AD9226 Analog Devices, AD9226 Datasheet - Page 20

AD9226
Manufacturer Part Number
AD9226
Description
12-Bit, 65 MSPS Analog-to-Digital Converter
Manufacturer
Analog Devices
Datasheet
1.AD9226.pdf
(28 pages)
Specifications of AD9226
Resolution (bits)
12bit
# Chan
1
Sample Rate
65MSPS
Interface
Par
Analog Input Type
Diff-Uni,SE-Uni
Ain Range
(Vref) p-p,1 V p-p,2 V p-p,Uni (Vref),Uni 1.0V,Uni 2.0V
Adc Architecture
Pipelined
Pkg Type
QFP,SOP
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
AD9226ARS
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
AD9226ARSZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
AD9226ARSZRL
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD9226AST
Manufacturer:
Analog Devices Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
AD9226AST
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD9226ASTRL
Manufacturer:
Analog Devices Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD9226ASTZ
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
AD9226ASTZ
Manufacturer:
INF
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
AD9226ASTZ
Manufacturer:
Analog Devices Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
AD9226ASTZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD9226ASTZRL
Manufacturer:
Analog Devices Inc
Quantity:
10 000
AD9226
Digital Output Driver Considerations
The AD9226 output drivers can be configured to interface with
5 V or 3.3 V logic families by setting DRVDD to 5 V or 3.3 V
respectively. The output drivers are sized to provide sufficient
output current to drive a wide variety of logic families. However,
large drive currents tend to cause glitches on the supplies and may
affect converter performance. Applications requiring the ADC to
drive large capacitive loads or large fan outs may require external
buffers or latches.
OEB Function (Three-State)
The LQFP-packaged AD9226 has Three-State (OEB) ability. If
the OEB pin is held low, the output data drivers are enabled. If
the OEB pin is high, the output data drivers are placed in a high
impedance state. It is not intended for rapid access to buss.
Clock Input Considerations
High-speed, high-resolution ADCs are sensitive to the quality of
the clock input. The clock input should be treated as an analog
signal in cases where aperture jitter may affect the dynamic
performance of the AD9226. Power supplies for clock drivers
should be separated from the ADC output driver supplies to
avoid modulating the clock signal with digital noise. Low-jitter
crystal controlled oscillators make the best clock sources.
The quality of the clock input, particularly the rising edge, is
critical in realizing the best possible jitter performance of the
part. Faster rising edges often have less jitter.
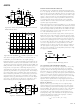
Clock Input and Power Dissipation
Most of the power dissipated by the AD9226 is from the analog
power supplies. However, lower clock speeds will reduce digital
current. Figure 16 shows the relationship between power and
clock rate.
GROUNDING AND DECOUPLING
Analog and Digital Grounding
Proper grounding is essential in any high-speed, high-resolution
system. Multilayer printed circuit boards (PCBs) are recom-
mended to provide optimal grounding and power schemes. The
use of ground and power planes offers distinct advantages:
1. The minimization of the loop area encompassed by a signal
2. The minimization of the impedance associated with ground
and its return path.
and power paths.
600
550
500
450
400
350
300
250
200
5
15
25
SAMPLE RATE – Msps
35
DRVDD = 5V
45
DRVDD = 3V
55
65
75
3. The inherent distributed capacitor formed by the power
It is important to design a layout that prevents noise from cou-
pling onto the input signal. Digital signals should not be run in
parallel with input signal traces and should be routed away from
the input circuitry. While the AD9226 features separate analog
and driver ground pins, it should be treated as an analog com-
ponent. The AVSS and DRVSS pins must be joined together
directly under the AD9226. A solid ground plane under the
ADC is acceptable if the power and ground return currents are
carefully managed.
Analog and Digital Driver Supply Decoupling
The AD9226 features separate analog and digital supply and
ground pins, helping to minimize digital corruption of sensitive
analog signals. In general, AVDD (analog power) should be
decoupled to AVSS (analog ground). The AVDD and AVSS
pins are adjacent to one another. Also, DRVDD (digital power)
should be decoupled to DRVDD (digital ground). The decoupling
capacitors (especially 0.1 µF) should be located as close to the
pins as possible. Figure 17 shows the recommended decoupling
for the pair of analog supplies; 0.1 µF ceramic chip and 10 µF
tantalum capacitors should provide adequately low impedance
over a wide frequency range.
Bias Decoupling
The CML and VR are analog bias points used internally by the
AD9226. These pins must be decoupled with at least a 0.1 µF
capacitor as shown in Figure 18. The dc level of CML is approxi-
mately AVDD/2. This voltage should be buffered if it is to be
used for any external biasing. CML and VR outputs are only
available in the LQFP package.
CML
The LQFP-packaged AD9226 has a midsupply reference point.
This midsupply point is used within the internal architecture of
the AD9226 and must be decoupled with a 0.1 µF capacitor. It
will source or sink a load of up to 300 µA. If more current is
required, it should be buffered with a high impedance amplifier.
plane, PCB insulation, and ground plane.
0.1 F
10 F
10 F
0.1 F
0.1 F
CML
AD9226
AVDD
DRVDD
AVSS
DRVSS
VR
AD9226
AD9226
0.1 F