ATXMEGA256A3B_09 ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation], ATXMEGA256A3B_09 Datasheet

ATXMEGA256A3B_09
Related parts for ATXMEGA256A3B_09
ATXMEGA256A3B_09 Summary of contents
Page 1
Features • High-performance, Low-power AVR 8/16-bit XMEGA • Non-volatile Program and Data Memories – 256 KB of In-System Self-Programmable Flash – Boot Code Section with Independent Lock Bits – EEPROM – Internal SRAM • ...
Page 2
Ordering Information Ordering Code Flash ATxmega256A3B-AU 256 ATxmega256A3B-MH 256 Notes: 1. This device can also be supplied in wafer form. Please contact your local Atmel sales office for detailed ordering information. ...
Page 3
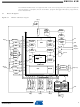
Pinout/Block Diagram Figure 2-1. Block diagram and pinout. INDEX CORNER PA3 PA4 PA5 PA6 PA7 PB0 PB1 PB2 PB3 PB4 PB5 PB6 PB7 GND VCC PC0 Note: for full details on pinout and pin functions refer to 8116F–AVR–09/09 1 ...
Page 4
Overview The XMEGA microcontrollers based on the AVR instructions in a single clock cycle, the XMEGA A3B achieves throughputs approaching 1 Million Instructions Per Second (MIPS) per MHz allowing the system designer to optimize power con- sumption versus processing ...
Page 5
The XMEGA A3B devices are supported with a full suite of program and system development tools including: C compilers, macro assemblers, program debugger/simulators, programmers, and evaluation kits. 3.1 Block Diagram Figure 3-1. XMEGA A3B Block Diagram PA[0..7] PORT A (8) ...
Page 6
... Resources A comprehensive set of development tools, application notes and datasheets are available for download on http://www.atmel.com/avr. 4.1 Recommended reading • XMEGA A Manual • XMEGA Application Notes This device data sheet only contains part specific information and a short description of each peripheral and module. The XMEGA A Manual describes the modules and peripherals in depth. ...
Page 7
AVR CPU 6.1 Features • 8/16-bit high performance AVR RISC Architecture – 138 instructions – Hardware multiplier • 32x8-bit registers directly connected to the ALU • Stack in SRAM • Stack Pointer accessible in I/O memory space • Direct ...
Page 8
The program memory is In- System Self-Programmable Flash memory. 6.3 Register File The fast-access Register File contains 32 x 8-bit general purpose working registers with single clock cycle access time. ...
Page 9
Memories 7.1 Features • Flash Program Memory – One linear address space – In-System Programmable – Self-Programming and Bootloader support – Application Section for application code – Application Table Section for application code or data storage – Boot Section ...
Page 10
In-System Programmable Flash Program Memory The XMEGA A3B devices contain On-chip In-System Programmable Flash memory for program storage, see Flash address location is 16 bits. The Program Flash memory space is divided into Application and Boot sections. Both sections ...
Page 11
Figure 7-2. 7.4.1 I/O Memory All peripherals and modules are addressable through I/O memory locations in the data memory space. All I/O memory locations can be accessed by the Load (LD/LDS/LDD) and Store (ST/STS/STD) instructions, transferring data between the 32 ...
Page 12
Production Signature Row The Production Signature Row is a separate memory section for factory programmed data. It contains calibration data for functions such as oscillators and analog modules. The production signature row also contains a device ID that identify ...
Page 13
Production Signature Row The Production Signature Row is a separate memory section for factory programmed data. It contains calibration data for functions such as oscillators and analog modules. The production signature row also contains a device ID that identify ...
Page 14
Flash and EEPROM Page Size The Flash Program Memory and EEPROM data memory are organized in pages. The pages are word accessible for the Flash and byte accessible for the EEPROM. Table 7-2 on page 14 operations are performed ...
Page 15
DMAC - Direct Memory Access Controller 8.1 Features • Allows High-speed data transfer – From memory to peripheral – From memory to memory – From peripheral to memory – From peripheral to peripheral • 4 Channels • From 1 ...
Page 16
Event System 9.1 Features • Inter-peripheral communication and signalling with minimum latency • CPU and DMA independent operation • 8 Event Channels allows for signals to be routed at the same time • Events can be ...
Page 17
Figure 9-1. The Event Routing Network can directly connect together ADCs, DACs, Analog Comparators (ACx), I/O ports (PORTx), the Real-time Counter (RTC), Timer/Counters (T/C) and the IR Com- munication Module (IRCOM). Events can also be generated from software (CPU). All ...
Page 18
System Clock and Clock options 10.1 Features • Fast start-up time • Safe run-time clock switching • Internal Oscillators: – 32 MHz run-time calibrated RC oscillator – 2 MHz run-time calibrated RC oscillator – 32.768 kHz calibrated RC oscillator ...
Page 19
Figure 10-1. Clock system overview Internal Oscillator Calibrated Internal Run-Time Calibrated Internal Oscillator Run-time Calibrated Internal Oscillator Each clock source is briefly described in the following sub-sections. 10.3 Clock Options 10.3.1 32 kHz Ultra Low Power Internal Oscillator The 32 ...
Page 20
Crystal Oscillator The 32.768 kHz Crystal Oscillator is a low power driver for an external watch crystal. It can be used as system clock source or as asynchronous clock source for the Real Time Counter. 10.3.4 0.4 ...
Page 21
Power Management and Sleep Modes 11.1 Features • 5 sleep modes – Idle – Power-down – Power-save – Standby – Extended standby • Power Reduction registers to disable clocks to unused peripherals 11.2 Overview The XMEGA A3B provides various ...
Page 22
Extended Standby Mode Extended Standby mode is identical to Power-save mode with the exception that all enabled system clock sources are kept running while the CPU and Peripheral clocks are stopped. This reduces the wake-up time when external crystals ...
Page 23
System Control and Reset 12.1 Features • Multiple reset sources for safe operation and device reset – Power-On Reset – External Reset – Watchdog Reset – Brown-Out Reset – JTAG Reset – PDI reset – Software reset • Asynchronous ...
Page 24
JTAG reset The MCU is reset as long as there is a logic one in the Reset Register in one of the scan chains of the JTAG system. Refer to IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Boundary-scan for details. 12.3.6 PDI reset ...
Page 25
Battery Backup System 13.1 Features • Battery Backup voltage supply from dedicated V – One Ultra Low-power 32-bit Real Time Counter – One 32.768 kHz crystal oscillator with failure detection monitor – Two Backup Registers • Typical power consumption ...
Page 26
Figure 13-1. Battery Backup Module and its power domain implementation VBAT V BAT power supervisor XOSC monitor TOSC1 XOSC TOSC2 RTC Backup Registers 8116F–AVR–09/09 Power Watchdog w/ switch independent RCOSC OCD & Programming Interface Peripherals Internal RAM XMEGA A3B Main ...
Page 27
PMIC - Programmable Multi-level Interrupt Controller 14.1 Features • Separate interrupt vector for each interrupt • Short, predictable interrupt response time • Programmable Multi-level Interrupt Controller – 3 programmable interrupt levels – Selectable priority scheme within low level interrupts ...
Page 28
Table 14-1. Reset and Interrupt Vectors (Continued) Program Address (Base Address) Source 0x040 NVM_INT_base 0x044 PORTB_INT_base 0x048 ACB_INT_base 0x04E ADCB_INT_base 0x056 PORTE_INT_base 0x05A TWIE_INT_base 0x05E TCE0_INT_base 0x06A TCE1_INT_base 0x074 USARTE0_INT_base 0x080 PORTD_INT_base 0x084 PORTA_INT_base 0x088 ACA_INT_base 0x08E ADCA_INT_base 0x09A TCD0_INT_base ...
Page 29
I/O Ports 15.1 Features • Selectable input and output configuration for each pin individually • Flexible pin configuration through dedicated Pin Configuration Register • Synchronous and/or asynchronous input sensing with port interrupts and events – Sense both edges – ...
Page 30
Push-pull Figure 15-1. I/O configuration - Totem-pole 15.3.2 Pull-down Figure 15-2. I/O configuration - Totem-pole with pull-down (on input) 15.3.3 Pull-up Figure 15-3. I/O configuration - Totem-pole with pull-up (on input) 15.3.4 Bus-keeper The bus-keeper’s weak output produces the ...
Page 31
Figure 15-4. I/O configuration - Totem-pole with bus-keeper 15.3.5 Others Figure 15-5. Output configuration - Wired-OR with optional pull-down Figure 15-6. I/O configuration - Wired-AND with optional pull-up 8116F–AVR–09/09 DIRn OUTn INn OUTn INn INn OUTn XMEGA A3B Pn Pn ...
Page 32
Input sensing • Sense both edges • Sense rising edges • Sense falling edges • Sense low level Input sensing is synchronous or asynchronous depending on the enabled clock for the ports, and the configuration is shown in Figure ...
Page 33
T/C - 16-bit Timer/Counter with PWM 16.1 Features • Seven 16-bit Timer/Counters – Four Timer/Counters of type 0 – Three Timer/Counters of type 1 • Four Compare or Capture (CC) Channels in Timer/Counter 0 • Two Compare or Capture ...
Page 34
Figure 16-1. Overview of a Timer/Counter and closely related peripherals Timer/Counter Base Counter Timer Period Compare/Capture Channel B Compare/Capture Channel A Comparator The Hi-Resolution Extension can be enabled to increase the waveform generation resolution by 2 bits (4x). This is ...
Page 35
AWEX - Advanced Waveform Extension 17.1 Features • Output with complementary output from each Capture channel • Four Dead Time Insertion (DTI) Units, one for each Capture channel • 8-bit DTI Resolution • Separate High and Low Side Dead-Time ...
Page 36
Hi-Res - High Resolution Extension 18.1 Features • Increases Waveform Generator resolution by 2-bits (4x) • Supports Frequency, single- and dual-slope PWM operation • Supports the AWEX when this is enabled and used for the same Timer/Counter 18.2 Overview ...
Page 37
RTC32 - 32-bit Real-Time Counter 19.1 Features • 32-bit resolution • One 32-bit Compare register • One 32-bit Period register • Clear Timer on overflow • Optional Interrupt/ Event on overflow and compare match • Selectable clock reference – ...
Page 38
TWI - Two Wire Interface 20.1 Features • Two Identical TWI peripherals • Simple yet Powerful and Flexible Communication Interface • Both Master and Slave Operation Supported • Device can Operate as Transmitter or Receiver • 7-bit Address Space ...
Page 39
SPI - Serial Peripheral Interface 21.1 Features • Two Identical SPI peripherals • Full-duplex, Three-wire Synchronous Data Transfer • Master or Slave Operation • LSB First or MSB First Data Transfer • Seven Programmable Bit Rates • End of ...
Page 40
USART 22.1 Features • Six Identical USART peripherals • Full Duplex Operation (Independent Serial Receive and Transmit Registers) • Asynchronous or Synchronous Operation • Master or Slave Clocked Synchronous Operation • High-resolution Arithmetic Baud Rate Generator • Supports Serial ...
Page 41
IRCOM - IR Communication Module 23.1 Features • Pulse modulation/demodulation for infrared communication • Compatible to IrDA 1.4 physical for baud rates up to 115.2 kbps • Selectable pulse modulation scheme – 3/16 of baud rate period – Fixed ...
Page 42
Crypto Engine 24.1 Features • Data Encryption Standard (DES) CPU instruction • Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Crypto module • DES Instruction – Encryption and Decryption – Single-cycle DES instruction – Encryption/Decryption in 16 clock cycles per 8-byte block • ...
Page 43
ADC - 12-bit Analog to Digital Converter 25.1 Features • Two ADCs with 12-bit resolution • 2 Msps sample rate for each ADC • Signed and Unsigned conversions • 4 result registers with individual input channel control for each ...
Page 44
Figure 25-1. ADC overview Each ADC has four MUX selection registers with a corresponding result register. This means that four channels can be sampled within 1.5 µs without any intervention by the application other than starting the conversion. The results ...
Page 45
DAC - 12-bit Digital to Analog Converter 26.1 Features • One DAC with 12-bit resolution • Msps conversion rate for each DAC • Flexible conversion range • Multiple trigger sources • 1 continuous output or 2 ...
Page 46
AC - Analog Comparator 27.1 Features • Four Analog Comparators • Selectable Power vs. Speed • Selectable hysteresis – mV • Analog Comparator output available on pin • Flexible Input Selection – All pins on ...
Page 47
Figure 27-1. Analog comparator overview Pin inputs Internal inputs Pin inputs Internal inputs VCC scaled Pin inputs Internal inputs Pin inputs Internal inputs VCC scaled 8116F–AVR–09/09 XMEGA A3B + Pin 0 output AC0 - Interrupts Interrupt sensitivity control + AC1 ...
Page 48
Input Selection The Analog comparators have a very flexible input selection and the two comparators grouped in a pair may be used to realize a window function. One pair of analog comparators is shown in Figure 27-1 on page ...
Page 49
OCD - On-chip Debug 28.1 Features • Complete Program Flow Control – Go, Stop, Reset, Step into, Step over, Step out, Run-to-Cursor • Debugging on C and high-level language source code level • Debugging on Assembler and disassembler level ...
Page 50
Program and Debug Interfaces 29.1 Features • PDI - Program and Debug Interface (Atmel proprietary 2-pin interface) • JTAG Interface (IEEE std. 1149.1 compliant) • Boundary-scan capabilities according to the IEEE Std. 1149.1 (JTAG) • Access to the OCD ...
Page 51
Pinout and Pin Functions The pinout of XMEGA A3B is shown in I/O functionality, each pin may have several functions. This will depend on which peripheral is enabled and connected to the actual pin. Only one of the alternate ...
Page 52
XCKn RXDn TXDn SS MOSI MISO SCK 30.1.6 Oscillators, Clock and Event TOSCn XTALn CLKOUT EVOUT 30.1.7 Debug/System functions RESET PDI_CLK PDI_DATA TCK TDI TDO TMS 8116F–AVR–09/09 Transfer Clock for USART n Receiver Data for USART n Transmitter Data for ...
Page 53
Alternate Pin Functions The tables below show the primary/default function for each pin on a port in the first column, the pin number in the second column, and then all alternate pin functions in the remaining columns. The head ...
Page 54
Table 30-4. Port D - Alternate functions PORT D PIN # INTERRUPT GND 24 VCC 25 PD0 26 SYNC PD1 27 SYNC PD2 28 SYNC/ASYNC PD3 29 SYNC PD4 30 SYNC PD5 31 SYNC PD6 32 SYNC PD7 33 SYNC ...
Page 55
Table 30-7. Port R- Alternate functions PORT R PIN # INTERRUPT PDI 56 PDI_DATA RESET 57 PDI_CLK PRO 58 SYNC PR1 59 SYNC 8116F–AVR–09/09 PDI XMEGA A3B XTAL XTAL2 XTAL1 55 ...
Page 56
Peripheral Module Address Map The address maps show the base address for each peripheral and module in XMEGA A3B. For complete register description and summary for each peripheral module, refer to the XMEGA A Manual. Base Address 0x0000 0x0010 ...
Page 57
Instruction Set Summary Mnemonics Operands Description ADD Rd, Rr Add without Carry ADC Rd, Rr Add with Carry ADIW Rd, K Add Immediate to Word SUB Rd, Rr Subtract without Carry SUBI Rd, K Subtract Immediate SBC Rd, Rr ...
Page 58
Mnemonics Operands Description CALL k call Subroutine RET Subroutine Return RETI Interrupt Return CPSE Rd,Rr Compare, Skip if Equal CP Rd,Rr Compare CPC Rd,Rr Compare with Carry CPI Rd,K Compare with Immediate SBRC Rr, b Skip if Bit in Register ...
Page 59
Mnemonics Operands Description LD Rd, -Y Load Indirect and Pre-Decrement LDD Rd, Y+q Load Indirect with Displacement LD Rd, Z Load Indirect LD Rd, Z+ Load Indirect and Post-Increment LD Rd, -Z Load Indirect and Pre-Decrement LDD Rd, Z+q Load ...
Page 60
Mnemonics Operands Description ROL Rd Rotate Left Through Carry ROR Rd Rotate Right Through Carry ASR Rd Arithmetic Shift Right SWAP Rd Swap Nibbles BSET s Flag Set BCLR s Flag Clear SBI A, b Set Bit in I/O Register ...
Page 61
Packaging information 33.1 64A PIN 0°~7° L Notes: 1.This package conforms to JEDEC reference MS-026, Variation AEB. 2. Dimensions D1 and E1 do not include mold protrusion. Allowable protrusion is 0.25 mm per side. Dimensions D1 ...
Page 62
D Marked Pin TOP VIEW BOTTOM VIEW Note: 1. JEDEC Standard MO-220, (SAW Singulation) Fig. 1, VMMD. 2. Dimension and tolerance conform to ASMEY14.5M-1994. 2325 Orchard Parkway San Jose, CA ...
Page 63
Electrical Characteristics 34.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings* Operating Temperature.................................. -55°C to +125°C Storage Temperature ..................................... -65°C to +150°C Voltage on any Pin with respect to Ground..-0. Maximum Operating Voltage ............................................ 3.6V DC Current per I/O Pin ............................................... 20.0 ...
Page 64
Table 34-1. Current Consumption Symbol Parameter (2) Module current consumption RC32M RC32M w/DFLL RC2M RC2M w/DFLL RC32K PLL Watchdog normal mode BOD Continuous mode BOD Sampled mode Internal 1.00 V ref Temperature reference RTC with int. 32 kHz RC as ...
Page 65
Operating Voltage and Frequency Table 34-2. Symbol Clk The maximum System clock frequency of the XMEGA A3 devices is depending on V shown in 1.8V < V Figure 34-1. Maximum Frequency vs. Vcc 8116F–AVR–09/09 Operating voltage and voltage and ...
Page 66
Flash and EEPROM Memory Characteristics Table 34-3. Endurance Symbol Parameter Flash EEPROM Table 34-4. Programming time Symbol Parameter Chip Erase Flash EEPROM Notes: 1. Programming is timed from the internal 2 MHz oscillator. 2. EEPROM is not erased if ...
Page 67
ADC Characteristics Table 34-5. ADC Characteristics Symbol Parameter RES Resolution INL Integral Non-Linearity DNL Differential Non-Linearity Gain Error Offset Error ADC ADC Clock frequency clk Conversion rate Conversion time (propagation delay) Sampling Time Conversion range VREF Reference voltage Input ...
Page 68
DAC Characteristics Table 34-7. DAC Characteristics Symbol Parameter INL Integral Non-Linearity DNL Differential Non-Linearity F Conversion rate clk AREF External reference voltage Reference input impedance DC output impedance Max output voltage Min output voltage Offset factory calibration accuracy Gain ...
Page 69
Brownout Detection Characteristics Table 34-10. Brownout Detection Characteristics Symbol Parameter BOD level 0 falling Vcc BOD level 1 falling Vcc BOD level 2 falling Vcc BOD level 3 falling Vcc BOD level 4 falling Vcc BOD level 5 falling ...
Page 70
POR Characteristics Table 34-12. Power-on Reset Characteristics Symbol Parameter V POR threshold voltage falling Vcc POT- V POR threshold voltage rising Vcc POT+ 34.12 Reset Characteristics Table 34-13. Reset Characteristics Symbol Parameter Minimum reset pulse width Reset threshold voltage ...
Page 71
VBAT and Battery Backup Characteristics Table 34-18. VBAT and Battery Backup Characteristics Symbol Parameter Vbat supply voltage range Vcc Power-down slope range BOD threshold voltage Vbbbod BBBOD threshold voltage BBBOD detection speed Current consumption VBAT pin leackage 8116F–AVR–09/09 Condition ...
Page 72
Typical Characteristics 35.1 Active Supply Current Figure 35-1. Active Supply Current vs. Frequency Figure 35-2. Active Supply Current vs. Frequency 8116F–AVR–09/ 1.0 MHz External clock 25°C SYS 900 800 700 600 500 400 ...
Page 73
Figure 35-3. Active Supply Current vs. Vcc Figure 35-4. Active Supply Current vs. VCC 8116F–AVR–09/ 1.0 MHz External Clock SYS 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2 ...
Page 74
Figure 35-5. Active Supply Current vs. Vcc Figure 35-6. Active Supply Current vs. Vcc 8116F–AVR–09/ 2.0 MHz internal RC SYS 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2 ...
Page 75
Figure 35-7. Active Supply Current vs. Vcc 35.2 Idle Supply Current Figure 35-8. Idle Supply Current vs. Frequency 8116F–AVR–09/ MHz internal RC SYS 2.7 2.8 2 ...
Page 76
Figure 35-9. Idle Supply Current vs. Frequency Figure 35-10. Idle Supply Current vs. Vcc 8116F–AVR–09/ MHz 25°C SYS Frequency [MHz] ...
Page 77
Figure 35-11. Idle Supply Current vs. Vcc Figure 35-12. Idle Supply Current vs. Vcc 8116F–AVR–09/ 32.768 kHz internal RC SYS 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2 2.0 MHz ...
Page 78
Figure 35-13. Idle Supply Current vs. Vcc Figure 35-14. Idle Supply Current vs. Vcc 8116F–AVR–09/ MHz internal RC prescaled to 8 MHz SYS 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 f ...
Page 79
Power-down Supply Current Figure 35-15. Power-down Supply Current vs. Temperature Figure 35-16. Power-down Supply Current vs. Temperature 8116F–AVR–09/09 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 -40 -30 -20 - Temperature [°C] With WDT ...
Page 80
Power-save Supply Current Figure 35-17. Power-save Supply Current vs. Temperature 35.5 Pin Pull-up Figure 35-18. Reset Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Reset Pin Voltage 8116F–AVR–09/09 With WDT, sampled BOD and RTC from ULP enabled 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 ...
Page 81
Figure 35-19. Reset Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Reset Pin Voltage Figure 35-20. Reset Pull-up Resistor Current vs. Reset Pin Voltage 8116F–AVR–09/ 3.0V CC 160 140 120 100 0 3.3V ...
Page 82
Pin Output Voltage vs. Sink/Source Current Figure 35-21. I/O Pin Output Voltage vs. Source Current Figure 35-22. I/O Pin Output Voltage vs. Source Current 8116F–AVR–09/09 Vcc = 1.8V 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 ...
Page 83
Figure 35-23. I/O Pin Output Voltage vs. Source Current Figure 35-24. I/O Pin Output Voltage vs. Sink Current 8116F–AVR–09/09 Vcc = 3.3V 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 -20 -18 -16 -14 -12 Vcc = 1.8V 1.8 1.6 ...
Page 84
Figure 35-25. I/O Pin Output Voltage vs. Sink Current Figure 35-26. I/O Pin Output Voltage vs. Sink Current 8116F–AVR–09/09 Vcc = 3.0V 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0 Vcc = 3.3V 0.7 0.6 ...
Page 85
Pin Thresholds and Hysteresis Figure 35-27. I/O Pin Input Threshold Voltage vs. V Figure 35-28. I/O Pin Input Threshold Voltage vs. V 8116F–AVR–09/ I/O Pin Read as “1” IH 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 1.6 1.8 ...
Page 86
Figure 35-29. I/O Pin Input Hysteresis vs. V Figure 35-30. Reset Input Threshold Voltage vs. V 8116F–AVR–09/09 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2 I/O Pin Read as “1” IH 1.8 1.6 ...
Page 87
Figure 35-31. Reset Input Threshold Voltage vs. V 35.8 Bod Thresholds Figure 35-32. BOD Thresholds vs. Temperature 8116F–AVR–09/ I/O Pin Read as “0” IL 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 ...
Page 88
Figure 35-33. BOD Thresholds vs. Temperature 35.9 Internal Oscillator Speed 35.9.1 Internal 32.768 kHz Oscillator Figure 35-34. Internal 32.768 kHz Oscillator Calibration Step Size 8116F–AVR–09/09 BOD Level = 2.9V 3.06 3.04 3.02 3 2.98 2.96 2.94 2.92 2.9 -40 -30 ...
Page 89
Internal 2 MHz Oscillator Figure 35-35. Internal 2 MHz Oscillator CALA Calibration Step Size -0.10 % -0.20 % -0.30 % Figure 35-36. Internal 2 MHz Oscillator CALB Calibration Step Size 8116F–AVR–09/09 ° - ...
Page 90
Internal 32 MHZ Oscillator Figure 35-37. Internal 32 MHz Oscillator CALA Calibration Step Size Figure 35-38. Internal 32 MHz Oscillator CALB Calibration Step Size 8116F–AVR–09/09 ° - 0.60 % 0.50 ...
Page 91
Module current consumption Figure 35-39. AC current consumption vs. Vcc Figure 35-40. Power-up current consumption vs. Vcc 8116F–AVR–09/09 Low-power Mode 120 100 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 ...
Page 92
Reset Pulsewidth Figure 35-41. Minimum Reset Pulse Width vs. Vcc 8116F–AVR–09/09 120 100 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 XMEGA A3B 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3 °C 25 °C -40 °C ...
Page 93
Errata 36.1 ATxmega256A3B 36.1.1 rev. C • Bandgap voltage input for the ACs cannot be changed when used for both ACs simultaneously • ADC gain stage output range is limited to 2.4V • Sampled BOD in Active mode will ...
Page 94
Problem fix/Workaround If the bandgap is used as reference for either the ADC, DAC and Analog Comparator, the BOD must not be set in sampled mode. 4. Bandgap measurement with the ADC is non-functional when V The ADC cannot be ...
Page 95
Figure 36-1. Analog Comparator Voltage Scaler vs. Scalefac Problem fix/Workaround Use external voltage input for the analog comparator if accurate voltage levels are needed. 9. Maximum operating frequency below 1.76V is 8 MHz To ensure correct operation, the maximum operating ...
Page 96
Datasheet Revision History 37.1 8116F - 09/ 37.2 8116E - 06/ 37.3 8116D - 04/ 37.4 8116C - 02/09 1. 37.5 8116B - 12/08 1. 37.6 8116A - 11/08 1. ...
Page 97
Table of Contents Features ..................................................................................................... 1 Typical Applications ................................................................................ 1 1 Ordering Information ............................................................................... 2 2 Pinout/Block Diagram .............................................................................. 3 3 Overview ................................................................................................... 4 4 Resources ................................................................................................. 6 5 Disclaimer ................................................................................................. 6 6 AVR CPU ................................................................................................... 7 7 Memories .................................................................................................. ...
Page 98
Power Management and Sleep Modes ................................................. 21 12 System Control and Reset .................................................................... 23 13 Battery Backup System ......................................................................... 25 14 PMIC - Programmable Multi-level Interrupt Controller ....................... 27 15 I/O Ports .................................................................................................. 29 16 T/C - 16-bit Timer/Counter ...
Page 99
RTC32 - 32-bit Real-Time Counter ........................................................ 37 20 TWI - Two Wire Interface ....................................................................... 38 21 SPI - Serial Peripheral Interface ............................................................ 39 22 USART ..................................................................................................... 40 23 IRCOM - IR Communication Module .................................................... 41 24 Crypto Engine ........................................................................................ ...
Page 100
Program and Debug Interfaces ............................................................. 50 30 Pinout and Pin Functions ...................................................................... 51 31 Peripheral Module Address Map .......................................................... 56 32 Instruction Set Summary ...................................................................... 57 33 Packaging information .......................................................................... 61 34 Electrical Characteristics ...................................................................... 63 35 Typical Characteristics ...
Page 101
Output Voltage vs. Sink/Source Current .........................................................82 35.7Pin Thresholds and Hysteresis ..............................................................................85 35.8Bod Thresholds .....................................................................................................87 35.9Internal Oscillator Speed .......................................................................................88 35.10Module current consumption ...............................................................................91 35.11Reset Pulsewidth .................................................................................................92 36 Errata ....................................................................................................... 93 36.1ATxmega256A3B ..................................................................................................93 37 Datasheet Revision History .................................................................. 96 37.18116F - ...
Page 102
Headquarters Atmel Corporation 2325 Orchard Parkway San Jose, CA 95131 USA Tel: 1(408) 441-0311 Fax: 1(408) 487-2600 Disclaimer: The information in this document is provided in connection with Atmel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to ...