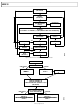
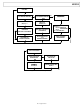
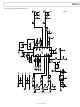
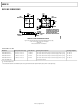
EVAL-AD9838SDZ Analog Devices Inc, EVAL-AD9838SDZ Datasheet - Page 24

EVAL-AD9838SDZ
Manufacturer Part Number
EVAL-AD9838SDZ
Description
EVALUATION BOARD
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Series
-r
Specifications of EVAL-AD9838SDZ
Main Purpose
Timing, Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS)
Embedded
No
Utilized Ic / Part
AD9838
Primary Attributes
USB Powered or External Supply
Secondary Attributes
SPI Interface
Kit Application Type
Clock & Timing
Application Sub Type
Clock Generator
Kit Contents
Software CD, USB Cable
Silicon Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Silicon Core Number
AD9838
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
AD9838
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The various output options available from the AD9838 make
the part suitable for a wide variety of applications, including
modulation applications. The AD9838 can be used to perform
simple modulation, such as frequency shift keying (FSK). More
complex modulation schemes, such as Gaussian minimum shift
keying (GMSK) and quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK), can
also be implemented using the AD9838.
In an FSK application, the two frequency registers of the AD9838
are loaded with different values. One frequency represents the
space frequency, and the other represents the mark frequency. The
digital data stream is fed to the FSELECT pin, causing the AD9838
to modulate the carrier frequency between the two values.
The AD9838 has two phase registers, enabling the part to per-
form phase shift keying (PSK). With PSK, the carrier frequency
is phase shifted, that is, the phase is altered by an amount that
is related to the bit stream input to the modulator.
The AD9838 is also suitable for signal generator applications.
Using the on-board comparator, the device can be used to gen-
erate a square wave.
With its low current consumption, the part is also suitable for
applications in which it can be used as a local oscillator.
GROUNDING AND LAYOUT
The printed circuit board that houses the AD9838 should be
designed so that the analog and digital sections are separated
and confined to certain areas of the board. This facilitates the use
of ground planes that can be separated easily. A minimum etch
technique is generally best for ground planes because it provides
the best shielding. Digital and analog ground planes should be
joined in one place only. If the AD9838 is the only device that
requires an AGND to DGND connection, the ground planes
should be connected at the AGND and DGND pins of the
AD9838. If the AD9838 is in a system where multiple devices
require AGND to DGND connections, the connection should
be made at one point only, a star ground point that should be
established as close as possible to the AD9838.
Avoid running digital lines under the device; these lines couple
noise onto the die. The analog ground plane should be allowed
to run under the AD9838 to avoid noise coupling. The power
supply lines to the AD9838 should use as large a track as possible
to provide low impedance paths and reduce the effects of glitches
on the power supply line. Fast switching signals, such as clocks,
should be shielded with digital ground to avoid radiating noise
to other sections of the board.
Rev. A | Page 24 of 32
Avoid crossover of digital and analog signals. Traces on opposite
sides of the board should run at right angles to each other to
reduce the effects of feedthrough through the board. A micro-
strip technique is by far the best but is not always possible with
a double-sided board. In this technique, the component side of
the board is dedicated to ground planes and signals are placed
on the other side.
Good decoupling is important. The analog and digital supplies
to the AD9838 are independent and separately pinned out to
minimize coupling between the analog and digital sections of the
device. All analog and digital supplies should be decoupled to
AGND and DGND, respectively, with 0.1 μF ceramic capacitors
in parallel with 10 μF tantalum capacitors. To achieve the best
performance from the decoupling capacitors, they should be
placed as close as possible to the device, ideally right up against
the device.
In systems where a common supply is used to drive both the
AVDD and DVDD pins of the AD9838, it is recommended that
the system’s AVDD supply be used. This supply should have the
recommended analog supply decoupling between the AVDD
pin of the AD9838 and AGND, as well as the recommended
digital supply decoupling capacitors between the DVDD pin
and DGND.
Proper operation of the comparator requires good layout strategy.
The layout must minimize the parasitic capacitance between V
and the SIGN BIT OUT pin by using a ground plane to add
isolation. For example, in a multilayered board, the V
can be connected to the top layer, and the SIGN BIT OUT pin
can be connected to the bottom layer. In this way, isolation is
provided by the power and ground planes between V
SIGN BIT OUT pin.
INTERFACING TO MICROPROCESSORS
The AD9838 has a standard serial interface that allows the part to
interface directly with several microprocessors. The device uses
an external serial clock to write the data or control information
into the device. The serial clock can have a frequency of 40 MHz
maximum. The serial clock can be continuous, or it can idle high
or low between write operations. When data or control informa-
tion is written to the AD9838, FSYNC is taken low and is held
low until the 16 bits of data are written into the AD9838. The
FSYNC signal frames the 16 bits of information that are loaded
into the AD9838.
IN
IN
and the
signal
IN