TORX141P Toshiba, TORX141P Datasheet - Page 3

TORX141P
Manufacturer Part Number
TORX141P
Description
Manufacturer
Toshiba
Datasheet
1.TORX141P.pdf
(5 pages)
Specifications of TORX141P
Optical Fiber Type
RX
Data Transfer Rate
15Mbps
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.7V
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
3V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
3.6V
Operating Temp Range
-20C to 70C
Mounting
Snap in
Pin Count
5
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
TORX141P
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA
Quantity:
1 900
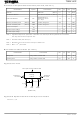
Board Layout Hole Pattern
Precautions on Use
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Maximum rating
The maximum ratings are the limit values which must not be exceeded during operation of device. None of
these rating value must not be exceeded. If the maximum rating value is exceeded, the characteristics of
devices may never be restored properly. In extreme cases, the device may be permanently damages.
Soldering
Optical modules are comprised of internal semiconductor devices. However, in principle, optical modules
are optical components. During soldering, ensure that flux does not contact with the emitting surface or
the detecting surface. Also ensure that proper flux removal is conducted after soldering.
Some optical modules come with a protective cap. The protective cap is used to avoid malfunction when the
optical module is not in use. Note that it is not dust or waterproof.
As mentioned before, optical modules are optical components. Thus, in principle, soldering where there
may be flux residue and flux removal after soldering is not recommended. Toshiba recommend that
soldering be performed without the optical module mounted on the board. Then, after the board has been
cleaned, the optical module should be soldered on to the board manually.
If the optical module cannot be soldered manually, use non-halogen (chlorine-free) flux and make sure,
without cleaning, there is no residue such as chlorine. This is one of the ways to eliminate the effects of
flux. In such a cases, be sure to check the devices' reliability.
Noise resistance
It is believed that the use of optical transfer devices improve noise resistance. In theory, optical fiber is not
affected by noise at all. However, receiving modules which handle signals whose level is extremely small,
are susceptible to noise.
TOSLINK improve noise resistance to use a conductive case. However, the current signal output by the
optical receiving modules' photodiode is extremely small. Thus, in some environments, shielding the case
may not achieve sufficient noise resistance.
First systems which incorporate TOSLINK, Toshiba recommend testing using the actual device to check its
noise resistance.
Use a simple noise filter on TOSLINK fiber optic transceiving module's power line. If the ripple in the
power supply used is significant, reinforce the filter.
The optical module is to be used in an area which is susceptible to radiated noise, increase the shielding by
covering the optical module and the power line filter with a metallic cover.
Vibration and shock
This module is plastic sealed and has its wire fixed by resin. This structure is relatively resistant to
vibration and shock. In actual equipment, there are sometime cases in which vibration, shock, or stress is
applied to soldered parts or connected parts, resulting in lines cut. A care must be taken in the design of
equipment which will be subject to high levels of vibration.
2 - f1.7 ± 0.05
2.61 typ.
(for reference)
2 - f1.1 ± 0.05
3 - f0.8 ± 0.05
2.625 typ.
3
Unit: mm
Recommended PCB thickness: 1.6 mm
TORX141P
2001-10-03