TLE 8386-2EL Infineon Technologies, TLE 8386-2EL Datasheet - Page 28

TLE 8386-2EL
Manufacturer Part Number
TLE 8386-2EL
Description
Manufacturer
Infineon Technologies
Datasheet
1.TLE_8386-2EL.pdf
(32 pages)
Specifications of TLE 8386-2EL
Packages
PG-SSOP-14
Comment
LS-sense-booster (prefered as voltage source);Can be used in SEPIC- or FLYBACK-configuration as wellMax. output current dependent on output voltage.
Vq (max)
adj (max 9-times of VS)
Iq (max)
-
Iq (typ)
7,000.0 µA
Output
Boost Converter
10.2
10.2.1
Introduction:
A boost converter is a potential source of electromagnetic disturbances which may affect the environment as well
as the device itself and cause sporadic malfunction up to damages depending on the amount of noise.
In principal we may consider the following basic effects:
•
•
•
Radiated magnetic fields:
Radiated magnetic fields are caused by circular currents occurring in so called “current windows”. These circular
currents are alternating currents which are driven by the switching transistor. The alternating current in these
windows are driving magnetic fields. The amount of magnetic emissions is mostly depending on the amplitude of
the alternating current and the size of the so-called “window” (this is the area, which is defined by the circular
current paths. We can divide into two windows:
•
•
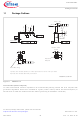
The area of these “windows” has to be kept as small as possible, with the relating elements placed next to each
others. It is highly recommended to use a ground plane as a single layer which covers the complete regulator area
with all components shown in this figure. All connections to ground shall be as short as possible
Radiated electric fields:
Radiated electric fields are caused by voltage oscillations occurring due to stray inductances and stray
capacitances at the connection between power MOSFET, output diode D
are also of course influenced by the commutation of the current from the power MOSFET to the output diode
D
diode and to keep the connections in this area as low inductive as possible. This can be achieved by using short
and broad connections and to arrange the related parts as close as possible. Following the recommendation of
using a ground layer these low inductive connections will form together with the ground layer small capacitances
which are desirable to damp the slope of these oscillations. The oscillations use connections or wires as antennas,
this effect can also be minimized by the short and broad connections.
Data Sheet
BOOST
Radiated magnetic fields caused by circular currents, occurring mostly with the switching frequency and their
harmonics
Radiated electric fields, often caused by (voltage) oscillations
Conducted disturbances (voltage spikes or oscillations) on the lines, mostly input and output lines.
the input current “window” (path consisting of C
of the input current I
the output current “window”: (path consisting of the power MOSFET, D
. Their frequencies might be between 10 and 100 MHz. Therefore it is recommended to use a fast Schottky
Further Information on TLE8386-2EL
General Layout recommendations
IN
is considered.
IN1
, L
BOOST
26
and the power MOSFET): Only the alternate content
BOOST
BOOST
and C
and output capacitor C
OUT
Application Information
): Output current ripple I
Rev. 1.0, 2010-10-25
TLE8386-2EL
OUT
. They