mic4452 Micrel Semiconductor, mic4452 Datasheet - Page 9
mic4452
Manufacturer Part Number
mic4452
Description
12a-peak Low-side Mosfet Driver Bipolar/cmos/dmos Process
Manufacturer
Micrel Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MIC4452.pdf
(12 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
mic4452VM
Manufacturer:
PULSE
Quantity:
3 100
Part Number:
mic4452YM
Manufacturer:
MICREL/麦瑞
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
mic4452YN
Manufacturer:
AvagoTechnologiesUSInc
Quantity:
2 000
Part Number:
mic4452YN
Manufacturer:
MICROCHI
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
mic4452ZT
Manufacturer:
FSC
Quantity:
7 000
MIC4451/4452
As this energy is lost in the driver each time the load is charged
or discharged, for power dissipation calculations the 1/2 is
removed. This equation also shows that it is good practice
not to place more voltage on the capacitor than is necessary,
as dissipation increases as the square of the voltage applied
to the capacitor. For a driver with a capacitive load:
where:
f = Operating Frequency
C = Load Capacitance
V
Inductive Load Power Dissipation
For inductive loads the situation is more complicated. For
the part of the cycle in which the driver is actively forcing
current into the inductor, the situation is the same as it is in
the resistive case:
However, in this instance the R
the on resistance of the driver when its output is in the high
state, or its on resistance when the driver is in the low state,
depending on how the inductor is connected, and this is still
only half the story. For the part of the cycle when the induc-
tor is forcing current through the driver, dissipation is best
described as
where V
(generally around 0.7V). The two parts of the load dissipation
must be summed in to produce P
Quiescent Power Dissipation
Quiescent power dissipation (P
section) depends on whether the input is high or low. A low
input will result in a maximum current drain (per driver) of
≤ 0.2mA; a logic high will result in a current drain of ≤ 3.0mA.
Quiescent power can therefore be found from:
where:
July 2005
S
= Driver Supply Voltage
V
I
D = fraction of time input is high (duty cycle)
I
H
S
L
= quiescent current with input high
= quiescent current with input low
= power supply voltage
P
P
P
P
P
D
L
L1
L2
is the forward drop of the clamp diode in the driver
L
Q
= f C (V
= P
= V
= I
= I V
2
L1
S
R
[D I
D
+ P
O
(1 – D)
S
D
)
H
L2
2
+ (1 – D) I
L
Q
]
, as described in the input
O
L
required may be either
9
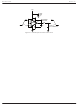
Transition Power Dissipation
Transition power is dissipated in the driver each time its
output changes state, because during the transition, for a
very brief interval, both the N- and P-channel MOSFETs in
the output totem-pole are ON simultaneously, and a current
is conducted through them from V
power dissipation is approximately:
where (A•s) is a time-current factor derived from the typical
characteristic curve “Crossover Energy vs. Supply Volt-
age.”
Total power (P
Definitions
P
R
P
C
P
V
P
D = Duty Cycle expressed as the fraction of time the
I
I
I
Q
O
H
D
D
S
T
L
f = Operating Frequency of the driver in Hertz
L
L
= Load Capacitance in Farads.
= Power supply current drawn by a driver when both
= Power supply current drawn by a driver when both
= Output current from a driver in Amps.
= Total power dissipated in a driver in Watts.
= Power dissipated in the driver due to the driver’s
= Power dissipated in a quiescent driver in Watts.
= Power dissipated in a driver when the output
= Output resistance of a driver in Ohms.
= Power supply voltage to the IC in Volts.
P
P
T
D
input to the driver is high.
inputs are high and neither output is loaded.
inputs are low and neither output is loaded.
load in Watts.
changes states (“shoot-through current”) in Watts.
NOTE: The “shoot-through” current from a dual
transition (once up, once down) for both drivers is
stated in Figure 7 in ampere-nanoseconds. This
figure must be multiplied by the number of repeti-
tions per second (frequency) to find Watts.
= 2 f V
= P
D
L
) then, as previously described is:
+ P
S
(A•s)
Q
+ P
T
S
to ground. The transition
MIC4451/4452
Micrel, Inc.