LM4857ITLX National Semiconductor, LM4857ITLX Datasheet - Page 28
LM4857ITLX
Manufacturer Part Number
LM4857ITLX
Description
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM4857ITLX.pdf
(37 pages)
Specifications of LM4857ITLX
Operational Class
Class-AB
Input Offset Voltage
40@5VmV
Single Supply Voltage (typ)
Not RequiredV
Dual Supply Voltage (typ)
3/5V
Supply Current (max)
21@5VmA
Power Supply Requirement
Dual
Rail/rail I/o Type
No
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
86dB
Single Supply Voltage (min)
Not RequiredV
Single Supply Voltage (max)
Not RequiredV
Dual Supply Voltage (min)
2.5/2.7V
Dual Supply Voltage (max)
5.5V
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
30
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LM4857ITLX
Manufacturer:
NationalS
Quantity:
15 280
Part Number:
LM4857ITLX
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LM4857ITLX/NOPB
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
33 000
www.national.com
Application Information
I
The LM4857 uses a serial bus, which conforms to the I
protocol, to control the chip’s functions with two wires: clock
(SCL) and data (SDA). The clock line is uni-directional. The
data line is bi-directional (open-collector). The maximum
clock frequency specified by the I
this discussion, the master is the controlling microcontroller
and the slave is the LM4857.
The I
ADR pin. The LM4857’s two possible I
of the form 111110X
low; and X
used to address a number of chips in a system, the
LM4857’s chip address can be changed to avoid any pos-
sible address conflicts.
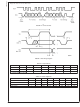
The bus format for the I
bus format diagram is broken up into six major sections:
The "start" signal is generated by lowering the data signal
while the clock signal is high. The start signal will alert all
devices attached to the I
dress against their own address.
The 8-bit chip address is sent next, most significant bit first.
The data is latched in on the rising edge of the clock. Each
address bit must be stable while the clock level is high.
After the last bit of the address bit is sent, the master
releases the data line high (through a pull-up resistor). Then
the master sends an acknowledge clock pulse. If the
LM4857 has received the address correctly, then it holds the
data line low during the clock pulse. If the data line is not
held low during the acknowledge clock pulse, then the mas-
ter should abort the rest of the data transfer to the LM4857.
The 8 bits of data are sent next, most significant bit first.
Each data bit should be valid while the clock level is stable
high.
After the data byte is sent, the master must check for another
acknowledge to see if the LM4857 received the data.
If the master has more data bytes to send to the LM4857,
then the master can repeat the previous two steps until all
data bytes have been sent.
The "stop" signal ends the transfer. To signal "stop", the data
signal goes high while the clock signal is high. The data line
should be held high when not in use.
I
The LM4857’s I
I
age level set by the I
dent to that of the main power supply pin V
whenever logic levels for the I
microcontroller or microprocessor that is operating at a lower
supply voltage than the main battery of a portable system.
NATIONAL 3D ENHANCEMENT
The LM4857 features a 3D audio enhancement effect that
widens the perceived soundstage from a stereo audio signal.
The 3D audio enhancement improves the apparent stereo
2
2
2
C COMPATIBLE INTERFACE
C INTERFACE POWER SUPPLY PIN (I
CV
DD
2
C address for the LM4857 is determined using the
pin. The LM4857’s I
1
= 1, if ADR is logic high. If the I
CD4
2
C interface is powered up through the
1
0 (binary), where X
2
CV
2
C interface is shown in Figure 2. The
2
DD
C bus to check the incoming ad-
2
pin which can be set indepen-
C interface operates at a volt-
2
C interface are dictated by a
2
C standard is 400kHz. In
2
C chip addresses are
1
= 0, if ADR is logic
TABLE 8. Earpiece Amplifier Gain Select
2
(Continued)
0
1
CV
DD
2
C interface is
DD
. This is ideal
)
2
C
28
channel separation whenever the left and right speakers are
too close to one another, due to system size constraints or
equipment limitations.
An external RC network, shown in Figure 1, is required to
enable the 3D effect. There are separate RC networks for
both the stereo loudspeaker outputs as well as the stereo
headphone outputs, so the 3D effect can be set indepen-
dently for each set of stereo outputs.
The amount of the 3D effect is set by the R
Decreasing the value of R
C
Increasing the value of C
frequency at which the 3D effect starts to occur, as shown by
Equation 1.
Activating the 3D effect will cause an increase in gain by a
multiplication factor of (1 + 9kΩ/R
result in a gain increase by a multiplication factor of (1+
9kΩ/9kΩ) = 2 or 6dB whenever the 3D effect is activated.
The volume control can be programmed through the I
compatible interface to compensate for the extra 6dB in-
crease in gain. For example, if the stereo volume control is
set at 0dB (11011 from Table 4) before the 3D effect is
activated, the volume control should be programmed to
–6dB (10111 from Table 4) immediately after the 3D effect
has been activated. Setting R
allows the LM4857 to produce a pronounced 3D effect with a
minimal increase in output noise.
EXPOSED-DAP MOUNTING CONSIDERATIONS
The LM4857’s exposed-DAP (die attach paddle) package
(SP) provides a low thermal resistance between the die and
the PCB to which the part is mounted and soldered. This
allows rapid heat transfer from the die to the surrounding
PCB copper area heatsink, copper traces, ground plane, and
finally, surrounding air. The result is a low voltage audio
power amplifier that produces 1.6W dissipation in a 4Ω load
at ≤ 1% THD+N and over 1.8W in a 3Ω load at 10% THD+N.
This high power is achieved through careful consideration of
necessary thermal design. Failing to optimize thermal design
may compromise the LM4857’s high power performance and
activate unwanted, though necessary, thermal shutdown
protection.
The SP package must have its DAP soldered to a copper
pad on the PCB. The DAP’s PCB copper pad is then, ideally,
connected to a large plane of continuous unbroken copper.
This plane forms a thermal mass, heat sink, and radiation
area. Place the heat sink area on either outside plane in the
case of a two-sided or multi-layer PCB. (The heat sink area
can also be placed on an inner layer of a multi-layer board.
The thermal resistance, however, will be higher.) Connect
the DAP copper pad to the inner layer or backside copper
heat sink area with 9 (3 X 3) (SP) vias. The via diameter
should be 0.012in - 0.013in with a 1.27mm pitch. Ensure
efficient thermal conductivity by plugging and tenting the vias
with plating and solder mask, respectively.
3D
0dB Earpiece Output Stage Gain Setting
6dB Earpiece Output Stage Gain Setting
capacitor sets the low cutoff frequency of the 3D effect.
f
3D(-3dB)
= 1 / 2π(R
3D
3D
will increase the 3D effect. The
3D
will decrease the low cutoff
3D
= 20kΩ and C
3D
). Setting R
)(C
3D
)
3D
3D
3D
to 9kΩ will
= 0.22µF
resistor.
(1)
2
C