transfers data, and the pro- gram memory (PM) bus transfers both instructions and data DMA DEVICE (see the functional block diagram 1). With the ADSP-21160x (OPTIONAL) DSP’s separate program and data memory buses and on-chip DATA instruction cache, the processor can simultaneously fetch four operands and an instruction (from the cache), all in a single cycle ...
Page 6
... The dual-ported memory in combination with three separate on-chip buses allows two data transfers from the core and one from I/O processor single cycle. The ADSP-21160x mem- ory can be configured as a maximum of 128K words of 32-bit data, 256K words of 16-bit data, 85K words of 48-bit instructions (or 40-bit data), or combinations of different word sizes up to four megabits ...
Page 7
... Any of these options is sufficient. Program Booting The internal memory of the ADSP-21160x can be booted at sys- tem power-up from an 8-bit EPROM, a host processor, or through one of the link ports. Selection of the boot source is Rev Page February 2010 ...
Page 8
... F AGND Figure 6. Analog Power (AV ) Filter Circuit DD DEVELOPMENT TOOLS The ADSP-21160x is supported with a complete set of ®† CROSSCORE software and hardware development tools, including Analog Devices emulators and the VisualDSP++ development environment. The same emulator hardware that supports other ADSP-2116x processors also fully emulates the ADSP-21160x ...
Page 9
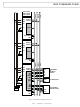
... ADSP-21160X #5 ADSP-21160X #4 ADSP-21160X #3 ADDR31–0 CLKIN DATA63–0 RESET RPBA 3 ID2–0 CONTROL 011 PA 5 BR1–2, BR4–6 BR3 ADSP-21160X #2 ADDR31–0 CLKIN DATA63–0 RESET RPBA 3 ID2–0 CONTROL 010 PA 5 BR1, BR3–6 BR2 ADSP-21160X #1 CLKIN ADDR31–0 RESET DATA63– ...
Page 10
... File (LDF), allowing the developer to move between the graphi- cal and textual environments. Analog Devices DSP emulators use the IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Test Access Port of the ADSP-21160x processor to monitor and con- trol the target board processor during emulation. The emulator provides full-speed emulation, allowing inspection and modifi- cation of memory, registers, and processor stacks. Nonintrusive in-circuit emulation is assured by the use of the processor’ ...
Page 11
... RDH has a 20 kΩ internal pull-up resistor that is enabled on the processor with ID2–0 = 00x. WRL I/O/T Memory Write Low Strobe. WRL is asserted when ADSP-21160x writes to the low word of external memory or internal memory of other ADSP-21160x DSPs. External devices must assert WRL for writing to ADSP-21160x DSP’s low word of internal memory multiprocessing system, WRL is driven by the bus master. WRL has a 20 kΩ ...
Page 12
... I/O Host Bus Grant. Acknowledges an HBR bus request, indicating that the host processor may take control of the external bus. HBG is asserted (held low) by the ADSP-21160x until HBR is released multiprocessing system, HBG is output by the processor bus master and is monitored by all others. After HBR is asserted, and before HBG is given, HBG will float for CLKIN cycle). To avoid erroneous grants, HBG should be pulled up with a 20 kΩ ...
Page 13
... Function ID2–0 I Multiprocessing ID. Determines which multiprocessing bus request (BR1–BR6) is used by the ADSP-21160x 001 corresponds to BR1 010 corresponds to BR2, and so on. Use ID = 000 001 in single-processor systems. These lines are a system configuration selection which should be hardwired or only changed at reset. DMAG1 O/T DMA Grant 1 (DMA Channel 11). Asserted by ADSP-21160x to indicate that the requested DMA starts on the next cycle. Driven by bus master only. DMAG1 has a 20 kΩ ...
Page 14
... TRST I/A Test Reset (JTAG). Resets the test state machine. TRST must be asserted (pulsed low) after power held low for proper operation of the ADSP-21160x. TRST has a 20 kΩ internal pull-up resistor. EMU O (O/D) Emulation Status. Must be connected to the ADSP-21160x emulator target board connector only. ...
Page 15
... SPECIFICATIONS OPERATING CONDITIONS—ADSP-21160M Table 5 shows the recommended operating conditions for the ADSP-21160M. Specifications are subject to change without notice. Table 5. Operating Conditions—ADSP-21160M Parameter V Internal (Core) Supply Voltage DDINT AV Analog (PLL) Supply Voltage DD V External (I/O) Supply Voltage DDEXT T Case Operating Temperature ...
Page 16
... For more information, see DD-INHIGH composite average based on a range of low activity code. For more information, see DD-INLOW 14 Idle denotes ADSP-21160M state during execution of IDLE instruction. For more information, see 15 Characterized, but not tested. 16 Applies to all signal pins. 17 Guaranteed, but not tested. ...
Page 17
... OPERATING CONDITIONS—ADSP-21160N Table 7 shows recommended operating conditions for the ADSP-21160N. These specifications are subject to change without notice. Table 7. Operating Conditions—ADSP-21160N Parameter V Internal (Core) Supply Voltage DDINT AV Analog (PLL) Supply Voltage DD V External (I/O) Supply Voltage DDEXT T Case Operating Temperature ...
Page 18
... For more information, see DD-INHIGH composite average based on a range of low activity code. For more information, see DD-INLOW 18 Idle denotes ADSP-21160N state during execution of IDLE instruction. For more information, see 19 Applies to all signal pins. 20 Guaranteed, but not tested. Test Conditions 1 ...
Page 19
... Stresses greater than those listed in Table 9 and Table 10 (ADSP-21160N) may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions greater than those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Table 9. Absolute Maximum Ratings— ...
Page 20
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N TIMING SPECIFICATIONS The ADSP-21160x DSP’s internal clock switches at higher fre- quencies than the system input clock (CLKIN). To generate the internal clock, the DSP uses an internal phase-locked loop (PLL). This PLL-based clocking minimizes the skew between the system clock (CLKIN) signal and the DSP’s internal clock (the clock source for the external port logic and I/O pads). The ADSP-21160x DSP’ ...
Page 21
... Voltage ramp rates can vary from microseconds to hundreds of milliseconds, DDINT DDEXT specification. If setup time is not met, one additional CLKIN cycle may be added to the core SRST t RSTVDD t IVDDEVDD t CLKVDD t CLKRST t PLLRST Figure 8. Power-Up Sequencing Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N Min Max 0 – 50 +200 0 200 4096t CK t CORERST ...
Page 22
... Core Clock Period CCLK V DDEXT VOLTAGE REGULATOR V DDINT VOLTAGE REGULATOR Figure 9. Dual Voltage Schottky Diode 10 CLKIN t t CKH CKL Figure 10. Clock Input Rev Page February 2010 V DDEXT ADSP-21160x V DDINT ADSP-21160M ADSP-21160N 80 MHz 100 MHz Min Max Min Max 10.5 40 7.5 40 10 12.5 40 ...
Page 23
... DD 2 Only required if multiple ADSP-21160x DSPs must come out of reset synchronous to CLKIN with program counters (PC) equal. Not required for multiple ADSP-21160x DSPs communicating over the shared bus (through the external port), because the bus arbitration logic automatically synchronizes itself after reset. ...
Page 24
... SIR HIR CLKIN IRQ2–0 Timer For timer, see Table 16 and Figure 13. Table 16. Timer Parameter Switching Characteristic t CLKIN High to TIMEXP DTEX 1 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 7 ns, maximum. CLKIN t DTEX TIMEXP 12 SIR t IPW Figure 12. Interrupts 1 Figure 13. Timer Rev Page February 2010 Min Max ...
Page 25
... DFOE t CLKIN High to FLAG3–0 OUT Disable DFOD 1 Flag inputs meeting these setup and hold times for instruction cycle N will affect conditional instructions in instruction cycle N+2. 2 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 12 ns, maximum. 3 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 5 ns, maximum. CLKIN t DFOE FLAG3–0 OUT CLKIN FLAG3– ...
Page 26
... CCLK . CK . SDS –11+W ns, maximum For the second and subsequent cycles of an asynchronous external memory access, the t DAAK DSAK SAKC Rev Page February 2010 18. These specifications apply when the ADSP-21160x Max t – 0.25t – 8.5+W CK CCLK t – 0. CCLK t – 0.5t – ...
Page 27
... ADDRESS MSx, BMS, CIF t DARL RD t DAD DATA t DSAK t DAAK ACK CLKIN WR, DMAG DRLD SDS t t HAKC SAKC Figure 15. Memory Read—Bus Master Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N t HDA t DRHA t HDRH t RWR ...
Page 28
... For the second and subsequent cycles of an asynchronous external memory access, the t DAAK DSAK SAKC –12.5+W ns, minimum. for calculation of hold times given capacitive and dc loads. Rev Page February 2010 19. These specifications apply when the ADSP-21160x Max t – 0.5t –12+W CK CCLK t – 0.75t – ...
Page 29
... ADDRESS MSx, BMS, CIF t DAWL WR t WDE DATA t DSAK t DAAK ACK CLKIN RD, DMAG Figure 16. Memory Write—Bus Master Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N t DAWH DATRWH t DDWH t DWHD t t SAKC HAKC t DWHA t WWR t DDWR ...
Page 30
... When accessing a slave ADSP-21160x, these switching charac- teristics must meet the slave’s timing requirements for synchronous read/writes (see Synchronous Read/Write–Bus Slave on page 32). The slave ADSP-21160x must also meet these (bus master) timing requirements for data and acknowledge setup and hold times. ...
Page 31
... PAGE ACK (IN) t DACKMO ACK (OUT) READ CYCLE t DRWL RDx DATA (IN) WRITE CYCLE t DRWL WRx t DDATO DATA (OUT) t CKOP t t CKWH CKWL t SACKC t ACKMTR t SSDATI Figure 17. Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Master Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N t HADDO t HACKC t DRDO t HSDATI t DWRO t HDATO ...
Page 32
... Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Slave See Table 21 and Figure 18. Use these specifications for ADSP-21160x bus master accesses of a slave’s IOP registers or internal memory (in multiprocessor memory space). The bus master must meet these (bus slave) timing requirements. Table 21. Synchronous Read/Write—Bus Slave Parameter Timing Requirements ...
Page 33
... Multiprocessor Bus Request and Host Bus Request See Table 22 and Figure 19. Use these specifications for passing of bus mastership between multiprocessing ADSP-21160x DSPs (BRx host processor, both synchronous and asynchronous (HBR, HBG). Table 22. Multiprocessor Bus Request and Host Bus Request Parameter Timing Requirements ...
Page 34
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N CLKIN HBR HBG (OUT) (OUT) BRx PA (OUT) (SLAVE) (OUT) PA (MASTER) (IN) HBG BRx, PA (IN) RPBA HRB REDY (O/ D) REDY (A/D) HBG (OUT) RDx WRx OPEN DRAIN, A/D = ACTIVE DRI Figure 19. Multiprocessor Bus Request and Host Bus Request Rev Page February 2010 ...
Page 35
... RDYPWR 1 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 7 ns, minimum. 2 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 12 ns, minimum After HBG is returned by the ADSP-21160x, the host can drive the RDx and WRx pins to access the ADSP-21160x DSP’s 24, Figure 20, and internal memory or IOP registers. HBR and HBG are assumed low for this timing ...
Page 36
... O/D = OPEN DRAIN, A/D = ACTIVE DRIVE t SDATRDY t t DRDYRDL RDYPRD Figure 20. Asynchronous Read—Host to ADSP-21160x t SADWRH t t SCSWRL HCSWRH t WWRL t SDATWH t t DRDYWRL RDYPWR Figure 21. Asynchronous Write—Host to ADSP-21160x Rev Page February 2010 t HADRDH t WRWH t HDARWH t DRDHRDY t HADWRH t WRWH t HDATWH t DWRHRDY ...
Page 37
... CCLK 6 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 3.5 ns (minimum addition to bus master transition cycles, these specs also apply to bus master and bus slave synchronous read/write. 8 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 1.5 ns (minimum) and 10 ns (maximum). 9 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 1.5 ns (minimum). 10 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 0.5 ns (minimum). 11 Not specified for ADSP-21160M. ...
Page 38
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N CLKIN SBTS MIENA, MIENS, MIENHG MEMORY INTERFACE t DATEN DATA t ACKEN ACK t CDCEN CLKOUT HBG t MEMORY INTERFACE MEMORY INTERFACE = ADDRESS, RDx, WRx, MSx, PAGE, DMAGx. BMS (IN EPROM BOOT MODE) t STSCK t HTSCK t t MITRA, MITRS, t DATTR t ACKTR t CDCTR MENHBG Figure 22. Three-State Timing—Bus Master, Bus Slave Rev ...
Page 39
... This parameter applies for synchronous access mode only. 12 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 18 ns, minimum. signals. For Paced Master mode, the data transfer is controlled by ADDR31–0, RDx, WRx, MS3–0, and ACK (not DMAGx). For Paced Master mode, the Memory Read-Bus Master, Mem- ory Write-Bus Master, and Synchronous Read/Write-Bus Master timing specifications for ADDR31– ...
Page 40
... DMARx DMAGx TRANSFERS BETWEEN ADSP-2116X INTERNAL MEMORY AND EXTERNAL DEVICE DATA (FROM ADSP-2116X TO EXTERNAL DRIVE) DATA (FROM EXTERNAL DRIVE TO ADSP-2116X) TRANSFERS BETWEEN EXTERNAL DEVICE AND EXTERNAL MEMORY* (EXTERNAL HANDSHAKE MODE) WRx (EXTERNAL DEVICE TO EXTERNAL MEMORY) RDx (EXTERNAL MEMORY TO EXTERNAL DEVICE) ADDR ...
Page 41
... For ADSP-21160M, specification is 6 ns, minimum. 4 LACK goes low with t relative to rise of LCLK after first nibble, but does not go low if the receiver’s link buffer is not about to fill. DLALC 5 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 12 ns, minimum. RECEIVE LCLK LDAT(7:0) LACK (OUT) maximum delay that can be introduced in LCLK, relative to ...
Page 42
... LCLKTWH t LCLK Low Delay After LACK High DLACLK 1 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 0.5t –1.5 ns (minimum) and 0.5t LCLK 2 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 0.5t –1.5 ns (minimum) and 0.5t LCLK 3 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 0. (minimum) and 3t LCLK TRANSMIT t t LCLKTWH LCLKTWL LCLK t DLDCH t HLDCH LDAT(7:0) ...
Page 43
... Receive Data Setup Before RCLK SDRI t Receive Data Hold After RCLK HDRI 1 Referenced to sample edge. 2 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 1 ns, minimum Table 31. Serial Ports—External or Internal Clock Parameter Switching Characteristics t RFS Delay After RCLK (Internally Generated RFS) DFSE t RFS Hold After RCLK (Internally Generated RFS) ...
Page 44
... DFSI t TFS Hold After TCLK (Internally Generated TFS) HOFSI t Transmit Data Delay After TCLK DDTI t Transmit Data Hold After TCLK HDTI 2 t TCLK/RCLK Width SCLKIW 1 Referenced to drive edge. 2 For ADSP-21160M, specification is 0.5t –2.5 ns (minimum) and 0.5t SCLK RCLK RFS DT TCLK TFS ...
Page 45
... HFSI RFS t HDRI DR SAMPLE EDGE TCLK t t HFSI HOFSE TFS DT TCLK / RCLK TCLK / RCLK Figure 27. Serial Ports Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N Min Max 13 1.0 DATA RECEIVE— EXTERNAL CLOCK DRIVE SAMPLE EDGE EDGE t SCLKW t DFSE t t HFSE SFSE t t SDRE HDRE DATA TRANSMIT— ...
Page 46
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N JTAG Test Access Port and Emulation For JTAG Test Access Port and emulation, see Figure 28. Table 36. JTAG Test Access Port and Emulation Parameter Timing Requirements t TCK Period TCK t TDI, TMS Setup Before TCK High STAP t TDI, TMS Hold After TCK High ...
Page 47
... VOLTAGE – V DDEXT Figure 29. ADSP-21160M Typical Drive Currents OUTPUT DRIVE CURRENTS—ADSP-21160N Figure 30 shows typical I–V characteristics for the output driv- ers of the ADSP-21160N. The curves represent the current drive capability of the output drivers as a function of output voltage 3.47V, –45°C DDEXT ...
Page 48
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N Table 37. ADSP-21160x Operation Types vs. Input Current Operation Peak Activity Instruction Type Multifunction Instruction Fetch Cache 2 Core Memory Access 2 per t (DM Internal Memory DMA 1 per 2 t External Memory DMA 1 per External Port Cycle ( 64) Data Bit Pattern for Core Worst Case Memory Access and DMA ...
Page 49
... Output Disable Time on Page Figure not be linear outside the ranges shown. plus the minimum 1.5V Figure 34. ADSP-21160M Typical Output Rise Time (10%–90%, V 1.5V Figure 35. ADSP-21160M Typical Output Rise Time (10%–90%, V Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N Figure 32). Figure 34, Figure ...
Page 50
... Figure 37. ADSP-21160N Typical Output Rise Time (20%–80%, V vs. Load Capacitance 150 200 Figure 38. ADSP-21160N Typical Output Rise Time (20%–80%, V FALL TIME + 1.4882 150 200 Figure 39. ADSP-21160N Typical Output Delay or Hold vs. Load Capacitance = Max) DDEXT Rev Page February 2010 25 20 RISE TIME Y = 0.0813x + 2.312 ...
Page 51
... ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS Thermal Characteristics The ADSP-21160x DSPs are provided in a 400-Ball PBGA (Plas- tic Ball Grid Array) package. The ADSP-21160x is specified for a case temperature (T To ensure that the T data sheet specification is not exceeded, CASE a heatsink and/or an air flow source may be used. Use the cen- terblock of ground pins (for ADSP-21160M, PBGA balls: H8-13, J8-13, K8-13, L8-13, M8-13, N8-13 ...
Page 52
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N 400-BALL PBGA PIN CONFIGURATIONS Table 40 lists the pin assignments for the PBGA package, and the pin configurations diagram in Figure 40 and Figure 41 (ADSP-21160N) show the pin assignment summary. Table 40. 400-Ball PBGA Pin Assignments Pin Name Pin No. Pin Name DATA[14] A01 DATA[22] ...
Page 53
... R20 V01 ADDR[5] W01 V02 ADDR[9] W02 V03 ADDR[12] W03 V04 ADDR[15] W04 V05 ADDR[17] W05 V06 ADDR[20] W06 Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N Pin Name Pin No. AV M01 DD CLK_CFG_3 M02 CLKOUT M03 2 NC M04 V M05 DDEXT V M06 DDINT GND M07 ...
Page 54
... L4DAT[1] U19 L5DAT[4] L4DAT[2] U20 L5DAT[6] 1 For ADSP-21160M, Pin Name and function is defined For ADSP-21160N, Pin Name and function is defined as GND. For ADSP-21160M, Pin Name and function is defined as No Connect (NC). (See Footnotes 1 and 2) Pin No. Pin Name V07 ADDR[23] V08 ADDR[26] V09 ...
Page 55
... AGND DDEXT NO CONNECTION 1 USE THE CENTER BLOCK OF GROUND PINS (PBGA BALLS: H8-13, J8-13, K8-13, L8-13, M8-13, N8-13) TO PROVIDE THERMAL PATHWAYS TO YOUR PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD’S GROUND PLANE. Figure 40. ADSP-21160M 400-Ball PBGA Pin Configurations (Bottom View, Summary) Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N ...
Page 56
... KEY: V DDINT V DDEXT NO CONNECTION 1 USE THE CENTER BLOCK OF GROUND PINS (PBGA BALLS: F7-14, G7-14, H7-14, J7-14, K7-14, L7-14, M7-14, N7-14, P7-14, R7-15) TO PROVIDE THERMAL PATHWAYS TO YOUR PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD’S GROUND PLANE. Figure 41. ADSP-21160N 400-Ball PBGA Pin Configurations (Bottom View, Summary ...
Page 57
... OUTLINE DIMENSIONS The ADSP-21160x processors are available mm, 400-ball PBGA lead-free package. 27.20 27.00 26.80 BALL A1 INDICATOR TOP VIEW 2.49 2.32 2.15 Figure 42. 400-Ball Plastic Grid Array (PBGA) (B-400) Compliant to JEDEC Standards MS-034-BAL-2 (Dimensions in Millimeters) SURFACE-MOUNT DESIGN The following table is provided as an aide to PCB design. ...
Page 58
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N ORDERING GUIDE 1 Model Temperature Range ADSP-21160MKBZ-80 0°C to +85°C ADSP-21160MKB-80 0°C to +85°C ADSP-21160NCBZ-100 –40°C to +100°C ADSP-21160NCB-100 –40°C to +100°C ADSP-21160NKBZ-100 0°C to +85°C ADSP-21160NKB-100 0°C to +85° RoHS compliant part. Instruction On-Chip Rate SRAM Package Description ...
Page 59
... Rev Page February 2010 ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N ...
Page 60
... ADSP-21160M/ADSP-21160N ©2010 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. D02426-0-2/10(B) Rev Page February 2010 ...