DSPIC33FJ128MC706T-I/PT Microchip Technology, DSPIC33FJ128MC706T-I/PT Datasheet - Page 24

DSPIC33FJ128MC706T-I/PT
Manufacturer Part Number
DSPIC33FJ128MC706T-I/PT
Description
IC,DSP,16-BIT,CMOS,TQFP,64PIN,PLASTIC
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
dsPIC™ 33Fr
Datasheets
1.DSPIC33FJ12GP201-ISO.pdf
(90 pages)
2.DSPIC33FJ64MC506-IPT.pdf
(340 pages)
3.DSPIC33FJ64MC506-IPT.pdf
(30 pages)
Specifications of DSPIC33FJ128MC706T-I/PT
Core Processor
dsPIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
40 MIPs
Connectivity
CAN, I²C, IrDA, LIN, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, DMA, Motor Control PWM, QEI, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
53
Program Memory Size
128KB (128K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
16K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 16x10b/12b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-TFQFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
MA330013 - MODULE PLUG-IN DSPIC33 100TQFPDV164033 - KIT START EXPLORER 16 MPLAB ICD2DM240001 - BOARD DEMO PIC24/DSPIC33/PIC32AC164327 - MODULE SKT FOR 64TQFP
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DSPIC33FJ128MC706T-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
dsPIC33F
DS70155C-page 22
7.0
Power
dsPIC33F devices include:
• Real-Time Clock Source Switching
• Power-Saving Modes
7.1
Configuration bits determine the clock source upon
Power-on Reset (POR) and Brown-out Reset (BOR).
Thereafter, the clock source can be changed between
permissible clock sources. The OSCCON register
controls the clock switching and reflects system clock
related status bits. To reduce power consumption, the
user can switch to a slower clock source.
7.2
The dsPIC33F devices have two reduced power
modes that can be entered through execution of the
PWRSAV instruction.
• Sleep Mode: The CPU, system clock source and
• Idle Mode: The CPU is disabled but the system
• Doze Mode: The CPU clock is temporarily slowed
These modes provide an effective way to reduce power
consumption during periods when the CPU is not in use.
7.2.1
When the device enters Sleep mode:
• System clock source is shut down. If an on-chip
• Device current consumption is at minimum
• Fail-Safe Clock Monitor (FSCM) does not operate
• LPRC clock continues to run in Sleep mode if the
• BOR circuit, if enabled, remains operative during
• WDT, if enabled, is automatically cleared prior to
• Some peripherals may continue to operate in
any peripherals that operate on the system clock
source are disabled. This is the lowest power
mode of the device.
clock source continues to operate. Peripherals
continue to operate but can optionally be disabled.
down relative to the peripheral clock by a
user-selectable factor.
oscillator is used, it is turned off.
provided that no I/O pin is sourcing current.
during Sleep mode because the system clock
source is disabled.
WDT is enabled.
Sleep mode
entering Sleep mode.
Sleep mode. These peripherals include I/O pins
that detect a change in the input signal, or
peripherals that use an external clock input. Any
peripheral that is operating on the system clock
source is disabled in Sleep mode.
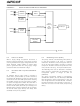
management
DEVICE POWER MANAGEMENT
Real-Time Clock Source Switching
Power-Saving Modes
SLEEP MODE
services
provided
Preliminary
by
the
The processor exits (wakes up) from Sleep on one of
these events:
• Any interrupt source that is individually enabled
• Any form of device Reset
• A WDT time-out
7.2.2
When the device enters Idle mode:
• CPU stops executing instructions
• WDT is automatically cleared
• System clock source remains active
• Peripheral modules, by default, continue to
• Peripherals, optionally, can be shut down in Idle
• If the WDT or FSCM is enabled, the LPRC also
The processor wakes from Idle mode on these events:
• Any interrupt that is individually enabled
• Any source of device Reset
• A WDT time-out
Upon wake-up from Idle, the clock is re-applied to the
CPU and instruction execution begins immediately
starting with the instruction following the PWRSAV
instruction, or the first instruction in the Interrupt
Service Routine (ISR).
7.2.3
The Doze mode provides the user software the ability
to temporarily reduce the processor instruction cycle
frequency relative to the peripheral frequency. Clock
frequency ratios of 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, 1:64
and 1:128 are supported.
For example, suppose the device is operating at
20 MIPS and the CAN module has been configured for
500 kbps bit rate based on this device operating speed.
If the device is now placed in Doze mode with a clock
frequency ratio of 1:4, the CAN module will continue to
communicate at the required bit rate of 500 kbps, but
the CPU now starts executing instructions at a
frequency of 5 MIPS.
This feature further reduces the power consumption
during periods where relatively less CPU activity is
required.
When the device is operating in Doze mode, the
hardware
synchronization between peripheral events and SFR
accesses by the CPU.
operate normally from the system clock source
mode using their ‘stop-in-idle’ control bit.
remains active
IDLE MODE
DOZE MODE
ensures
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
that
there
is
no
loss
of