IRF7807VTRPBF International Rectifier, IRF7807VTRPBF Datasheet - Page 3

IRF7807VTRPBF
Manufacturer Part Number
IRF7807VTRPBF
Description
MOSFET N-CH 30V 8.3A 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
International Rectifier
Series
HEXFET®r
Datasheet
1.IRF7807VTRPBF.pdf
(8 pages)
Specifications of IRF7807VTRPBF
Fet Type
MOSFET N-Channel, Metal Oxide
Fet Feature
Standard
Rds On (max) @ Id, Vgs
25 mOhm @ 7A, 4.5V
Drain To Source Voltage (vdss)
30V
Current - Continuous Drain (id) @ 25° C
8.3A
Vgs(th) (max) @ Id
3V @ 250µA
Gate Charge (qg) @ Vgs
14nC @ 5V
Power - Max
2.5W
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Transistor Polarity
N-Channel
Resistance Drain-source Rds (on)
25 mOhms
Drain-source Breakdown Voltage
30 V
Gate-source Breakdown Voltage
20 V
Continuous Drain Current
8.3 A
Power Dissipation
2.5 W
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Gate Charge Qg
9.5 nC
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
IRF7807VPBFTR
IRF7807VTRPBF
IRF7807VTRPBFTR
IRF7807VTRPBF
IRF7807VTRPBFTR
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
IRF7807VTRPBF
Manufacturer:
IR
Quantity:
20 000
Power MOSFET Selection for DC/DC
Converters
Control FET
in the switching elements of the circuit - Q1 and Q2.
Power losses in the high side switch Q1, also called
the Control FET, are impacted by the R
MOSFET, but these conduction losses are only about
one half of the total losses.
by;
P
and Q
charge that is included in all MOSFET data sheets.
The importance of splitting this gate-source charge
into two sub elements, Q
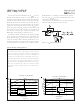
Fig 1.
the gate driver between the time that the threshold
voltage has been reached (t1) and the time the drain
current rises to I
age begins to change. Minimizing Q
tor in reducing switching losses in Q1.
put capacitance of the MOSFET during every switch-
ing cycle. Figure 2 shows how Q
parallel combination of the voltage dependant (non-
linear) capacitance’s C
the power supply input buss voltage.
www.irf.com
P
loss
loss
Special attention has been given to the power losses
Power losses in the control switch Q1 are given
This can be expanded and approximated by;
This simplified loss equation includes the terms Q
Q
Q
Q
gs2
gs2
oss
= I
= P
+ I ×
+ Q
+
oss
is the charge that must be supplied to the out-
indicates the charge that must be supplied by
(
is a sub element of traditional gate-source
⎛
⎜
⎝
(
⎛
⎝
which are new to Power MOSFET data sheets.
Q
rms
conduction
g
2
oss
× V
2
Q
× R
i
× V
g
gd
g
dmax
× f
ds(on )
in
× V
+ P
× f
(t2) at which time the drain volt-
)
in
)
switching
× f
⎞
⎠
ds
gs1
and C
⎞
⎟ + I ×
⎠
and Q
+ P
⎛
⎜
⎝
dg
gs2
drive
oss
when multiplied by
, can be seen from
gs2
Q
is formed by the
+ P
i
gs 2
g
is a critical fac-
× V
output
ds(on)
in
× f
of the
⎞
⎟
⎠
gs2
Figure 1: Typical MOSFET switching waveform
Synchronous FET
by;
*dissipated primarily in Q1.
P
P
loss
loss
The power loss equation for Q2 is approximated
t0
V
= P
= I
+ Q
+
GTH
(
(
⎛
⎜
⎝
conduction
rms
Q
t1
g
2
oss
2
× V
× R
× V
t2
g
+ P
ds(on)
× f
IRF7807VPbF
in
Drain Current
drive
× f
t3
)
)
⎞
⎠
+ P
+ Q
output
(
*
Drain Voltage
rr
× V
Gate Voltage
in
× f
4
1
2
)
3