LM12CL National Semiconductor, LM12CL Datasheet - Page 10
LM12CL
Manufacturer Part Number
LM12CL
Description
80W Operational Amplifier
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM12CL.pdf
(14 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM12CLK
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
www.national.com
Application Information
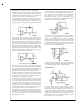
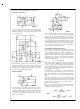
VOLTAGE REGULATORS
An op amp can be used as a positive or negative regulator.
Unlike most regulators, it can sink current to absorb energy
dumped back into the output. This positive regulator has a
0–50V output range.
Dual supplies are not required to use an op amp as a voltage
regulator if zero output is not required. This 4V to 50V regu-
lator operates from a single supply. Should the op amp not
be able to absorb enough energy to control an overvoltage
condition, a SCR will crowbar the output.
REMOTE SENSING
Remote sensing as shown above allows the op amp to cor-
rect for dc drops in cables connecting the load. Even so,
cable drop will affect transient response. Degradation can be
minimized by using twisted, heavy-gauge wires on the out-
put line. Normally, common and one input are connected to-
gether at the sending end.
DS008704-24
(Continued)
DS008704-22
DS008704-23
10
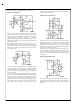
AUDIO AMPLIFIERS
A power amplifier suitable for use in high-quality audio equip-
ment is shown above. Harmonic distortion is about
0.01-percent. Intermodulation distortion (60 Hz/7 kHz, 4:1)
measured 0.015-percent. Transient response and saturation
recovery are clean, and the 9 V/µs slew rate of the LM12 vir-
tually eliminates transient intermodulation distortion. Using
separate amplifiers to drive low- and high-frequency speak-
ers gets rid of high-level crossover networks and attenua-
tors. Further, it prevents clipping on the low-frequency chan-
nel from distorting the high frequencies.
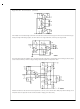
DETERMINING MAXIMUM DISSIPATION
It is a simple matter to establish power requirements for an
op amp driving a resistive load at frequencies well below
10 Hz. Maximum dissipation occurs when the output is at
one-half the supply voltage with high-line conditions. The in-
dividual output transistors must be rated to handle this power
continuously at the maximum expected case temperature.
The power rating is limited by the maximum junction tem-
perature as determined by
where T
of the package bottom, P
tion and
age of the output transistor. Recommended maximum junc-
tion temperatures are 200˚C within the power transistor and
150˚C for the control circuitry.
If there is ripple on the supply bus, it is valid to use the aver-
age value in worst-case calculations as long as the peak rat-
ing of the power transistor is not exceeded at the ripple peak.
With 120 Hz ripple, this is 1.5 times the continuous power
rating.
Dissipation requirements are not so easily established with
time varying output signals, especially with reactive loads.
Both peak and continuous dissipation ratings must be taken
into account, and these depend on the signal waveform as
well as load characteristics.
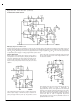
With a sine wave output, analysis is fairly straightforward.
With supply voltages of
dissipation of both output transistors is
C
is the case temperature as measured at the center
JC
is the thermal resistance at the operating volt-
T
J
= T
DISS
±
C
V
S
+ P
, the maximum average power
is the maximum power dissipa-
DISS
JC
,
DS008704-25