MT9076AB Mitel, MT9076AB Datasheet

MT9076AB
Related parts for MT9076AB
MT9076AB Summary of contents
Page 1
... ST-BUS CSTo Interface RxDLCLK RxDL T1/E1/J1 3.3V Single Chip Transceiver DS5289 MT9076AP MT9076AB Description The MT9076 is a highly featured single chip solution for terminating T1/E1/J1 trunks. It contains a long- haul LIU, an advanced framer, a high performance PLL, and 3 HDLCs mode, the MT9076 supports D4, ESF and SLC-96 formats meeting the latest recommendations including AT& ...
Page 2
MT9076 CS RESET IRQ VSS5 IC4 INT/MOT VDD5 R/W/WR AC0 RESET IRQ VSS5 IC4 INT/MOT VDD5 R/W/WR AC0 ...
Page 3
Preliminary Information Pin Description Pin # Name PLCC LQFP 1 51 OSC1 Oscillator (3V Input). This pin is either connected via a 20.000 MHz crystal to OSC2 where a crystal is used directly driven when a 20.000 MHz. ...
Page 4
MT9076 Pin Description (continued) Pin # Name PLCC LQFP 19 72 INT/MOT Intel/Motorola Mode Selection (5V tolerant Input). A high on this pin configures the processor interface for the Intel parallel non-multiplexed bus type. A low configures the processor interface ...
Page 5
Preliminary Information Pin Description (continued) Pin # Name PLCC LQFP 42 17 RxMF/ Receive Multiframe Boundary / Transmit Frame Boundary (5V tolerant Output). If TxFP the control bit Tx8KEN (page 02H address 10H bit 2) is low, this negative output ...
Page 6
MT9076 Pin Description (continued) Pin # Name PLCC LQFP 61 43 LOS Loss of Signal or Synchronization (5V tolerant Output). When high, and LOS/LOF (page 01H address 19H bit 0) is zero, this signal indicates that the receive portion of ...
Page 7
Preliminary Information LIU The MT9076 LIU interfaces the digital framer functions to either the DS1 (T1 mode) or PCM 30 (E1 mode) transformer-isolated four wire line mode, the LIU can pre-equalize the transmit signal to meet the T1.403 ...
Page 8
MT9076 Access to the Maintenance Channel The T1 ESF Facility Data Link (FDL) bits can be accessed in the following three ways: Through the data link pins TxDL, RxDL, RxDLC and TxDLC; through internal registers for Bit Oriented Messages; through ...
Page 9
Preliminary Information MT9076 Detailed Feature List Standards Compliance and Support T1/J1 Mode ANSI: T1.102,T1.231, T1.403, T1.408 AT&T: TR 62411, PUB43801 Telcordia: GR-303-CORE TTC: JT-G703, JT-G704, JT-G706 Line Interface Unit (LIU) • T1 and E1 modes use the same 1:2.4 transmit ...
Page 10
MT9076 Digital Framer Mode • The LIU can be disabled and bypassed to allow the MT9076 to be used as a digital framer • Single phase NRZ or two phase NRZ modes are software selectable • Line coding is software ...
Page 11
Preliminary Information Data Link T1/J1 Mode • Three methods are provided to access the datalink: 1. TxDL and RxDL pins support receive datalinks 2. Bit Oriented Messages are supported via internal registers 3. An internal HDLC can be assigned to ...
Page 12
MT9076 T1/J1 Mode HDLC0 • Assignable to the ESF Facility Data Link or any channel • Operates at 4 kbps, 56 kbps or 64 kbps HDLC1, HDLC2 • Assignable to any channel • Operates at 56 kbps or 64 kbps ...
Page 13
Preliminary Information Framing Algorithm T1/J1 Mode • Synchronizes with D4 or ESF protocols • Supports SLC-96 framing • Framing circuit is off-line • Transparent transmit and receive modes • mode the Fs bits can optionally be cross checked ...
Page 14
MT9076 Channel Associated Signaling • ABCD or AB bits can be automatically inserted and extracted • Transmit ABCD or AB bits can be passed via the microport or via the CSTi pin • Receive ABCD or AB bits are accessible ...
Page 15
Preliminary Information Maskable Interrupts T1/J1 Mode • Change of state of terminal synchronization • Change of state of multiframe synchronization • Change of received bit oriented message • Change of state of reception of AIS • Change of state of ...
Page 16
MT9076 Error Counters • All counters can be preset or cleared under software control • Maskable occurrence interrupt • Maskable overflow interrupt • Counters can be latched on one second intervals T1/J1 Mode • PRBS Error Counter (16-bit) • CRC ...
Page 17
MT9076 Line Interface Unit (LIU).................................................................................. 17 1.1 Receiver .................................................................................................................................................17 1.2 Transmitter .............................................................................................................................................18 1.3 20 Mhz Clock..........................................................................................................................................21 1.4 Phase Lock Loop (PLL)..........................................................................................................................22 2.0 Clock Jitter Attenuation Modes.................................................................................... 23 2.1 Jitter Attenuator FIFO.............................................................................................................................24 2.2 IMA Mode ...............................................................................................................................................24 2.2.1 T1 Mode ......................................................................................................................................... ...
Page 18
MT9076 8.2.5 Interframe Time Fill and Link Channel States ................................................................................ 37 8.2.6 Go-Ahead ....................................................................................................................................... 37 8.3 HDLC Functional Description .................................................................................................................37 8.3.1 HDLC Transmitter........................................................................................................................... 37 8.3.2 HDLC Receiver............................................................................................................................... 38 9.0 Slip Buffers .................................................................................................................... 40 9.1 Slip Buffer in T1 Mode............................................................................................................................40 9.2 ...
Page 19
Error Insertion................................................................................................................ 52 15.0 Per Time Slot Control Words ........................................................................................ 52 15.1 Clear Channel Capability........................................................................................................................52 15.2 Microport signaling .................................................................................................................................52 15.3 Per Time Slot Looping............................................................................................................................52 15.4 PRBS Testing.........................................................................................................................................53 15.5 Digital Milliwatt........................................................................................................................................53 15.6 Per Channel Inversion............................................................................................................................53 15.7 Transmit Message..................................................................................................................................54 16.0 Alarms ...
Page 20
MT9076 20.3.1 Master Control 1 (Page 01H) (E1).................................................................................................. 92 20.4 Master Control 2 (Page-2)....................................................................................................................103 20.4.1 Master Control 2 (Page 02H) (E1)................................................................................................ 103 20.5 Master Status 1 (Page03H) (E1) ..........................................................................................................109 20.6 Master Status 1 (Page03H) (E1) ..........................................................................................................110 21.0 Master Status 2 ...
Page 21
Preliminary Information 1.0 MT9076 Line Interface Unit (LIU) 1.1 Receiver The receiver portion of the MT9076 LIU consists of an input signal peak detector, an optional equalizer with separate high pass sections, a smoothing filter, data and clock slicers and ...
Page 22
MT9076 Peak to Peak Jitter Amplitude (log scale) 18UI 1.5UI 0.2UI 1.667Hz Figure 4 - Input Jitter Tolerance as Recommended by G.823 and ETSI 300 011 (E1) 1.2 Transmitter The transmit portion of the MT9076 LIU consists of a high ...
Page 23
Preliminary Information 0.47 TTIP R T TRING +3.3 V RTIP 17.36 RRING Name TXL2-0 Transmit Line Build Out Setting these bits shapes the transmit pulse as detailed in the table below: TXL2 0 0 ...
Page 24
MT9076 Name WR Winding Ratio. Set this pin low if a 1:2.4 transformer is used on the transmit side. Set this pin high if a 1:2 transformer is used. TX2-0 Transmit pulse amplitude. Select the TX2 –TX0 bits according to ...
Page 25
Preliminary Information Time (Nanoseconds) -499 -253 -175 -175 -78 Time U.I. -.77 Normalized Amplitude .05 Time (Nanoseconds) -499 -149 -149 -97 Time U.I. -.77 Normalized Amplitude -.05 Percentage of Nominal Peak Voltage 120 110 100 ...
Page 26
MT9076 Alternatively, a crystal oscillator may be used. A complete oscillator circuit made crystal, resistors and capacitors is shown in Figure 10. The crystal specification is as follows. Frequency: Tolerance: Oscillation Mode: Resonance Mode: Load Capacitance: Maximum ...
Page 27
Preliminary Information dB -0.5 0 19.5 10 Figure 62411 Jitter Attenuation Curve 2.0 Clock Jitter Attenuation Modes MT9076 has three basic jitter attenuation modes of operation, selected by the BS/LS and S/FR/Exclki control pins. • System Bus ...
Page 28
MT9076 In Line Synchronous mode, the clock extracted from the receive data is dejittered using the internal PLL • and then output on pin C4b. Pin Exclk provides the extracted receive clock before it has been dejittered. The transmit data ...
Page 29
... Preliminary Information It should be noted that the Mitel ST-BUS has 32 channels numbered 0 to 31. When mapping to the DS1 payload only the first 24 time slots and the last (time slot 31, for the overhead bit ST-BUS are used (see Table 6). All unused channels are tristate. ...
Page 30
MT9076 (i) It may free - run with the internal multiframe counters; (ii) The multiframe counters may be reset with the external hardware pin TxMF. If this signal is not synchronous with the current transmit frame count it may cause ...
Page 31
... This results in a single time slot data rate of 8 bits x 8000/sec kbits/sec. It should be noted that the Mitel ST-BUS also has 32 channels numbered 0 to 31, but the most significant bit of an eight bit channel is numbered bit 7 (see Mitel Application Note MSAN-126). Therefore, ST-BUS bit 7 is synonymous with PCM 30 bit 1 ...
Page 32
MT9076 3.3.1 Basic Frame Alignment Time slot 0 of every basic frame is reserved for basic frame alignment and contains either a Frame Alignment Signal (FAS Non-Frame Alignment Signal (NFAS). FAS and NFAS occur in time slot zero ...
Page 33
Preliminary Information 3.3.2 CRC-4 Multiframing in E1 mode The primary purpose for CRC-4 multiframing is to provide a verification of the current basic frame alignment, although it can also be used for other functions such as bit error rate estimation. ...
Page 34
MT9076 AUTC ARAI TALM Automatic CRC-interworking is activated valid CRC MFAS is being received, transmit RAI will flicker high with every reframe (8msec.), this cycle will continue for 400 msec., then transmit RAI will be ...
Page 35
Preliminary Information 4.2 Control and Status Register Access The controlling microprocessor gains access to specific registers of the MT9076 through a two step process. First, writing to the Command/Address Register (CAR) selects one of the 15 pages of control and ...
Page 36
MT9076 Per Time Slot Control word bit 1 "RPSIG" is set low, CSTi is used to control the transmit channel associated signaling. The DSTi and DSTo streams contain the transmit and receive voice and digital data. Only 30 of the ...
Page 37
Preliminary Information 6.0 Transmit Data All Ones (TxAO) Operation The TxAO (Transmit all ones) pin allows the PRI interface to transmit an all ones signal under hardware control. 7.0 Data Link Operation 7.1 Data Link Operation in E1 mode In ...
Page 38
MT9076 Octet # ...
Page 39
Preliminary Information 7.2.1 External Data Link In T1 mode, MT9076 has two pairs of pins (TxDL and TxDLCLK, RxDL and RxDLCLK) dedicated to transmitting and receiving bits in the selected overhead bit positions. Pins TxDLCLK and RxDLCLK are clock outputs ...
Page 40
MT9076 8.2 HDLC Description The HDLC handles the bit oriented packetized data transmission as per X.25 level two protocol defined by CCITT. It provides flag and abort sequence generation and detection, zero insertion and deletion, and Frame Check Sequence (FCS) ...
Page 41
Preliminary Information 8.2.4 Frame Abort The transmitter will abort a current packet by substituting a zero followed by seven contiguous 1s in place of the normal packet. The receiver will abort upon reception of seven contiguous 1s occurring between the ...
Page 42
MT9076 the TX FIFO. The Transmit Byte Count Registers may also be used to tag an end of packet. The total packet size may be programmed 65,535 bytes. For a packet length 255 ...
Page 43
Preliminary Information dual byte address is being received. If this bit is 0 then a two byte address is being received and then only the first six bits of the first address byte are compared. An all call condition is ...
Page 44
MT9076 9.0 Slip Buffers 9.1 Slip Buffer in T1 Mode In T1 mode, MT9076 contains two slip buffers, one on the transmit side, and one on the receive side. Both sides may perform a controlled slip. The mechanisms that govern ...
Page 45
Preliminary Information boundary is measured every frame and reported in the Transmit Slip Buffer Delay register- (page 3H, address 17H). In addition the relative offset between these frame boundaries may be programmed by writing to this register. Every write to ...
Page 46
MT9076 0 uS Write Pointer Read Pointer 4 uS Read Pointer 221 uS 512 Bit Elastic 188 uS Store 129 uS Read Pointer Read Pointer Read Vectors Frame 0 Minimum Delay Write Vectors Frame 0 Read Vectors - Maximum Delay ...
Page 47
Preliminary Information The minimum delay through the receive slip buffer is approximately two channels and the maximum delay is approximately 60 channels (see Figure 14). When the C4b and the Exclk clocks are not phase-locked, the rate at which data ...
Page 48
MT9076 Word, page 1H, address 10H), multiframe alignment is forced at the same time as terminal frame alignment. If only Ft bits are checked, multiframe alignment is forced separately, upon detection of the Fs bit history of 00111 (for normal ...
Page 49
Preliminary Information >914 CRC errors in one second No CRC multiframe alignment. 8 msec. timer expired* CRC-4 multi-frame alignment Start 400 msec timer. Note 7. Start 8 msec timer. Note 7. Find two CRC frame alignment signals. Note 7. CRC ...
Page 50
MT9076 10.2.1 Notes for Synchronization State Diagram (Figure 16) 1) The basic frame alignment, signaling multiframe alignment, and CRC-4 multiframe alignment functions operate in parallel and are independent. 2) The receive channel associated signaling bits and signaling multiframe alignment bit ...
Page 51
Preliminary Information ram. The transmit AB/ ABCD signaling nibbles can be passed either via the micro-ports (for channels with bit 1 set high in the Per Time Slot Control Word - pages 7H and 8H) or through related channels of ...
Page 52
MT9076 12.0 Loopbacks In order to meet PRI Layer 1 requirements and to assist in circuit fault sectioning, the MT9076 has six loopback functions. These are as follows: a) Digital loopback (DSTi to DSTo at the framer/LIU interface). Bit DLBK ...
Page 53
Preliminary Information 13.0 Performance Monitoring 13.1 Error Counters In T1 mode, MT9076 has eight error counters, which can be used for maintenance testing and ongoing measurement of the quality of a DS1 link and to assist the designer in meeting ...
Page 54
MT9076 There is one interrupt associated with the Out of Frame counter. A counter overflow interrupt may be enabled by setting control bit OOFO high - bit 5 of Interrupt Mask Word Two (page 1H, address 1DH). 13.2.3 Multiframes out ...
Page 55
Preliminary Information There are two maskable interrupts associated with the frame alignment signal error measurement. FERI (page 01H, address 1CH) is initiated when the least significant bit of the errored frame alignment signal counter toggles, and FERRO (page 01H, address ...
Page 56
MT9076 14.0 Error Insertion In T1 mode, six types of error conditions can be inserted into the transmit DS1 data stream through control bits, which are located on page 1, address 19H - Error Insertion Word. These error events include ...
Page 57
Preliminary Information 15.4 PRBS Testing If the control bit ADSEQ is zero (from master control page 1 - access control word), any channel or combination of transmit channels may be programmed to contain a generated pseudo random bit sequence (2 ...
Page 58
MT9076 15.7 Transmit Message When bit seven (TXMSG) in the Per Time Slot Control Word is set the data transmit in the selected channel is sourced from the transmit message word in Master Control page 1. 16.0 Alarms The following ...
Page 59
Preliminary Information 17.0 Detected Events 17.1 T1 mode 17.1.1 Severely Errored Frame Event In T1 mode, bit 5 page 3H address 10H toggles whenever a sliding window detects 2 framing errors events (Ft or ESF sliding window of ...
Page 60
MT9076 All the interrupts of the MT9076 in T1 and E1 mode are maskable. This is accomplished through interrupt mask words zero to three, which are located on page 1, addresses 1BH to 1EH and the (optional) HDLC interrupt mask ...
Page 61
Preliminary Information Interrupt Mask Word Three Bit JAI 1SECI 5SECI RCRI HDLC Interrupt Masks Bit 7 Ga EOPD TEOP EopR TxFl 19.0 Digital Framer Mode 19.1 T1 Mode Setting bit ...
Page 62
MT9076 20.0 Control and Status Registers 20.1 T1 Mode 20.1.1 Master Control 1 (Page 01H) (T1) Address ( 10H (Table 21) Framing Mode Select 11H (Table 22) Transmit Alarm Control ...
Page 63
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 ESF Extended Super Frame. Setting this bit enables transmission and reception of the 24 frame superframe DS1 protocol. 6 SLC96 SLC96 Mode Select. Setting this bit enables input and output of the Fs bit pattern ...
Page 64
MT9076 Bit Name 7 ESFYEL ESF Yellow Alarm. Setting this bit while in ESF mode causes a repeating pattern of eight 1’s followed by eight 0’ insert onto the transmit FDL (Japan Telecom bit set low - see ...
Page 65
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 EDL Enable Data Link. Setting this bit multiplexes the serial stream clocked in on pin TxDL into the FDL bit position (ESF mode) or the Fs position (D4 mode). 6 BIOMEn Bit Oriented Messaging Enable. ...
Page 66
MT9076 Bit Name 7 DSToEn DSTo Enable. If zero pin DSTo is tristate. If set the pin DSTo is enabled. 6 CSToEn CSTo Enable. If zero pin CSTo is tristate. If set the pin CSTo is enabled. 5 RBEn Robbed ...
Page 67
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7-0 TxSD7-0 Transmit Set Delay Bits 7-0. Writing to this register forces a one time setting of the delay through the transmit slip buffer. The delay is defined as the time interval between the write of ...
Page 68
MT9076 Bit Name 7 RST Software reset. Setting this bit is equivalent to performing a hardware reset. All counters are cleared and the control registers are set to their default values. This control bit is internally cleared after the reset ...
Page 69
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 TFSYNIM Terminal Frame Synchronization Interrupt Mask. When unmasked an interrupt is initiated whenever a change of state of loss of terminal frame synchronization condition exists unmasked masked. 6 MFSYNIM Multiframe ...
Page 70
MT9076 Bit Name 7 FEOM Framing Bit Error Counter Overflow Interrupt Mask. When unmasked an interrupt is initiated whenever the framing bit error counter changes from FFH to 00H unmasked masked. 6 CRCOM CRC-6 Error ...
Page 71
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 HDLC0IM HDLC0 Interrupt Mask. When unmasked an interrupt is triggered by an unmasked event in HDLC0 unmasked masked. 6 HDLC1IM HDLC1 Interrupt Mask. When unmasked an interrupt is triggered by ...
Page 72
MT9076 Bit Name 7 NRZ NRZ Format Selection. Only used in the digital framer only mode (LIU is disabled). A one sets the MT9076 to accept a unipolar NRZ format input stream on RxA as the line input, and to ...
Page 73
Preliminary Information 20.1.2 Master Control 2 (Page 02H) (T1) Address ( 10H (Table 37) Configuration Control Word 11H (Table 38) LIU Tx Word 12H Reserved 13H (Table 39) Jitter Attenuator ...
Page 74
MT9076 Bit Name 7 T1/E1 T1/E1 mode selection. when this bit is zero, the device mode. When set high, the device mode Reserved. Must be kept at 0 for normal operation. 5 ...
Page 75
Preliminary Information Bit Name Unused. 6 JFC Jitter Attenuator FIFO Centre. When this bit is toggled the read pointer on the jitter attenuator shall be centered. During this centering the jitter on the JA outputs is ...
Page 76
... Inverse Mux Mode. Setting this bit high the I/O ports to allow for easy connection to the Mitel MT90220. DSTi becomes a serial 1.544 data stream. C4b becomes a 1.544 MHz clock that clocks DSTi in on the falling edge. RXFP becomes a positive framing pulse that is high for the fi ...
Page 77
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 En Enable. Set high to attach the HDLC1 controller to the channel specified below. Set low to disconnect the HDLC1. 6-5 -- Reserved. Must be kept at 0 for normal operation. 4-0 CH4-0 Channel 4-0. ...
Page 78
MT9076 Bit Name Reserved. Must be kept at 0 for normal operation. 6-0 CP6-0 Custom Pulse. These bits provide the capability for programming the magnitude setting for the TTIP/TRING line driver A/D converter during the third phase ...
Page 79
Preliminary Information 20.1.3 Master Status 1 (Page03H) (T1) Address ( 10H (Table 52) Synchronization Status Word 11H (Table 53) Alarm Status Word 12H (Table 54) Timer Status Word 13H (Table ...
Page 80
MT9076 Bit Name 7 TFSYNC Terminal Frame Synchronization. Indicates the Terminal Frame Synchronization status (1 - loss acquired). For ESF links terminal frame synchronization and multiframe synchronization are synonymous. 6 MFSYNC Multiframe Synchronization. Indicates the Multiframe Synchronization status ...
Page 81
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 1SEC One Second Timer Status. This bit changes state once every 0.5 seconds. 6 2SEC Two Second Timer Status. This bit changes state once every second and is synchronous with the 1SEC timer. 5 5SEC ...
Page 82
MT9076 Bit Name 7 LLOS LIU Loss of Signal indication. This bit will be high when the received signal is less than 40 dB below the nominal value for a period of at least 1 msec. This bit will be ...
Page 83
Preliminary Information Bit Name ESP7-0 Analog Peak. This status register gives the output value bit A/D converter connected to a peak detector on RTIP/RRING. Table 61 - Equalized Signal Peak Detect Bit Name 7-0 ...
Page 84
MT9076 20.1.4 Master Status 2 (Page04H) (T1) Address ( 10H (Table 65) PRBS Error Counter 11H (Table 66) CRC Multiframe counter for PRBS 12H (Table 67) Alarm Reporting Latch 13H ...
Page 85
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 D4YALML D4 Yellow Alarm Latch. This bit is set yellow alarm is detected within a 600 millisecond integration period cleared after a read. 6 D4Y48L D4 Yellow Alarm (48 milliseconds) ...
Page 86
MT9076 Bit Name OOF3 - 0 Out Of Frame Counter. This four bit counter is incremented with every loss of receive frame synchronization COFA3 - 0 Change of Frame Alignment Counter. This four bit ...
Page 87
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 TFSYNI Terminal Frame Synchronization Interrupt. When unmasked this interrupt bit goes high whenever a change of state of terminal frame synchronization condition exists. Reading this register clears this bit. 6 MFSYNI Multiframe Synchronization Interrupt. When ...
Page 88
MT9076 Bit Name 7 FEI Framing Bit Error Interrupt. When unmasked this interrupt bit goes high whenever an erroneous framing bit is detected (provided the circuit is in terminal frame sync). Reading this register clears this bit. 6 CRCI CRC-6 ...
Page 89
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 FEO Framing Bit Error Counter Overflow Interrupt. When unmasked this interrupt bit goes high whenever the framing bit error counter changes from FFH to 00H. Reading this register clears this bit. 6 CRCO CRC-6 Error ...
Page 90
MT9076 Bit Name 7 HDLC0I HDLC0 Interrupt. Whenever an unmasked HDLC0 interrupt occurs this bit goes high. Reading this register clears this bit. 6 HDLC1I HDLC1 Interrupt. Whenever an unmasked HDLC1 interrupt occurs this bit goes high. Reading this register ...
Page 91
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 FEOL Framing Bit Error Counter Overflow Latch. This bit is set when the framing bit counter overflows cleared after being read. 6 CRCOL CRC-6 Error Counter Overflow Latch. This bit is set when ...
Page 92
MT9076 20.1.5 Per Channel Transmit signaling (Pages 5 and 6) (T1) Page 05H, addresses 10000 to 11111, and page 06H addresses 10000 to 10111 contain the Transmit signaling Control Words for DS1 channels and ...
Page 93
Preliminary Information Bit Name A(n), Transmit signaling Bits for Channel n. When control bit MSN = 1 and RPSIG = 1 this nibble is used. For ESF links these 4 bits are transmitted on the associated DS1 ...
Page 94
MT9076 20.2 Per Time Slot Control Words (Pages 7 and 8) (T1) The control functions described by Table 80 are repeated for each DS1 time slot. Page 7 addresses 10000 to 11111 correspond to DS1 time slot 1 to 16, ...
Page 95
Preliminary Information 20.2.1 Per Channel Receive signaling (T1 and E1 mode) (Pages 9 and 0AH) Page 09H, addresses 10000 to 11111, and page 1AH addresses 10000 to 10111 contain the Receive signaling Control Words for DS1 channels ...
Page 96
MT9076 20.3 E1 Mode 20.3.1 Master Control 1 (Page 01H) (E1) Address ( 10H (Table 88) Mode Selection Control Word 11H (Table 89) Transmit Alarm Control Word 12H (Table 90) ...
Page 97
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 ASEL AIS Select. This bit selects the criteria on which the detection of a valid Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) is based. If zero, the criteria is less than three zeros in a two frame period ...
Page 98
MT9076 Bit Name Reserved. Must be kept at 0 for normal operation Transmit E bits. When zero and CRC-4 synchronization is achieved, the E-bits transmit the received CRC-4 comparison results to the distant end of ...
Page 99
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7-4 TMA1-4 Transmit Multiframe Alignment Bits One to Four. These bits are transmitted on the PCM 30 2048 kbit/sec. link in bit positions one to four of time slot 16 of frame zero of every signaling ...
Page 100
MT9076 Bit Name 7 RxHDB3 High Density Bipolar 3 Encoding. If one, HDB3 encoding is enabled in the receive direction. If zero, AMI signal without HDB3 encoding is received. 6 MLBK Metallic Loopback. If one, then the external RRTIP and ...
Page 101
Preliminary Information Bit Name Unused 6 MFSEL Multiframe Select. This bit determines which receive multiframe signal (CRC-4 or signaling) the RxMF (pin 42 in PLCC MQFP) signal is aligned with. If zero, RxMF is ...
Page 102
MT9076 Bit Name 7 BPVE Bipolar Violation Error Insertion. A zero to one transition of this bit inserts a single bipolar violation error into the transmit PCM 30 data. A one, zero or one to zero transition has no function. ...
Page 103
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 RST Reset. When this bit is changed from zero to one the device will reset to its default mode. See the Reset Operation section for the default settings. 6 SPND Suspend Interrupts. If one, the ...
Page 104
MT9076 Bit Name 7 SYNIM Synchronization Interrupt Mask. When unmasked (SYNI = 1) an interrupt is initiated whenever a change of state of loss of basic frame synchronization condition exists unmasked masked. 6 MFSYIM Multiframe Synchronization ...
Page 105
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 FEOM Frame Alignment Signal Error Counter Overflow Interrupt Mask. When unmasked an interrupt is initiated when the frame alignment signal error counter overflows unmasked masked. 6 CRCOIM CRC-4 Error Counter ...
Page 106
MT9076 Bit Name 7 HDLC0IM HDLC0 Interrupt Mask. When unmasked an interrupt is triggered by an unmasked event in HDLC0 unmasked masked. 6 HDLC1IM HDLC1 Interrupt Mask. When unmasked an interrupt is triggered by an ...
Page 107
Preliminary Information 20.4 Master Control 2 (Page-2) 20.4.1 Master Control 2 (Page 02H) (E1) Address ( 10H (Table 105) Configuration Control Word 11H (Table 106) LIU Tx Word 12H Reserved ...
Page 108
MT9076 Bit Name 7 T1/E1 E1 mode selection. when this bit is one, the device mode Reserved. Must be kept at 0 for normal operation. 5 TxEN Transmit Enable. Setting this bit low turns ...
Page 109
Preliminary Information Bit Name Unused. 6 JFC Jitter Attenuator FIFO Centre. When this bit is toggled the read pointer on the jitter attenuator shall be centered. During this centering the jitter on the JA outputs is ...
Page 110
... Inverse Mux Mode. Setting this bit high the I/O ports to allow for easy connection to the Mitel MT90220. DSTi becomes a serial 2.048 data stream. C4b becomes a 2.048 MHz clock that clocks DSTi in on the falling edge. RXFP becomes a positive framing pulse that is high for the fi ...
Page 111
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 En Enable. Set high to attach the HDLC1 controller to the channel specified below. Set low to disconnect the HDLC1. 6 Reserved. Must be kept at 0 for normal operation. 4-0 CH4-0 Channel ...
Page 112
MT9076 Bit Name Reserved. Must be kept at 0 for normal operation. 6-0 CP6-0 Custom Pulse. These bits provide the capability for programming the magnitude setting for the TTIP/TRING line driver A/D converter during the third phase ...
Page 113
Preliminary Information 20.5 Master Status 1 (Page03H) (E1) Address ( 12H (Table 119) Timer Status Word 13H (Table 120) Most Significant Phase Status Word 14H (Table 121) Least Significant Phase ...
Page 114
MT9076 20.6 Master Status 1 (Page03H) (E1) Bit Name 7 SYNC Receive Basic Frame Alignment. SYNC indicates the basic frame alignment status (1 - loss acquired). 6 MFSYNC Receive Multiframe Alignment. MFSYNC indicates the multiframe alignment status (1 ...
Page 115
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 CRCS1 Receive CRC Error Status One. If one, the evaluation of the last received submultiframe 1 resulted in an error. If zero, the last submultiframe 1 was error free. Updated on a submultiframe 1 basis. ...
Page 116
MT9076 Bit Name 7 1SEC One Second Timer Status. This bit changes state once every 0.5 second and is synchronous with the 2SEC timer. This feature is not available when the device is operated in freerun mode. 6 2SEC Two ...
Page 117
Preliminary Information Bit Name RxTS4 - 0 Receive Time Slot. A five bit counter that indicates the number of time slots between the receive elastic buffer internal write frame boundary and the ST-BUS read frame boundary. The ...
Page 118
MT9076 Bit Name 7 JACS Jitter Attenuated Clock Slow. If one it indicates that the dejittered clock period is increased by 1/16 UI. If zero the clock is at normal speed. 6 JACF Jitter Attenuated Clock Fast. If one it ...
Page 119
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7-4 RMAI1-4 Receive Multiframe Alignment Bits One to Four. These bits are received on the PCM 30 2048 kbit/sec. link in bit positions one to four of time slot 16 of frame zero of every signaling ...
Page 120
MT9076 Bit Name 7 RAIS Remote Alarm Indication Status. If one, there is currently a remote alarm condition (i.e., received A bit is one). If zero, normal operation. Updated on a non-frame alignment frame basis. 6 AISS Alarm Indication Status ...
Page 121
Preliminary Information 21.0 Master Status 2 (Page-4) 21.1 Master Status 2 (Page 04H) (E1) Address ( 10H (Table 134) PRBS Error Counter 11H (Table 135) CRC Multiframe counter for PRBS ...
Page 122
MT9076 Bit Name 7 RAI Remote Alarm Indication. This bit is set to one in the event of receipt of a remote alarm, i.e. A(RAI cleared when the register is read. 6 AIS Alarm Indication Signal. ...
Page 123
Preliminary Information Bit Name LCV7 - 0 Least Significant Bits of the LCV Counter. The least significant eight bits bit counter that is incremented once for every line code violation received. A line code ...
Page 124
MT9076 Bit Name 7 TFSYNI Terminal Frame Synchronization Interrupt. When unmasked this interrupt bit goes high whenever a change of state of terminal frame synchronization condition exists. Reading this register clears this bit. 6 MFSYNI Multiframe Synchronization Interrupt. When unmasked ...
Page 125
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 FERRI Errored Framing Alignment Signal Interrupt. When unmasked this interrupt bit goes high whenever an erroneous bit in frame alignment signal is detected (provided the circuit is in terminal frame sync). Reading this register clears ...
Page 126
MT9076 Bit Name 7 FERRO Errored Framing Alignment Signal Counter Overflow Interrupt. When unmasked this interrupt bit goes high whenever the errored frame alignment signal counter changes from FFH to 00H. Reading this register clears this bit. 6 CRCO CRC ...
Page 127
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 HDLC0I HDLC0 Interrupt. Whenever an unmasked HDLC0 interrupt occurs, this bit goes high. Reading this register clears this bit. 6 HDLC1I HDLC1 Interrupt. Whenever an unmasked HDLC1 interrupt occurs, this bit goes high. Reading this ...
Page 128
MT9076 21.2 Per Channel Transmit signaling (Pages 5 and 6) (E1) Page 05H, addresses 10000 to 11111, and page 06H addresses 10000 to 10111 contain the Transmit signaling Control Words for Channel Associated signaling (CAS) channels and ...
Page 129
Preliminary Information 21.3 Per Time Slot Control Words (Pages 7 and 8) (E1) The control functions described by Table 152 are repeated for each PCM-30 channel. Page 07H addresses 10H to 1FH correspond to time slots 0 to 15, while ...
Page 130
MT9076 21.4 Per Channel Receive signaling (Pages 9 and 0AH) (E1) Page 09H, addresses 10001 to 11111, and page 1AH addresses 10001 to 11111 contain the Receive signaling Control Words for CAS channels and 18 to 32. ...
Page 131
Preliminary Information 22.0 HDLC Control and Status (Page B for HDLC0, Page C for HDLC1 and Page D for HDLC2) Address Control (Write/Verify) 10H(Table 157) Address Recognition 1 11H(Table 158) Address Recognition 2 12H (Table159/160) TX FIFO 13H(Table 161) HDLC ...
Page 132
MT9076 Bit Name ADR16-11 Address 16 - 11. A six bit address used for comparison with the first byte of the received address. ADR16 is MSB. 1 ADR10 Address 10. This bit is used in address comparison ...
Page 133
Preliminary Information Bit Name BIT7-0 This is the received data byte read from the RX FIFO. The status bits of this byte can be read from the status register. The FIFO status is not changed immediately when ...
Page 134
MT9076 Bit Name 7 INTGEN Interrupt Generated. Set to 1 when an interrupt (in conjunction with the Interrupt Mask Register) has been generated by the HDLC. This is an asynchronous event reset when the interrupt Register is read. ...
Page 135
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7 INTSEL Interrupt Selection. When high, this bit will cause bit 2 of the Interrupt Register to reflect a TX FIFO underrun (TXunder). When low, this interrupt will reflect a frame abort (FA). 6 CYCLE Cycle. ...
Page 136
MT9076 Bit Name Ahead. Indicates a go-ahead pattern was detected by the HDLC receiver. This bit is reset after a read. 6 RxEOP End Of Packet Detected. This bit is set when an end of packet (EOP) ...
Page 137
Preliminary Information Bit Name 7-0 TxCNT7-0 Low Transmit Byte Count Register. This register, along with the Extended Transmit Byte Count Register indicates the length of the packet about to be transmitted. For a packet size of 255 or less it ...
Page 138
MT9076 Bit Name 7 These bits are reserved. 3 RxCLK Receive Clock. This bit represents the receiver clock generated after the RXEN control bit, but before zero deletion is considered. 2 TxCLK Transmit Clock. This bit represents the ...
Page 139
Preliminary Information Bit Name Unused. 6-4 RFD2-0 These bits select the Rx FIFO full status level: RFD2 Unused. 2-0 TFD2-0 These bits select the Tx HDLC ...
Page 140
MT9076 Bit Name Unused. 6-4 RFFS2-0 These bits select the RXFF (Rx FIFO Full) interrupt threshold level: RFFS2 Unused. 2-0 TFLS2-0 These bits select the TXFL ...
Page 141
Preliminary Information 23.0 Transmit National Bit Buffer (Page 0EH) Page 0EH, address 10H to 14H contain the five bytes of the transmit national bit buffer (TNBB0 - TNBB4 respectively). This feature is functional only when control bit NBTB (page 01H, ...
Page 142
MT9076 25.0 AC/DC Electrical Characteristics Absolute Maximum Ratings* Parameter 1 Supply Voltage 2 Voltage at Digital Inputs 3 Current at Digital Inputs 4 Voltage at Digital Outputs 5 Current at Digital Outputs 6 Storage Temperature * Exceeding these values may ...
Page 143
Preliminary Information AC Electrical Characteristics Characteristics 1 DS low 2 DS High 3 CS Setup 4 R/W Setup 5 Address Setup 6 CS Hold 7 R/W Hold 8 Address Hold 9 Data Delay Read 10 Data Hold Read 11 Data ...
Page 144
MT9076 AC Electrical Characteristics Characteristics 1 RD low 2 RD High 3 CS Setup 4 CS Hold 5 Address Setup 6 Address Hold 7 Data Delay Read 8 Data Active to High Z Delay 9 Data Setup Write 10 Data ...
Page 145
Preliminary Information AC Electrical Characteristics - Transmit Data Link Timing (T1 mode) Characteristic 1 Data Link Clock Pulse Width 2 Data Link Setup 3 Data Link Hold TxDLCLK TxDL Figure 18 - Transmit Data Link Timing Diagram (T1 mode) AC ...
Page 146
MT9076 AC Electrical Characteristics - Receive Data Link Timing (T1 mode) Characteristic 1 Data Link Clock Output Delay 2 Data Link Output Delay 3 RxFP Output Delay RxFP RxDLCLK RxDL Figure 21 - Receive Data Link Functional Timing (T1 mode) ...
Page 147
Preliminary Information AC Electrical Characteristics - Receive Data Link Timing (E1 mode) Characteristic 1 Data Link Clock Output Delay 2 Data Link Output Delay 3 RxFP Output Delay RxFP TIME SLOT 0 Bits 4,3,2,1,0 RxDLCLK RxDL RxDLCLK RxDL Figure 23 ...
Page 148
MT9076 AC Electrical Characteristics - ST-BUS Timing ( mode) Characteristic 1 C4b Clock Width High or Low 2 C4b Clock Width High or Low 3 Frame Pulse Hold 4 Frame Pulse Setup 5 Frame Pulse Low 6 Serial ...
Page 149
Preliminary Information ST-BUS Bit Bit Cell Stream F0b (Input) C4b (Input) All Input Streams All Output Streams Figure 27 - ST-BUS Timing Diagram (Input Clocks) ST-BUS Bit Bit Cell Stream F0b (Output) t FPD C4b (Output) All Input Streams All ...
Page 150
MT9076 AC Electrical Characteristics - Multiframe Timing ( mode) Characteristic 1 Receive Multiframe Output Delay 2 Transmit Multiframe Setup 3 Transmit Multiframe Hold Frame DSTo BIt Cells Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 F0b C4b ...
Page 151
Preliminary Information F0b t MOD C4b (1,2) RxMF t MS (1) TxMF (1) Note : These two signals do not have a defined phase relationship Note (2): Control bit Tx8KEN set low. Figure 32 - Multiframe Timing Diagram (T1 mode ...
Page 152
MT9076 AC Electrical Characteristics - TXA/TXB ( mode) Characteristic 1 Serial Output Delay 2 TxFP Output Delay Channel 23 TXA/TXB Bit 0 RxMF/TxFP (Tx8KEN= 1) E1.5o/Exclk (LIUEN = 1) Figure 33 - TXA/TXB Functional Timing (T1 mode) Channel ...
Page 153
Preliminary Information AC Electrical Characteristics - IMA Timing ( mode) Characteristic 1 C4b Clock Width High or Low 2 Frame Pulse Setup 3 Frame Pulse Hold 4 Serial Input Setup 5 Serial Input Hold 6 Serial Output Delay ...
Page 154
MT9076 DSTo RXFP Exclk 2.048 MHz Figure IMA Functional Timing (E1 mode) ST-BUS Bit Stream F0b (Input) C4b (Input) DSTi Figure IMA Timing Diagram (T1 mode or E1 mode) ST-BUS Bit Stream RxFP (Output) ...
Page 155
Preliminary Information FRAME FRAME 12 1 CHANNEL Sbit Most BIT Significant Bit (First) FRAME FRAME 15 0 TIME SLOT Most Significant Bit (First) CHANNEL CHANNEL 0 31 Most Significant Bit (First) Figure 44 - ST-BUS Stream Format - 2.048 Mb/s ...
Page 156
MT9076 CHANNEL CHANNEL 0 127 Most Significant Bit (First) Figure 45 - ST-BUS Stream Format 8.192 Mb/s 152 125 s CHANNEL • • • 126 BIT BIT BIT BIT BIT 0.977 s Preliminary Information CHANNEL ...
Page 157
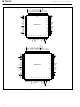
Preliminary Information Dim D (lead coplanarity) A Notes Not to ...
Page 158
MT9076 Notes: 1) Not to scale 2) Dimensions in inches 3) (Dimensions in millimeters) 4) Ref. JEDEC Standard MS-026 80-Pin Dim Min Max Min A - 0.063 (1.60) A1 0.002 0.006 0.002 (0.05) (0.15) (0.05) A2 0.053 ...
Page 159
Preliminary Information Notes: MT9076 155 ...
Page 160
... Mitel. This publication is issued to provide information only and (unless agreed by Mitel in writing) may not be used, applied or reproduced for any purpose nor form part of any order or contract nor to be regarded as a representation relating to the products or services concerned. The products, their specifications, services and other information appearing in this publication are subject to change by Mitel without notice. No warranty or guarantee express or implied is made regarding the capability, performance or suitability of any product or service. Information concerning possible methods of use is provided as a guide only and does not constitute any guarantee that such methods of use will be satisfactory in a specifi ...