ADS8472I BURR-BROWN [Burr-Brown Corporation], ADS8472I Datasheet - Page 24

ADS8472I
Manufacturer Part Number
ADS8472I
Description
16-BIT, 1-MSPS, PSEUDO-BIPOLAR, FULLY DIFFERENTIAL INPUT, MICROPOWER SAMPLING ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER WITH PARALLEL INTERFACE, REFERENCE
Manufacturer
BURR-BROWN [Burr-Brown Corporation]
Datasheet
1.ADS8472I.pdf
(30 pages)
ADS8472
SLAS514 – DECEMBER 2006
24
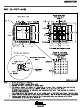
Conversions are initiated by bringing the CONVST pin low for a minimum of 20 ns (after the 20 ns minimum
requirement has been met, the CONVST pin can be brought high), while CS is low. The ADS8472 switches from
the sample to the hold mode on the falling edge of the CONVST command. A clean and low jitter falling edge of
this signal is important to the performance of the converter. The BUSY output is brought high immediately
following CONVST going low. BUSY stays high throughout the conversion process and returns low when the
conversion has ended.
Sampling starts with the falling edge of the BUSY signal when CS is tied low or starts with the falling edge of CS
when BUSY is low.
Both RD and CS can be high during and before a conversion with one exception (CS must be low when
CONVST goes low to initiate a conversion). Both the RD and CS pins are brought low in order to enable the
parallel output bus with the conversion.
Reading Data
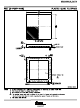
The ADS8472 outputs full parallel data in straight binary format as shown in
active when CS and RD are both low. There is a minimal quiet zone requirement around the falling edge of
CONVST. This is 50 ns prior to the falling edge of CONVST and 40 ns after the falling edge. No data read
should attempted within this zone. Any other combination of CS and RD sets the parallel output to 3-state. BYTE
is used for multiword read operations. BYTE is used whenever lower bits on the bus are output on the higher
byte of the bus. Refer to
The output data is a full 16-bit word (D15–D0) on DB15–DB0 pins (MSB–LSB) if BYTE is low.
The result may also be read on an 8-bit bus for convenience. This is done by using only pins DB15–DB8. In this
case two reads are necessary: the first as before, leaving BYTE low and reading the 8 most significant bits on
pins DB15–DB8, then bringing BYTE high. When BYTE is high, the low bits (D7–D0) appear on pins
DB15–DB8.
All of these multiword read operations can be performed with multiple active RD (toggling) or with RD held low
for simplicity. This is referred to as the AUTO READ operation.
RESET
On power-up, internal POWER-ON RESET circuitry generates the reset required for the device. The first three
conversions after power-up are used to load factory trimming data for a specific device to assure high accuracy
of the converter. The results of the first three conversions are invalid and should be discarded.
The device can also be reset through the use of the combination fo CS and CONVST. Since the BUSY signal is
held at high during the conversion, either one of these conditions triggers an internal self-clear reset to the
converter.
DESCRIPTION
Full scale range
Least significant bit (LSB)
+Full scale
Midscale
Midscale – 1 LSB
Zero
Table 1
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION (continued)
for ideal output codes.
BYTE
High
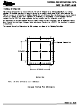
Table 1. Ideal Input Voltages and Output Codes
Low
Table 2. Conversion Data Read Out
Submit Documentation Feedback
ANALOG VALUE
2
(+V
0 V – 1 LSB
(+V
ref
+V
–V
) – 1 LSB
0 V
ref
DB15–DB8
ref
ref
D15–D8
)/65536
D7–D0
PINS
DATA READ OUT
0111 1111 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
1111 1111 1111 1111
1000 0000 0000 0000
DIGITAL OUTPUT STRAIGHT BINARY
BINARY CODE
DB7–DB0
All One's
D7–D0
PINS
Table
1. The parallel output is
HEX CODE
1FFF
3FFF
0000
2000
www.ti.com