ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C LATTICE [Lattice Semiconductor], ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C Datasheet - Page 33

ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C
Manufacturer Part Number
ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C
Description
In-System Programmable, Zero-Delay, Universal Fan-Out Buffer, Single-Ended
Manufacturer
LATTICE [Lattice Semiconductor]
Datasheet
1.ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C.pdf
(56 pages)
Lattice Semiconductor
outputs in Figure 27 show how the various sources of skew error stack up in this case. Note that if two or more out-
puts are programmed to the same skew setting, then the contribution of the t
When outputs are configured or loaded differently, this also has an effect on skew matching. If an output is set to
support a different logic type, this can be accounted for by using the t(ioo) output adders specified in the table
‘Switching Characteristics’. That table specifies the additional skew added to an output using SSTL, HSTL, EHSTL
as a base-line. For instance, if one output is specified as LVTTL, it has a delay adder relative to SSTL of 0.25ns. If
another output is specified as SSTL3, then one would expect 0.25ns of additional skew between the two outputs
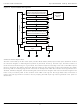
due to this adder. This timing relationship is shown in Figure 28a.
Figure 28. Output Timing Adders for Logic Type (a) and Output Slew Rate (b)
By selecting the same feedback logic type and clock output, the output delay adders for the clock output are auto-
matically compensated for. Similarly, a reference clock delay adder can be compensated for by selecting the same
feedback input logic type and reference clock.
When the internal feedback mode is selected, however, one should add both input and output delay adders to t
specified in the Performance Characteristics PLL table to calculate the input-to-output delay.
Similarly, when one changes the slew rate of an output, the output slew rate adders (t
the resulting skew. In this case, the fastest slew setting (1) is used as the baseline against which other slews are
measured. For example, in the case of outputs configured to the same logic type (e.g. LVCMOS 1.8V), if one output
is set to the fastest slew rate (1, t
950ps of skew between the two outputs, as shown in Figure 28b.
Static Phase Offset and Input-Output Skew
The ispClock5300S’s external feedback inputs can be used to obtain near-zero effective delays from the clock ref-
erence input pins to a designated output pin. Using external feedback (Figure 29), the PLL will attempt to force the
output phase so that the rising edge phase (t φ) at the feedback input matches the rising edge phase at the refer-
ence input. The residual error between the two is specified as the static phase error. Note that any propagation
delay (t
the output. For this reason, if zero input-to-output delays are required, the length of the signal path between the
output pin and the feedback pin should be minimized.
SSTL3 Output
FBK
LVTTL Output
) in the external feedback path drives the phase of the output signal backwards in time as measured at
(a)
IOS
0.25ns
= 0ps), and another set to slew rate 3 (t
33
LVCMOS Output
LVCMOS Output
(Slew rate=1)
(Slew rate=3)
ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet
SKERR
IOS
= 950ps), then one could expect
skew error term does not apply.
(b)
950ps
IOS
) can be used to predict
DELAY