z85c30 ZiLOG Semiconductor, z85c30 Datasheet

z85c30
Available stocks
Related parts for z85c30
z85c30 Summary of contents
Page 1
... Z80C30/Z85C30 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Product Specification PS011705-0608 ® Copyright ©2008 by Zilog , Inc. All rights reserved. www.Zilog.com ...
Page 2
DO NOT USE IN LIFE SUPPORT Warning: LIFE SUPPORT POLICY Zilog'S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS PRIOR WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL COUNSEL OF Zilog ...
Page 3
Revision History Each instance in Revision History reflects a change to this document from its previous revision. For more details, refer to the corresponding pages and appropriate links in the table below. Date June 2008 September 2004 PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC ...
Page 4
... Table of Contents Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Other Features for Z85C30 Only . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Z85C30/Z80C30 Common Pin Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 Z85C30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Z80C30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 I/O Interface Capabilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Z85C30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Z80C30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 Z85C30/Z80C30 Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 Z85C30 Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 Z80C30 Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37 Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Standard Test Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Capacitance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 Miscellaneous . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 Z80C30/Z85C30 ...
Page 5
... Overview The features of Zilog’s Z80C30 and Z85C30 devices include: • Z85C30 — Optimized for Non-Multiplexed Bus Microprocessors. • Z80C30 — Optimized for Multiplexed Bus Microprocessors. • Pin Compatible to NMOS Versions. • Two Independent 4.1 Mbit/Second, Full-Duplex Channels. Each channel with Separate Crystal Oscillator, Baud Rate Generator (BRG), and Digital Phase-Locked Loop (DPLL) for Clock Recovery ...
Page 6
... Other Features for Z85C30 Only Some of the features listed below are available by default. Some of them (features with *) are disabled on default to maintain compatibility with the existing Serial Communications Controller (SCC) design, and “program to enable through WR7”: • New programmable WR7 (Write register 7 prime) to enable new features. ...
Page 7
PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Product Specification 3 Overview ...
Page 8
... General Description The Z80C30/Z85C30 Serial Communications Controller (SCC pin and software compatible CMOS member of the SCC family introduced by Zilog channel, multi-protocol data communications peripheral that easily interfaces with CPU’s with either multiplexed or non-multiplexed address/data buses. The advanced CMOS process offers lower power consumption, higher performance, and superior noise immunity ...
Page 9
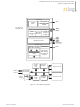
Channel A Exploded View Databus CPU & DMA Bus Interface Control INT INTACK Interrupt IEI Control IEO PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Transmit Logic Transmit MUX Transmit Buffer Data Encoding & CRC Generation Receive and Transmit Clock Multiplexer Crystal ...
Page 10
... Pin Descriptions Z85C30/Z80C30 Common Pin Functions The following sections describe the pin functions common to Z85C30 and Z80C30 devices: • CTSA, CTSB • DCDA, DCDB • DTR/REQA, DTR/REQB • IEI • IEO • INT • INTACK • PCLK • RxDA, RxDB • ...
Page 11
DTR/REQA, DTR/REQB Data Terminal Ready/Request (outputs, active Low) — programmed into the Request lines for a DMA controller. IEI Interrupt Enable In (input, active High) — daisy-chain when there is more than one interrupt driven device. A high IEI indicates ...
Page 12
RTSA, RTSB Request To Send (outputs, active Low) — Write Register 5 (see bit is reset in the Asynchronous mode and Auto Enable is ON, the signal goes High after the transmitter is empty. In Synchronous mode, it strictly follows ...
Page 13
... Z85C30 A/B Channel A/Channel B (input) — Write operation occurs. CE Chip Enable (input, active Low) — operation. D7–D0 Data Bus (bidirectional, tri-state) — the SCC. D/C Data/Control Select (input) — or from the SCC. A High indicates a data transfer; a Low indicates a command. RD Read (input, active Low) — ...
Page 14
... CS1 must remain active throughout the transaction. DS Data strobe (input, active Low) — into and out of the SCC and DS coincide, this confluence is interpreted as a reset. R/W Read/Write (input) — Read or a Write. Figure 2 displays the pin assignments for Z85C30 and Z80C30 DIP package ...
Page 15
... Figure 3 displays the pin assignments for Z85C30 and Z80C30 PLCC package IEO IEI 8 INTACK 9 +5V 10 W/REQA 11 Z85C30 SYNCA 12 RTxCA 13 RxDA 14 TRxCA 15 TxDA Figure 3. Z85C30 and Z80C30 PLCC Pin Assignments Figure 4 displays the pin functions for the Z85C30 device ...
Page 16
Figure 5 displays the pin functions for the Z80C30 device. Data Bus Bus Timing and Reset Control Interrupt PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller TxDA AD7 RxDA AD6 TRxCA AD5 RTxCA AD4 SYNCA AD3 W/REQA AD2 DTR/REQA AD1 RTSA AD0 ...
Page 17
Functional Description The architecture of the SCC is described below: • data communications device which transmits and receives data in various protocols. • microprocessor peripheral in which the SCC offers valuable features such as vectored interrupts ...
Page 18
Upper Byte (WR13) Time Constant BRG 16-Bit Down Counter Input DPLL IN DPLL Internal TXD 1-Bit RXD I/O Interface Capabilities System communication to and from the SCC is performed through the SCC’s register set. There are sixteen Write registers and ...
Page 19
Table 1. SCC Read Register Functions Register RR0 RR1 RR2 RR3 RR8 RR10 RR12 RR13 RR15 Table 2. SCC Write Register Functions Register WR0 WR1 WR2 WR3 WR4 WR5 WR6 WR7 WR7* WR8 WR9 WR10 PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications ...
Page 20
Table 2. SCC Write Register Functions (continued) Register WR11 WR12 WR13 WR14 WR15 Following three methods move data, status, and control information in and out of the SCC: • Polling • Interrupts (vectored and non-vectored) • CPU/DMA Block Transfer under ...
Page 21
Interrupt Pending (IP), Interrupt Under Service (IUS), and Interrupt Enable (IE). Opera- tion of the IE bit is straight forward. If the IE bit is set for a given interrupt source, then that source can request interrupts. The exception is ...
Page 22
External/Status Each interrupt type is enabled under program control with Channel A having higher priority than Channel B, and with Receiver, Transmit, and External/Status interrupts prioritized in that order within each channel. When enabled, the receiver interrupts the CPU ...
Page 23
When the INTACK and IEI pins are not being used, they should be pulled through a resistor (10 K CPU/DMA Block Transfer The SCC provides a Block Transfer mode to accommodate CPU block transfer functions and DMA ...
Page 24
Asynchronous Modes Send and Receive is accomplished independently on each channel with five to eight bits per character, plus optional even or odd parity. The transmitters can supply one, one-and- a-half, or two stop bits per character and can provide ...
Page 25
Both CRC-16 (X polynomials are supported. Either polynomial can be selected in all Synchronous modes. You can preset the CRC generator and checker to all 1’s or all 0’s. The SCC also provides a feature that automatically transmits CRC data ...
Page 26
SCC operating in regular SDLC mode acts as a controller (see on page 22). The SDLC loop mode can be selected by setting WR10 bit D1. A secondary station in an SDLC Loop is always listening to ...
Page 27
Baud Rate Generator Each channel in the SCC contains a programmable Baud Rate Generator (BRG). Each generator consists of two 8-bit time constant registers that form a 16-bit time constant, a 16-bit down counter, and a flip-flop on the output ...
Page 28
Data Encoding The SCC can be programmed to encode and decode the serial data in four different methods (Figure 12). In NRZ encoding represented by a High level and represented by a Low level. ...
Page 29
RxD is ignored (except to be echoed out through TxD). The CTS and DCD inputs are also ignored as transmit and receive enables. However, transitions on these inputs can still cause interrupts. Local Loopback works in ...
Page 30
Read Operation When WR15 bit D2 sets and the FIFO is not empty, the next read to status register RR1 or registers RR7 and RR6, is from the FIFO. Reading status register RR1 causes one location of the FIFO to ...
Page 31
... The SCC contains Write registers in each channel that are programmed by the system separately to configure the functional personality of the channels. Z85C30 In the SCC, the data registers are directly addressed by selecting a High on the D/C pin. With all other registers (except WR0 and RR0), programming the Write registers requires two Write operations and reading the read registers requires both a Write and a Read oper- ation ...
Page 32
... AD5 is ignored. In the Shift Left mode, the channel select A/B is taken from AD5 and the state of AD0 is ignored. AD7 and AD6 are always ignored as address bits and the register address occupies AD4-AD1. Z85C30/Z80C30 Setup Initialization The system program first issues a series of commands to initialize the basic mode of operation ...
Page 33
Write Register 0 (non-multiplexed bus mode Register Register Register Register Register 4 1 ...
Page 34
Write Register Sync Modes Enable Stop Bit/Character 1/2 Stop Bits/Character Stop Bits/Character 8-Bit Sync Character 16-Bit ...
Page 35
Sync7 Sync6 Sync1 Sync0 Sync7 Sync6 Sync3 Sync2 ADR6 ADR7 ADR7 ADR6 Write Register 7 Sync6 Sync7 Sync5 Sync4 Sync15 Sync14 Sync11 Sync10 7’ Prime (85C30 only Figure 17. ...
Page 36
Write Register Reset Channel Reset B Channel Reset Force Hardware Reset 1 Write Register ...
Page 37
Read Register Read Register Read Register Modified in B Channel Figure 19. ...
Page 38
... RD in the first transaction involving the SCC to the falling edge the second transaction involving the SCC. This time must be at least 3 PCLKs regardless of which register or channel is being accessed. The Z85C30 timings are described below: • Read Cycle Timing • ...
Page 39
Read Cycle Timing Figure 21 displays Read cycle timing. Addresses and D/C and the status on INTACK must remain stable throughout the cycle falls after RD falls rises before RD rises, the ...
Page 40
Write Cycle Timing Figure 22 displays Write cycle timing. Addresses on A/B and D/C and the status on INTACK must remain stable throughout the cycle falls after WR falls rises before WR rises, the effective ...
Page 41
Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Timing Figure 23 displays an Interrupt Acknowledge cycle timing. Between the time INTACK goes Low and the falling edge of RD, the internal and external IEI/IEO daisy chains settle. If there is an interrupt pending in the ...
Page 42
Read Cycle Timing Figure 24 displays the Read cycle timing. The address on AD7–AD0 and the state of CS0 and INTACK are latched by the rising edge of AS. R/W must be High to indicate a Read cycle. CS1 must ...
Page 43
Write Cycle Timing Figure 25 displays the Write cycle timing. The address on AD7–AD0 and the state of CS0 and INTACK are latched by the rising edge of AS. R/W must be Low to indicate a Write cycle. CS1 must ...
Page 44
Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Timing Figure 26 displays the Interrupt Acknowledge cycle timing. The address on AD7–AD0 and the state of CS0 and INTACK are latched by the rising edge of AS. If INTACK is Low, the address and CS0 are ...
Page 45
... Electrical Characteristics The electrical characteristics of the Z80C30 and the Z85C30 devices are described in the following sections. Absolute Maximum Ratings Stresses greater than those listed in This is a stress rating only. Operation of the device at any condition above those indicated in the operational sections of these specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability ...
Page 46
From Output Under Test 100 pF From Output 50 pF Capacitance Table 4 lists the input, output, and bidirectional capacitance. PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller 2.1 KΩ 250 μA Figure 27. Standard Test Load 2.2 KΩ Figure 28. Open-Drain ...
Page 47
... Bidirectional Capacitance I/O Notes MHz, over specified temperature range. 2. Unmeasured pins returned to Ground. Miscellaneous The Gate Count is 6800. DC Characteristics Z80C30/Z85C30 Table 5 lists the DC characteristics for the Z80C30/Z85C30 devices. PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Min Max Unit Test Condition Unmeasured Pins ...
Page 48
... CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Min Typ Max 1 2.2 V +0.3 CC -0.3 0.8 2 0.8 0.4 ±10.0 ±10 (10 MHz (16.384 MHz Figure 32 display the Z85C30 Read/Write timing diagrams. Product Specification Unit Condition -1 -250 μ +2 μ μA 0 2.4 V OUT ...
Page 49
... PCLK A/B, D/C INTACK D7–D0 Read WR D7–D0 Write W/REQ Wait W/REQ Request DTR/REQ Request INT Figure 29. Z85C30 Read/Write Timing Diagram PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Active Valid ...
Page 50
... PCLK INTACK RD D7–D0 IEI 43 IEO INT Figure 30. Z85C30 Interrupt Acknowledge Timing Diagram 49b PCLK Figure 31. Z85C30 Cycle Timing Diagram Figure 32. Z85C30 Reset Timing Diagram PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Active Valid 49a ...
Page 51
... Table 6. Z85C30 Read/Write Timing No Symbol Parameter 1 TwPCI PCLK Low Width 2 TwPCh PCLK High Width 3 TfPC PCLK Fall Time 4 TrPC PCLK Rise Time 5 TcPC PCLK Cycle Time 6 TsA(WR) Address to WR Fall Setup Time 7 ThA(WR) Address to WR Rise Hold Time 8 TsA(RD) Address to RD Fall ...
Page 52
... Table 6. Z85C30 Read/Write Timing (continued) No Symbol Parameter 1 19 TsCEI(RD) CE Low to RD Fall Setup Time 1 20 ThCE(RD Rise Hold Time 1 21 TsCEh(RD) CE High to RD Fall Setup Time 1 22 TwRDI RD Low Width 23 TdRD(DRA) RD Fall to Read Data Active Delay 24 TdRDr(DR) RD Rise to Data Not ...
Page 53
... Table 6. Z85C30 Read/Write Timing (continued) No Symbol Parameter 36 TdRDrrREQ) RD Rise to DTR/REQ Not Valid Delay 37 TdPC(INT) PCLK Fall to INT Valid Delay d 38 TdIAi(RD) INTACK to RD Fall (Ack) Delay 39 TwRDA RD (Acknowledge) Width 40 TdRDA(DR) RD Fall (Ack) to Read Data Valid Delay 41 TsiEI(RDA) IEI to RD Fall (Ack) ...
Page 54
... TdPC(IEO) for the highest priority device in the daisy chain. TsiEI(RDA) for the SCC and TdIEI(IEO) for each device separating them in the daisy chain. e. Parameter applies only between transactions involving the Z85C30 SL1480, if WR/RD falling edge is synchronized to PCLK falling edge, then TrC = 3TcPc. ...
Page 55
... SYNC External CTS/TRxC, RTxC Transmit TxD CTS/TRxC Output RTxC CTS/TRxC CTS/TRxC DCD SYNC Input Figure 33. Z85C30 General Timing Diagram Table 7. Z85C30 General Timing Table No Symbol Parameter 1 TdPC(REQ) PCLK to W/REQ Valid 2 TdPC(W) PCLK to Wait Inactive 3 TsRXC(PC) RxC to PCLK Setup Time 4 TsRXD(RXCr) RxD to RxC Setup Time ...
Page 56
... Table 7. Z85C30 General Timing Table (continued) No Symbol Parameter 6 TsRXD(RXCf) RxD to /RXC Setup Time 7 ThRXD(RXCf) RxD to /RXC Hold Time 8 TsSY(RXC) SYNC to RxC Setup Time 9 ThSY(RXC) SYNC to RxC Hold Time 10 TsTXC(PC) TxC to PCLK Setup Time 11 TdTXCf(TXD) TxC to TxD Delay 12 TdTxCr(TXD) TxC to TxD Delay ...
Page 57
... Transmit W/REQ Request W/REQ Wait DTR/REQ Request INT CTS, DCD SYNC Input INT Figure 34. Z85C30 System Timing Diagram Table 8. Z85C30 System Timing Table No Symbol Parameter 1 TdRXC(REQ) RxC High to W/REQ Valid 2 TdRXC(W) RxC High to Wait Inactive 3 TdRdXC(SY) RxC High to SYNC Valid PS011705-0608 ...
Page 58
... Table 8. Z85C30 System Timing Table (continued) No Symbol Parameter 4 TsRXC(INT) RxC High to INT Valid 5 TdTXC(REQ) TxC Low to W/REQ Valid 6 TdTXC(W) TxC Low to Wait Inactive 7 TdTXC(DRQ) TxC Low to DTR/REQ Valid 8 TdTXC(INT) TxC Low to INT Valid 9a TdSY(INT) SYNC to INT Valid 9b TdSY(INT) SYNC to INT Valid ...
Page 59
AS 4 CS0 7 CS1 INTACK 7 R/W Read R/W Write Write DS AD7–AD0 Write 15 AD7–AD0 Read 15 W/REQ Wait W/REQ Request DTR/REQ Request INT PCLK 40 Figure 35. Z80C30 Read/Write Timing Diagram PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller ...
Page 60
AS INTACK DS AD7–AD0 IEI 34 IEO INT Figure 36. Z80C30 Interrupt Acknowledge Timing Diagram Figure 37. Z80C30 Reset Timing Diagram Table 10. Z80C30 Read/Write Timing No Symbol Parameter 1 TwAS AS Low Width 2 TdDS(AS) DS ...
Page 61
Table 10. Z80C30 Read/Write Timing No Symbol Parameter 5 TsCS1(DS) CS1 to DS Fall Setup Time 6 ThCS1(DS) CS1 to DS Rise Hold Time 7 TsiA(AS) INTACK to AS Rise Setup Time 8 ThIA(AS) INTACK to AS Rise Hold Time ...
Page 62
Table 10. Z80C30 Read/Write Timing No Symbol Parameter 31 TdDSA(DR) DS Fall (Acknowledge) to Read Data Valid Delay 32 TsiEI(DSA) IEI to DS Fall (Acknowledge) Setup Time 33 ThIEI(DSA) IEI to DS Rise (Acknowledge) Hold Time 34 TdIEI(IEO) IEI to ...
Page 63
PCLK W/REQ Request W/REQ Wait RTxC, TRxC Receive 4 RxD 8 SYNC External TRxC, RTxC Transmit TxD TRxC Output RTxC TRxC CTS, DCD SYNC Input Figure 38. Z80C30 General Timing Diagram Table 11. Z80C30 General Timing No Symbol Parameter 1 ...
Page 64
Table 11. Z80C30 General Timing No Symbol Parameter 4 TsRXD(RXCr) RxD to RxC High Setup Time 5 ThRXD(RxCr) RxD to RxC High Hold Time 6 TsRXD(RXCf) RxD to RxC Low Setup Time 7 ThRXD(RXCf) RxD to RxC Low Hold Time ...
Page 65
PCLK W/REQ Request W/REQ Wait RTxC, TRxC Receive 4 RxD 8 SYNC External TRxC, RTxC Transmit TxD TRxC Output RTxC TRxC CTS, DCD SYNC Input Figure 39. Z80C30 System Timing Diagram Table 12. Z80C30 System Timing No Symbol Parameter 1 ...
Page 66
Table 12. Z80C30 System Timing (continued) No Symbol Parameter d,2 Note 5 TdTXC(REQ) TxC Low to W/REQ Valid 6 TdTXC(W) TxC Low to Wait Inactive 7 TdTXC(DRQ) TxC Low to DTR/REQ Valid 8 TdTXC(INT) TxC Low to INT Valid 2,4 ...
Page 67
... Packaging Figure 40 displays the 40-pin DIP package available for Z80C30 and Z85C30 devices. Figure 40. 40-Pin DIP Package Diagram PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Product Specification 63 Packaging ...
Page 68
... Figure 41 displays the 44-pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carriers (PLCC) package diagram available for Z80C30 and Z85C30 devices. Figure 41. 44-Pin PLCC Package Diagram PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller Product Specification 64 Packaging ...
Page 69
... Z80C30 and the Z85C30 devices. Table 13. Z80C30/Z85C30 Ordering Information 8 MHz Z80C3008PSC Z80C3008VSC Z85C3008PSC/PEC Z85C3008VSCNEC For complete details on Z80C30 and Z85C30 devices, development tools and downloadable software, visit www.zilog.com. PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller 10 MHz 16 MHz Z80C3010PSC ...
Page 70
Part Number Suffix Designations Zilog ® part numbers consist of a number of components, as indicated in the following example: Example Part number Z80C3016PSG is a Z80C30, 16 MHz, PLCC 80C30 PS011705-0608 CMOS SCC Serial Communications Controller 16 ...
Page 71
Customer Support For answers to technical questions about the product, documentation, or any other issues with Zilog’s offerings, please visit Zilog’s Knowledge Base at http://www.zilog.com/kb. For any comments, detail technical questions, or reporting problems, please visit Zilog’s Technical Support at ...